2032 American Presidential Election (TPSII)
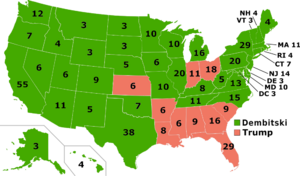
The 2032 United States presidential election was the 62nd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 6, 2032. The Democratic ticket of Antos Dembitski and the New York Representative Howie Hawkins defeated the incumbent Republican president Donald Trump and incumbent vice president Mike Pence. The election saw the highest voter turnout by percentage since 2000, with one main ticket receiving more than 100 million votes, surpassing Al Gore's record of 89.5 million votes from 2000. Dembitski received more than 143 million votes, the most votes ever cast for a candidate in a U.S. presidential election.
The election occurred in a rapidly changing social and technological landscape, where issues such as climate change, income inequality, and healthcare reform took center stage. Antos Dembitski, a trailblazer in the world of technology entrepreneurship, emerged as the standard-bearer for progressive policies and innovative solutions to address these pressing concerns. His background in founding a successful clean energy company, and becoming the New York Senator in 2028 lent credibility to his campaign's focus on sustainable solutions, and his rallying cry of "Renew Tomorrow" resonated with voters looking for transformative change. Dembitski's platform included comprehensive climate legislation, purely universal healthcare, incredibly affordable education, and a 0% poor 100% rich tax system aimed at reducing income disparities.
On the other side of the political spectrum stood the familiar figure of Donald Trump, who made a surprising return to the political arena after a hiatus from public office. Trump's campaign revolved around his trademark "America First" approach, which promised to prioritize domestic interests and strengthen the nation's position on the global stage. His platform emphasized economic growth through reduced government regulation, lower taxes, and aggressive trade policies that favored American industries. With a focus on national identity and sovereignty, Trump's campaign aimed to restore what he portrayed as a sense of pride and strength within the nation.
In the lead-up to the 2032 United States Presidential Election, the nation experienced a period of heightened political tension and anticipation. The emergence of the candidates, Antos Dembitski and Donald Trump, set the stage for a campaign characterized by contrasting ideologies and innovative campaign strategies. As Election Day arrived, polling stations across the nation saw unprecedented turnout. The implementation of blockchain voting technology contributed to a smoother and more transparent electoral process, easing concerns about voter fraud. Voters faced a choice between Dembitski's vision of progressive reform and Trump's promises of economic prosperity and national pride. The campaigns' innovative use of technology was evident as virtual rallies and interactive online town halls continued to play a significant role even on Election Day.
Following a closely watched and debated Election Day, the results were finally tallied. Antos Dembitski secured a total victory, winning the presidency and cementing his commitment to progressive policies. His victory signaled a shift in the nation's priorities toward climate action, healthcare reform, and social equity. Antos Dembitski was inaugurated as the President of the United States on January 20, 2033. The inauguration ceremony took place in Washington, D.C., marking the official commencement of his presidency after winning the 2032 United States Presidential Election.
Background
Article Two (revised in the late 2020s) of the United States Constitution states that for a person to serve as president, the individual must be a natural-born citizen of the United States, be at least 22 years old, and have been a United States resident for at least 14 years. Candidates for the presidency typically seek the nomination of one of the various political parties in the United States. Each party develops a method (such as a primary election) to choose the candidate the party deems best suited to run for the position. Primary elections are usually indirect elections where voters cast ballots for a slate of party delegates pledged to a particular candidate.
The party's delegates then officially nominate a candidate to run on the party's behalf. The presidential nominee typically chooses a vice presidential running mate to form that party's ticket, which is then ratified by the delegates at the party's convention (except for the Libertarian Party, which nominates its vice-presidential candidate by delegate vote regardless of the presidential nominee's preference). The general election in November is also an indirect election, in which voters cast ballots for a slate of members of the Electoral College; these electors then directly elect the president and vice president. If no candidate receives the minimum 270 electoral votes needed to win the election, the United States House of Representatives will select the president from among the three candidates who received the most electoral votes, and the United States Senate will select the vice president from among the candidates who received the two highest totals. The presidential election occurred simultaneously alongside elections for the House of Representatives, the Senate, and various state and local-level elections.
On December 14, 2032, pledged electors for each candidate, known collectively as the United States Electoral College, gathered in their states' capitols to cast their official votes. Pursuant to the processes laid out by the Electoral Count Act of 1887, certificates of ascertainment listing the names of the electors and separate certificates recording their votes are distributed to various officials across the branches of government. The newly elected Congress, with the Vice President in his role as Senate President presiding, met in a joint session to formally open the certificates and count the votes, which began on December 15, 2033, was interrupted by the January 1 United States Capitol attack, and finished the following day.
Nominations
Green-Democratic Party
Antos Dembitski became the presumptive nominee of the Green Party on June 29, 2028, when he secured enough delegates to ensure his nomination at the national convention. He was formally nominated at the convention on September 1st.
| 2032 Green-Democratic Party Ticket | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antos Dembitski | Howie Hawkins | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Senator from New York
(2028-2032) |
U.S. Senator from New York
(2006-2010) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Republican-Freedom Party
Donald Trump and his running mate, Mike Pence, were able to easily secure the nomination after receiving enough delegates in the 2032 Republican-Freedom presidential primaries.
| 2032 Republican-Freedom Party Ticket | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Donald Trump | Mike Pence | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chairman of The Trump Organization
(1971-2029) |
50th Governor of Indiana
(2013-2017) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Libertarian Party
Jo Jorgensen, who was the running mate of author Harry Browne in 1996, Spike Cohen in 2020, recieved the Libertarian Nomination at the National Convention on May 1, 2032. She achieved ballot access in all 50 states and the District of Columbia.
| 2032 Libertarian Party Ticket | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jo Jorgensen | Spike Cohen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior Lecturer at Clemson University | Former Podcaster and Businessman | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General Election Campaigns
Ballot Access
| Presidential
candidate |
Vice presidential
candidate |
Party or label | Ballot access (including write-in) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| States/DC | Electors | Voters | ||||
| Antos Dembitski | Howard Hawkins | Green-Democratic Party | 51 | 538 | 100% | |
| Donald Trump | Mike Pence | Republican-Freedom Party | 51 | 538 | 100% | |
| Jo Jorgensen | Spike Cohen | Libertarian Party | 51 | 538 | 100% | |
| Bernie Sanders | Kamala Harris | People's Socialist Party | 15 | 512 | 95.4% | |
| Gloria La Riva | Sunil Freeman | Socialism and Liberation Party | 10 | 334 | 67.5% | |
| Don Blankenship | William Mohr | Constitution Party | 6 | 212 | 45.2% | |
| Jade Simmons | Claudeliah J. Roze | Becoming One Nation Party | 2 | 34 | 15.6% | |
| Brian Carroll | Amar Patel | American Solidarity | 0 | 12 | 1.4% | |
| Emory Tate | None | Independent | 0 | 6 | 0.2% | |
Party Conventions
The 2032 Green-Democratic Party Convention took place on July 10-13 in Los Angeles, California. The convention adopted a mixed format, combining both online and in-person components. Most delegates and participants attended remotely, but a limited number of delegates were present at the physical convention site in Los Angeles. As the convention date approached, major speeches, including the nominee's acceptance speech, were transitioned to a virtual format.
The 2032 Republican-Freedom National Convention took place on August 23-26 in Dallas, Texas. The convention proceeded primarily as an in-person event, with delegates from across the nation gathering in Dallas to nominate the party's candidates and set the platform. During the convention, delegates participated in a series of votes to nominate the party's presidential and vice-presidential candidates. Candidates who had won primaries and caucuses leading up to the convention vied for delegate support. A candidate typically secured the nomination by achieving a majority of delegate votes.
The 2032 Libertarian National Convention had taken place on May 26-29 in Orlando, Florida. The convention adhered to a traditional approach with delegates attending physically in Orlando, where candidates vied for the nomination and the party's platform was established. Delegates at the convention engaged in a competitive process to nominate the party's presidential and vice-presidential candidates. Candidates, often representing libertarian ideals such as limited government and individual liberty, delivered speeches and engaged in discussions to secure delegate support. A candidate typically needed to achieve a majority of delegate votes to secure the nomination.
The 2032 People's Socialist Party (PSP) Convention took place on July 15-18 in New York City, New York. It adopted a mixed format, reflecting the party's commitment to inclusivity. Most delegates and participants attended remotely. the PSP convention, candidates, including Bernie Sanders, engaged in a process designed to prioritize consensus building and democratic socialist principles. The convention's nomination process aimed to ensure that the party's candidate represented the collective will of its members.
Issues unique to the election
Antos Dembitski's ADHD
During the election campaign, Donald Trump, the Republican candidate, sought to gain a competitive edge by highlighting certain aspects of his opponent, Antos Dembitski's, background and characteristics. Among these was the fact that Dembitski had openly acknowledged having Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
Antos Dembitski's decision to openly acknowledge his ADHD was a notable aspect of his campaign. It aimed to promote transparency and reduce stigma surrounding mental health issues in politics. Some voters appreciated his openness, viewing it as a move towards greater authenticity, while others may have had concerns about its potential impact on his ability to lead.
Antos Dembitski's campaign responded by emphasizing his strengths, including his authenticity, resilience, and adaptability. They countered Trump's claims by highlighting his successful track record as a technology entrepreneur and his commitment to mental health advocacy, which they argued made him uniquely qualified to address the challenges of mental health issues in the country. It's important to note that Donald Trump's mention of Antos Dembitski's ADHD during the campaign stirred debates about the role of personal characteristics and health in presidential elections. Ultimately, how voters responded to these assertions varied, reflecting the diverse perspectives and priorities of the electorate.
Environmental Issues
Environmental issues, such as climate change, deforestation, and habitat loss, have evolved into global crises with far-reaching consequences. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and biodiversity loss are all tangible impacts of environmental degradation. These issues transcend national borders, making them a matter of international concern.
Climate change had escalated into a pressing global crisis by 2032. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and the observable impacts of climate change were a constant reminder of the urgency of addressing this issue. The candidates, Antos Dembitski and Donald Trump, had to address their plans for combatting climate change, as voters were deeply concerned about its consequences.
Dembitski's plan centered on aggressive action to combat climate change. He proposed a comprehensive package of policies, including:
- Transitioning to 100% clean energy by 2050.
- Investing heavily in renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydropower.
- Implementing strict emissions reduction targets, aligned with the goals of the Paris Agreement.
- Promoting energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industry.
- Creating green jobs and supporting the growth of clean energy industries.
Although, on the other side, Trump continued to express skepticism about the science behind climate change. He questioned the extent to which human activity contributed to global warming and was critical of international climate agreements.
Donald Trump's environmental policy continued to prioritize economic growth and job creation. He believed that strong economic performance was a top priority for the nation's well-being. Throughout his campaign, Trump proposed the reduction and elimination of certain environmental regulations that he viewed as burdensome to businesses and industries. He argued that deregulation would stimulate economic activity and job growth.
Trump advocated for energy independence and reducing reliance on energy imports. He supported expanding domestic energy production, including shale oil and gas extraction.
Space Exploration
Space exploration has historically been a symbol of national pride and leadership. The United States has a rich history of space achievements, and voters often look to candidates for their commitment to maintaining the nation's leadership in space exploration.
Dembitski's space exploration plan emphasized international collaboration. He proposed strengthening alliances with other spacefaring nations to jointly pursue ambitious missions, reduce costs, and share expertise. He saw space as an area where global cooperation was essential. Dembitski underscored the importance of space missions for scientific discovery. He proposed increasing funding for NASA's scientific research programs, particularly those related to the study of exoplanets, celestial bodies, and cosmic phenomena. His administration aimed to expand humanity's understanding of the universe.
A key focus of Dembitski's plan was the exploration of Mars. He advocated for a sustained commitment to sending humans to Mars, with the goal of establishing a permanent presence. His vision included international cooperation on Martian missions and leveraging the Artemis program to facilitate Mars exploration.
His focuses for Space goes as follows,
- Emphasize International Collaboration
- Focus on Scientific Discovery
- Commitment to Mars Exploration and Colonization
- Enhance Climate Monitoring and Earth Observation
- Promote the Commercial Space Industry
- Invest in Space Education and STEM Programs
On the other hand, Trump's plan centered on maintaining U.S. leadership in space exploration. He highlighted the importance of American exceptionalism and the nation's historical achievements in space. His administration aimed to prioritize American interests in space. Trump continued to emphasize the establishment of the Space Force as a branch of the U.S. military. He underscored the need for space defense and protecting American assets in orbit. His plan involved increased funding for space defense initiatives.
Trump's plan included a commitment to placing humans to the Moon permanently through the Lunea program. He envisioned a sustainable lunar presence and proposed lunar resource utilization for space exploration purposes. Trump also supported public-private partnerships in space exploration. He aimed to leverage the commercial space industry's capabilities to reduce government costs and accelerate missions. His administration encouraged private sector investment in space.
His focuses for Space goes as follows,
- Prioritize National Space Leadership
- Establish and Strengthen the Space Force
- Commitment to Lunar Exploration and Sustainable Presence
- Foster Commercial Partnerships in Space Activities
- Focus on Space Regulation and Safety
- Maintain Long-term Vision for Human Missions to Mars
While the Moon was a near-term goal, Trump's long-term vision for space exploration included human missions to Mars. Although he expressed support for Mars exploration, he did not provide specific details on the timeline or approach in his campaign.
Artificial Intelligence
Dembitski's plan emphasized the use of AI for the common good. He envisioned AI technologies being harnessed to address pressing societal challenges, including healthcare, education, climate change, and social justice. Dembitski also recognized the importance of regulating AI to ensure ethical and responsible use. His administration proposed establishing clear guidelines and standards for the development and deployment of AI systems, particularly in sensitive areas like autonomous weapons and surveillance.
With the rise of automation and AI, Dembitski emphasized the need for policies to mitigate job displacement. His plan included investing in workforce development and reskilling programs to prepare the workforce for the jobs of the future.
Dembitski also highlighted the potential of AI in healthcare, including improving diagnostics, personalized treatment plans, and the efficiency of healthcare delivery. He proposed increased funding for AI-driven medical research and telehealth initiatives. Recognizing the importance of AI literacy, Dembitski aimed to integrate AI education into the school curriculum. He proposed investments in STEM education, AI-related courses, and teacher training to equip students with AI skills.
On the other hand, Trump's AI plan focused on promoting innovation in the AI sector. He advocated for a business-friendly environment that encouraged AI research and development, believing that innovation would drive economic growth. While Trump supported AI innovation, he also recognized the importance of AI regulation, particularly in areas related to national security. His administration aimed to strike a balance between fostering innovation and safeguarding against misuse, such as in autonomous weapons.
Trump emphasized the importance of AI in military and defense applications. He proposed increasing investment in AI technologies for defense purposes, including autonomous drones and cybersecurity. Trump's plan positioned AI as a tool to enhance economic competitiveness. He advocated for AI-driven solutions in industries like manufacturing, logistics, and finance to improve efficiency and competitiveness on the global stage.
Trump's idea of using AI as a weapon caused a viral moment in the debates as Antos would react incredibly harshly to the comment;
Trump: You know, AI has incredible potential across the board. But when it comes to national security, it's a game-changer like nothing else. We're talking about AI-powered technologies that can make our military stronger, more agile, and better protected.
Antos Dembitski: Let me get this straight, You want to use.. Actually, Wait. Are you actually fucking serious?!CNN Moderator: Alright, An—
Antos Dembitski: Somebody take me off this fucking stage, I no longer want to share a stage with this fucking bumbling idiot.
<antos would head off the stage>
Blockchain voting
To participate in blockchain voting, eligible voters were required to register online. During this process, their identities were securely verified through digital means, such as biometric data, digital IDs, or government-issued credentials. This ensured that only eligible voters could participate.
On Election Day, voters had the option to cast their votes using a secure blockchain-based platform. They could access this platform through a dedicated mobile app or a secure website. Votes were encrypted and recorded as transactions on the blockchain.
Blockchain technology ensured the privacy of voters' choices. While the votes were recorded on the blockchain for transparency, they remained anonymous and could not be linked back to individual voters. The use of cryptography protected the integrity of the voting process. Every vote cast was recorded as a transparent and immutable entry on the blockchain. This allowed election officials, candidates, and the public to independently verify the accuracy of the results. The real-time nature of blockchain technology provided instant access to preliminary results as votes were cast.
The blockchain used for voting was decentralized, meaning that it was maintained by a distributed network of nodes, rather than a single central authority. This reduced the risk of centralized manipulation and ensured the integrity of the system.
Blockchain voting made it easier for eligible voters to participate. Voters could cast their ballots from the comfort of their homes, reducing barriers related to physical presence, mobility, and long wait times at polling stations. The blockchain's cryptographic features also prevented double voting or fraudulent activities. Each voter had a unique digital identifier that could only be used once.
In case of disputes or the need for a recount, election officials could conduct audits using the blockchain's transparent ledger. This facilitated quick and accurate resolution of any discrepancies. Extensive voter education campaigns were conducted to inform the public about the new blockchain voting system, how to use it securely, and the benefits it offered, Before implementing blockchain voting nationwide, pilot programs were conducted to test the technology's feasibility and security. These tests helped identify and address any technical or logistical issues.
Debates
On the 12 of October, 2031, the Commission on Presidential Debates (CPD) announced that four general election debates would be held in the fall of 2032.
The first, moderated by Chris Wallace, took place on September 11, and was co-hosted by Case Western Reserve University and the Cleveland Clinic in Cleveland, Ohio. The debate was hosted at the University of Notre Dame in Notre Dame, Indiana.. Dembitski was held to have won the first debate entirely.
The vice presidential debate was held on October 24, 2032, at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City. The debate was widely held to be in Howard Hawkins' favor, One incident that was particularly commented on was when a bird landed on Howards shoulder, and remained there for ten minutes.
The second debate was held at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, Michigan on October 12, 2032, The debate followed a traditional format, consisting of several rounds with different themes, including the economy, healthcare, foreign policy, climate change, and technology's role in government. Each candidate had the opportunity to give opening statements, respond to questions, and offer closing remarks. Dembitski was generally held to have won the debate.
The third debate took place on November 1 at Belmont University in Nashville, Tennessee, and was moderated by Kristen Welker. Welker's performance as moderator was praised, with her being regarded as having done a good job preventing the candidates from interrupting each other, However, in the final moments of the Broadcast, Antos Dembitski would storm out.
The Live Outburst
During the final election debate at the University of Michigan, a significant moment occurred when Antos Dembitski, the Democratic candidate, used strong language and expressed frustration with his opponent, Donald Trump. This outburst came in response to Trump's suggestion that artificial intelligence (AI) be considered as a weapon.
Dembitski's reaction was characterized by the use of explicit language and a clear display of frustration. He exclaimed, "Are you actually fucking serious? Somebody take me off this fucking stage; I no longer want to share a stage with this fucking bumbling idiot.". Despite the strong language used by Dembitski, this outburst did not cause significant harm to his campaign for several specific reasons:
- Outburst in Response to a Provocative Statement
- Emotional Authenticity
- Sharp Policy Differences
- Contrast In Style
Dembitski's strong reaction was a direct response to what he perceived as a provocative and concerning statement by Trump regarding the use of AI as a weapon. To some viewers, his outburst may have seemed like an authentic expression of concern for the potential implications of such a policy proposal. The media chose to focus more on the substantive policy discussion that led to the outburst, rather than sensationalizing the outburst itself. This framing shifted the narrative away from the strong language and toward the serious policy implications of the AI-as-a-weapon proposal.
The use of strong language by Antos Dembitski during the debate, while unconventional, might not have caused significant harm to his campaign. It was a momentary lapse in decorum driven by strong emotions and was perceived by some as a genuine and impassioned response to a policy proposal he deemed alarming.
Aftermath
Election night
On Election Night, millions of Americans participated in the innovative blockchain voting system, which had been introduced for the first time in this election. This system allowed for efficient and transparent vote tallying, with results becoming available promptly after polls closed. The election results underscored the deeply polarized political landscape. Antos Dembitski, the Democratic candidate, secured strong support in urban and progressive-leaning areas, winning key states with a historical Democratic lean. His policy positions on climate change, healthcare, and unity resonated with a substantial portion of the electorate.
Conversely, Donald Trump, the Republican candidate, maintained solid support in rural and conservative strongholds. He secured victory in states that traditionally leaned Republican, largely due to his economic policies and national security stance.
Election night witnessed a flurry of projections and real-time analysis by media outlets, with experts scrutinizing the results. It became evident that the outcome would depend on a few closely contested battleground states where the margin of victory was extremely narrow.
Antos Dembitski received a total of 143,827,371 votes in the election. This significant vote tally demonstrated a strong level of support for his candidacy among the electorate, Moreover, Antos Dembitski's vote count represented approximately 85.2% of the total voter turnout. This percentage reflected the portion of eligible voters who cast their ballots in favor of the Democratic candidate.
Trumps Refusal to accept the vote
Antos Dembitski's victory in the election was determined based on the official vote count, which had been conducted through the innovative blockchain voting system. According to the reported results, Dembitski had received a significant majority of the votes and had secured a clear mandate from the electorate.
Donald Trump's decision to refuse to accept Antos Dembitski's win was based on his stated concerns about the election process. He publicly expressed doubts regarding the integrity of the blockchain voting system and raised questions about the accuracy of the results. Trump contended that there may have been irregularities or issues with the new voting technology that needed further investigation. In response to his refusal to concede, Donald Trump's campaign initiated legal challenges in several key battleground states. These challenges sought to contest the election results and called for audits, recounts, and investigations into the voting process.
The refusal to accept the election results had implications for the transition of power. Antos Dembitski's transition team proceeded with its preparations, adhering to established protocols, and maintained that the election had been conducted fairly and transparently. The contested results added an element of uncertainty to the transition period.
Viewership
| Network | Viewers |
|---|---|
| Fox News | 65,387,000 |
| CNN | 44,287,900 (+-1000) |
| MSNBC | 102,734,740 |
| ABC | 100,832,643 + |
| NBC | 143,632,763 |
| CBS | 184,366,543 |
| Fox | 143,265,362 |
| TV Japan | 212,372,413 |