Povaschia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| imagesize = | | imagesize = | ||
| image_alt = | | image_alt = | ||
| image_caption = Clockwise from the top: | | image_caption = Clockwise from the top: Trentschin Castle, Freedom monument in Vsetin, and the rolling hills of Povaschian Wallachia | ||
| image_flag = | | image_flag = | ||
| flag_alt = | | flag_alt = | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
| shield_alt = | | shield_alt = | ||
| etymology = | | etymology = | ||
| nickname = ''Pova'' | | nickname = ''Pova'', "Arch to Europe" | ||
| motto = | | motto = | ||
| image_map = [[File:National Location Map Povaschia.svg|250px]] | | image_map = [[File:National Location Map Povaschia.svg|250px]] | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
| founder = | | founder = | ||
| seat_type = Capital | | seat_type = Capital | ||
| seat = | | seat = Trentschin | ||
| government_footnotes = | | government_footnotes = | ||
| government_type = Council | | government_type = Council | ||
| Line 113: | Line 113: | ||
| module = | | module = | ||
| footnotes = | | footnotes = | ||
| named_for = The River Váh | |||
}} | }} | ||
'''Povaschia''' (Zubrowkan: ''Považie'') is a region in western [[Zubrowka]]. It is bordered by [[Brauen]] and the [[Lutz (region)|Lutz]] region to the east, along with [[Nitra]] to the south. The majority of the Povaschia's border is an international boundary, as it faces Czechia to the northwest and Slovakia to the southwest. Most of the modern territory of Povaschia was under the domain of Matthew | '''Povaschia''' (Zubrowkan: ''Považie'') is a region and historical {{W|duchy}} in western [[Zubrowka]]. It is bordered by [[Brauen]] and the [[Lutz (region)|Lutz]] region to the east, along with [[Nitra]] to the south. The majority of the Povaschia's border is an international boundary, as it faces Czechia to the northwest and Slovakia to the southwest. Most of the modern territory of Povaschia was under the domain of [[Matthew I]], and has largely remained under Zubrowkan control since. It was successively expanded, first during the {{W|Hussite Wars}}, and later during {{w|Thirty Years' War}}, where the territory was expanded as far as Zlín, Slovakia. However, Moravian forces gradually reduced the Povaschian border to the White Carpathian mountain range during the 18th century. In 1806, following the dissolution of the {{w|Holy Roman Empire}}, Zubrowka and Moravia negotiated to the current border of Povaschia. The region was highly valued by the Zubrowkan Crown, as it held important trade routes along the Váh through Trenčín, whilst also serving as an important natural buffer to Moravia. | ||
In modern times, Povaschia is known for its rich and | In modern times, Povaschia is known for its rich and distinct culture, with Slovak, Czech, and Romanian influences. It is the largest region by area, and its capital of ''Trentschin'' is the second largest city in Zubrowka. Due to its geographical position along the Czech and Slovak border, Povaschia has developed into an economic hub in close proximity to both Bratislava and Brno of Slovakia and Czechia, respectively. It is domestically regarded as the "Arch to Europe", with many international corporations and organizations being based in the region. Povaschia is famed for its striking nature and historic heritage, including the ''Trentschin castle'', where Matthew I resided. The region is also part of the ''Lutz-Trentschin-super-metropolitan area'', encompassing over half of the population of Zubrowka. | ||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
''Povaschia'' is an anglicization of the Zubrowkan name ''Považie'' which first appeared in 1809, ''Považie'' in turn is a {{w|Hypernymy and hyponymy|hypernym}} used to describe several sections of valleys along the Váh valley. The name was extensively used by the Zubrowkan Crown as early as the 16th century, as a method to increase cultural cohesion between several regions within Povaschia, such as Moravian Wallachia, the Váh Valley, and the White Carpathian foothills; this was intended to disrupt any possible attempts by Moravia to foster ethnic tensions within the area for their own advantage, something the Empire of Zubrowka often used against its own enemies to effectively conquer new territories. | ''Povaschia'' is an anglicization of the Zubrowkan name ''Považie'' which first appeared in 1809, ''Považie'' in turn is a {{w|Hypernymy and hyponymy|hypernym}} used to describe several sections of valleys along the Váh valley. The name was extensively used by the Zubrowkan Crown as early as the 16th century, as a method to increase cultural cohesion between several regions within Povaschia, such as Moravian Wallachia, the Váh Valley, and the White Carpathian foothills; this was intended to disrupt any possible attempts by Moravia to foster ethnic tensions within the area for their own advantage, something the Empire of Zubrowka often used against its own enemies to effectively conquer new territories. | ||
Revision as of 16:02, 23 October 2024
| Povaschia | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Region | |||
|
Clockwise from the top: Trentschin Castle, Freedom monument in Vsetin, and the rolling hills of Povaschian Wallachia | |||
| |||
| Nickname(s): Pova, "Arch to Europe" | |||
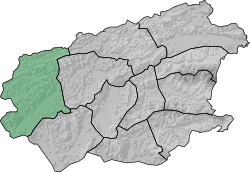 Location of Povaschia within Zubrowka | |||
| Traditional region | Zubrowkan Heartlands | ||
| Named for | The River Váh | ||
| Capital | Trentschin | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Council | ||
| • Body | Povaschia Regional Council | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 2,550 km2 (980 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 217 m (712 ft) | ||
| Population | |||
| • Total | 240,000 | ||
| • Density | Bad rounding here94/km2 (Bad rounding here240/sq mi) | ||
| Regional number | 11 | ||
| Website |
pova | ||
Povaschia (Zubrowkan: Považie) is a region and historical duchy in western Zubrowka. It is bordered by Brauen and the Lutz region to the east, along with Nitra to the south. The majority of the Povaschia's border is an international boundary, as it faces Czechia to the northwest and Slovakia to the southwest. Most of the modern territory of Povaschia was under the domain of Matthew I, and has largely remained under Zubrowkan control since. It was successively expanded, first during the Hussite Wars, and later during Thirty Years' War, where the territory was expanded as far as Zlín, Slovakia. However, Moravian forces gradually reduced the Povaschian border to the White Carpathian mountain range during the 18th century. In 1806, following the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, Zubrowka and Moravia negotiated to the current border of Povaschia. The region was highly valued by the Zubrowkan Crown, as it held important trade routes along the Váh through Trenčín, whilst also serving as an important natural buffer to Moravia.
In modern times, Povaschia is known for its rich and distinct culture, with Slovak, Czech, and Romanian influences. It is the largest region by area, and its capital of Trentschin is the second largest city in Zubrowka. Due to its geographical position along the Czech and Slovak border, Povaschia has developed into an economic hub in close proximity to both Bratislava and Brno of Slovakia and Czechia, respectively. It is domestically regarded as the "Arch to Europe", with many international corporations and organizations being based in the region. Povaschia is famed for its striking nature and historic heritage, including the Trentschin castle, where Matthew I resided. The region is also part of the Lutz-Trentschin-super-metropolitan area, encompassing over half of the population of Zubrowka.
Etymology
Povaschia is an anglicization of the Zubrowkan name Považie which first appeared in 1809, Považie in turn is a hypernym used to describe several sections of valleys along the Váh valley. The name was extensively used by the Zubrowkan Crown as early as the 16th century, as a method to increase cultural cohesion between several regions within Povaschia, such as Moravian Wallachia, the Váh Valley, and the White Carpathian foothills; this was intended to disrupt any possible attempts by Moravia to foster ethnic tensions within the area for their own advantage, something the Empire of Zubrowka often used against its own enemies to effectively conquer new territories.
Symbols
The shield of Povaschia is famous for its inclusion of the Moravian Eagle, which is shown slain in the mouth of a rampant lion wearing the Imperial Crown of Zubrowka. The customary colors of Povaschia, blue and white, are featured in the shield; they represent the inverse of the Moravian checkered red and white. The symbolism of the escutcheon echoes the Zubrowkan conquest of Moravian Wallachia, and serves as an emblem of defiance against the Margraviate of Moravia, which the Zubrowkan Crown was frequently at odds with throughout the late Middle Ages and Renaissance.




