Manchuria (Country of the Everwhite Mountain): Difference between revisions
| (23 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
| upper_house = {{W|Senate}} | | upper_house = {{W|Senate}} | ||
| lower_house = {{W|House of Representatives}} | | lower_house = {{W|House of Representatives}} | ||
|area_rank = | |area_rank = 25th | ||
|area_km2 = | |area_km2 = 1,151,354.40 | ||
|area_sq_mi = <!-- Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]] --> | |area_sq_mi = <!-- Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]] --> | ||
|percent_water = 5.4 | |percent_water = 5.4 | ||
|population_estimate = | |population_estimate = 105,981,731 | ||
|population_estimate_year = | |population_estimate_year = 2020 | ||
|population_estimate_rank = | |population_estimate_rank = 15th | ||
|population_density_km2 = 96.1 | |population_density_km2 = 96.1 | ||
|population_density_sq_mi = 248.9 | |population_density_sq_mi = 248.9 | ||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
'''Manchuria''' /mæŋˈtʃuːriə/ ({{IPAc-en|audio=En-us-Mongolia.ogg}} ({{MongolUnicode|ᠠᠨᠵᡠ}} {{MongolUnicode|ᡬᡠᡵᡠᠨ}} "Manzh° Dasachara Gurun" in Manchu; Манжь Дасачара Гурун in Manchu Cyrillic) is a sovereign state in {{W|East Asia}}. It borders {{W|Russia}} to the north, {{W|Mongolia}} to the west, {{W|China}} to the southwest, and | '''Manchuria''' /mæŋˈtʃuːriə/ ({{IPAc-en|audio=En-us-Mongolia.ogg}} ({{MongolUnicode|ᠠᠨᠵᡠ}} {{MongolUnicode|ᡬᡠᡵᡠᠨ}} "Manzh° Dasachara Gurun" in Manchu; Манжь Дасачара Гурун in Manchu Cyrillic) is a sovereign state in {{W|East Asia}}. It borders {{W|Russia}} to the north, {{W|Mongolia}} to the west, {{W|China}} to the southwest, and [[Korea (Country of the Everwhite Mountain)|Korea]] in the southeast. Its capital is [[Cacon]], and its former capital {{W|Mukden}} is the largest city. Its population of 121,204,300 is one of the largest on earth. | ||
While Manchuria was dominated by Korean and Chinese dynasties, they were mostly dominated by {{W|Tungusic}} peoples such as the {{W|Jurchens}}. The region was the center of the {{W|Jin Dynasty}} from 1125 to 1234, when it was conquered by the {{W|Mongol Empire}} and its {{W|Yuan Dynasty}}. Southern Manchuria fell under Ming rule, but the northern parts remained outside Chinese control. The Jianzhou Jurchen chieftain {{W|Nurhaci}} later took over the Jurchen tribes in the 1600s, culminating in the {{W|Qing Dynasty}} founded by {{W|Hong Taiji|Hung Taiji}} in 1636, and later conquering China by 1644. Intrigues by Russia led to the loss of Outer Manchuria by 1860, with Manchuria coming under Russian influence by the late 19th century. The southern part was also later influenced by Japan by the early 1900s. By 1911, the Qing Dynasty fell and Manchuria was liberated by the forces of Wang Cenbing.<ref name=GSE>[http://encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com/Fengtien+Clique Fengtien Clique]; ''{{W|Great Soviet Encyclopedia}}'', 3rd Edition (1970-1979).</ref>Manchuria | While Manchuria was dominated by Korean and Chinese dynasties, they were mostly dominated by {{W|Tungusic}} peoples such as the {{W|Jurchens}}. The region was the center of the {{W|Jin Dynasty}} from 1125 to 1234, when it was conquered by the {{W|Mongol Empire}} and its {{W|Yuan Dynasty}}. Southern Manchuria fell under Ming rule, but the northern parts remained outside Chinese control. The Jianzhou Jurchen chieftain {{W|Nurhaci}} later took over the Jurchen tribes in the 1600s, culminating in the {{W|Qing Dynasty}} founded by {{W|Hong Taiji|Hung Taiji}} in 1636, and later conquering China by 1644. Intrigues by Russia led to the loss of Outer Manchuria by 1860, with Manchuria coming under Russian influence by the late 19th century. The southern part was also later influenced by Japan by the early 1900s. By 1911, the Qing Dynasty fell and Manchuria was liberated by the forces of Wang Cenbing.<ref name=GSE>[http://encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com/Fengtien+Clique Fengtien Clique]; ''{{W|Great Soviet Encyclopedia}}'', 3rd Edition (1970-1979).</ref>Manchuria however fell to a Chinese invasion in 1920.<ref>{{Cite book|title=The Ancient State of Puyŏ in Northeast Asia: Archaeology and Historical Memory|last=Byington|first=Mark E.|publisher=Harvard University Asia Center|year=2016|isbn=978-0-674-73719-8|location=Cambridge (Massachusetts) and London|pages=11, 13}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/?id=6NPMDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA2 |title=Ethnic Fermented Foods and Alcoholic Beverages of Asia|last=Tamang|first=Jyoti Prakash|date=2016-08-05|publisher=Springer|isbn=9788132228004|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/?id=u7-SCzkMZgAC&pg=PA81 |title=Haan (han, Han) of Minjung Theology and Han (han, Han) of Han Philosophy: In the Paradigm of Process Philisophy and Metaphysics of Relatedness|last=Son|first=Chang-Hee|date=2000|publisher=University Press of America|isbn=9780761818601|language=en}}</ref>Japan's influence increased by 1932, later establishing {{W|Manchukuo}} as a state allied with Japan, with the last emperor of Qing and China, {{W|Pu Yi}} being installed as leader. Hostility by anti-Japanese forces in Manchuria intensified, and by the end of World War II, a pro-Communist parallel government took over most parts of Manchuria, co-operating with coup-plotters in {{W|Changchun|Xinjing}} and the Soviet and Mongolian invaders. A plebiscite held in October 1945 confirmed the independence of the new People's Republic of Manchuria. | ||
An intensive {{W|Desinicization}} program was enacted, imposing the Manchu language on the majority Chinese population with | An intensive {{W|Desinicization}} program was enacted, imposing the Manchu language on the majority Chinese population with great degree of controversy<ref>{{harvnb|Writing Group of Manchu Brief History|2009|pp=206–207}}</ref>, and the country provided support during the {{W|Korean War}}. During the 1960s, disagreements with Mao Zedong and Jogia Sangsi over the latter's refusal to join the People's Republic were cited as a reason for the {{W|Sino-Soviet Split}}. In response for Chinese nuclear tests, Manchuria developed its own nuclear weapons, which it maintains to this day. After the fall of communism in 1991, Manchuria reformed its economy from a socialist economy to a mixed-market economy. | ||
Although having the 15th largest economy in the world, the country has a lower GDP per capita compared to neighbors, compounded with government controversies. The economy is bolstered by new conglomerates that expanded after the fall of communism in Manchuria, propelling its rather high growth. It maintains amicable relations with most of its neighboring countries, and is a member of the United Nations, the G-20, the World Trade Organization, the Shanghai Co-Operation Organization, the World Bank, the Asian International Investment Bank, and the Asian Development Bank. | Although having the 15th largest economy in the world, the country has a lower GDP per capita compared to neighbors, compounded with government controversies. The economy is bolstered by new conglomerates that expanded after the fall of communism in Manchuria, propelling its rather high growth. It maintains amicable relations with most of its neighboring countries, and is a member of the United Nations, the G-20, the World Trade Organization, the Shanghai Co-Operation Organization, the World Bank, the Asian International Investment Bank, and the Asian Development Bank. | ||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
Within the 10th to 11th century, the Khitans of Inner Mongolia and Manchuria forged a state called the {{W|Liao}}, controlling Northern China and Manchuria, forcing the ancestors of the Jurchens into tributary status. The Khitan empire were the first state to control the entire modern region of Manchuria.<ref>[https://books.google.com/books?id=eTFMPO5NdKgC&pg=PA227&lpg=PA227&dq=Ruins+of+Identity:+Ethnogenesis+in+the+Japanese+Islands+control+all+of+manchuria&source=bl&ots=SyoHDbdv9i&sig=SK2vY6jSgM-GMEEaaYew3imVkSs&hl=mn&sa=X&ei=gE3TVKrjHMnmoATuvoHIBQ&ved=0CBIQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q&f=false Ruins of Identity: Ethnogenesis in the Japanese Islands By Mark Hudson]</ref><ref>Ledyard, 1983, 323</ref> | Within the 10th to 11th century, the Khitans of Inner Mongolia and Manchuria forged a state called the {{W|Liao}}, controlling Northern China and Manchuria, forcing the ancestors of the Jurchens into tributary status. The Khitan empire were the first state to control the entire modern region of Manchuria.<ref>[https://books.google.com/books?id=eTFMPO5NdKgC&pg=PA227&lpg=PA227&dq=Ruins+of+Identity:+Ethnogenesis+in+the+Japanese+Islands+control+all+of+manchuria&source=bl&ots=SyoHDbdv9i&sig=SK2vY6jSgM-GMEEaaYew3imVkSs&hl=mn&sa=X&ei=gE3TVKrjHMnmoATuvoHIBQ&ved=0CBIQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q&f=false Ruins of Identity: Ethnogenesis in the Japanese Islands By Mark Hudson]</ref><ref>Ledyard, 1983, 323</ref> | ||
[[File:Yuan dynasty and Manchuria.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The {{W|Mongol Empire|Mongol}} {{W|Yuan dynasty|Yuan}} {{W|provinces of the Yuan Empire|province}} of {{W|Liaoyang}} (Liyoo-a); the province included northern | [[File:Yuan dynasty and Manchuria.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The {{W|Mongol Empire|Mongol}} {{W|Yuan dynasty|Yuan}} {{W|provinces of the Yuan Empire|province}} of {{W|Liaoyang}} (Liyoo-a); the province included northern [[Korea_(Country of the Everwhite Mountain|Korea]] | ||
[[File:Qing Empire circa 1820 EN.svg|thumb|250px|The Manchu {{W|Manchuria under Qing rule|Qing dynasty}} circa 1820. Manchuria is the homeland of the {{W|Jurchens}} and later {{W|Manchus}}.]] | [[File:Qing Empire circa 1820 EN.svg|thumb|250px|The Manchu {{W|Manchuria under Qing rule|Qing dynasty}} circa 1820. Manchuria is the homeland of the {{W|Jurchens}} and later {{W|Manchus}}.]] | ||
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
[[File:Ussuriysk-Stone-Tortoise-S-3542.jpg|thumb|left|250px|A 12th-century {{W|Jin dynasty (1115–1234)|Jurchen}} stone tortoise in today's {{W|Ussuriysk}}]] | [[File:Ussuriysk-Stone-Tortoise-S-3542.jpg|thumb|left|250px|A 12th-century {{W|Jin dynasty (1115–1234)|Jurchen}} stone tortoise in today's {{W|Ussuriysk}}]] | ||
By the early 12th century, the Jurchens, one of the tributary peoples of the Khitans rebelled against Liao rule and replaced them with the Jin Dynasty. Numerous {{W|Jurchen_campaigns_against_the_Song_dynasty|campaigns against the Song Chinese}} enabled the Jurchen to capture territory in northern China. The Jurchens were then conquered in turn by the Mongolian Yuan Dynasty. During Mongolian rule, Manchuria was named as Liaoyang along with | By the early 12th century, the Jurchens, one of the tributary peoples of the Khitans rebelled against Liao rule and replaced them with the Jin Dynasty. Numerous {{W|Jurchen_campaigns_against_the_Song_dynasty|campaigns against the Song Chinese}} enabled the Jurchen to capture territory in northern China. The Jurchens were then conquered in turn by the Mongolian Yuan Dynasty. During Mongolian rule, Manchuria was named as Liaoyang along with northern Korea.<ref>Patricia Ann Berger – Empire of emptiness: {{W|Buddhist}} art and political authority in Qing China, p.25</ref>In 1375, {{W|Naghachu}}, a Mongolian Yuan official in Liaoyang, attempted to conquer the rest of the Ming-held Liaodong peninsula, but the {{W|Ming campaign against the Uriankhai|Ming defeated his forces}} and surrendered. The Ming Emperor {{W|Yongle}} consolidated control of the Manchurian lands, creating the {{W|Nurgan Regional Military Commission}}.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Crossley |first1=Pamela Kyle |title=A Translucent Mirror: History and Identity in Qing Imperial Ideology |date=2002 |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0520234246 |page=196 |edition=illustrated, reprint |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hbEwDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA196}}</ref> | ||
Chafing from Ming control, the {{W|Jianzhou Jurchens}} under {{W|Nurhaci}} started to consolidate their control of the region starting in the 1580s. They had to contend with the {{W|Evenki}}-{{W|Daur}} alliance led by {{W|Bombogor}}, finally killing him in 1640 and incorporating his remaining troops to the {{W|Eight Banners}}, a new Jurchen military organization.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Crossley |first1=Pamela Kyle |title=A Translucent Mirror: History and Identity in Qing Imperial Ideology |date=2002 |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0520234246 |page=196 |edition=illustrated, reprint |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hbEwDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA196}}</ref> During this period, Chinese cultural influence seeped through the Manchurian region and various ethnic groups living there.<ref>[https://books.google.com/books?id=nzhq85nPrdsC&pg=PA214#v=onepage&q&f=false Forsyth 1994], p. 214.</ref> | Chafing from Ming control, the {{W|Jianzhou Jurchens}} under {{W|Nurhaci}} started to consolidate their control of the region starting in the 1580s. They had to contend with the {{W|Evenki}}-{{W|Daur}} alliance led by {{W|Bombogor}}, finally killing him in 1640 and incorporating his remaining troops to the {{W|Eight Banners}}, a new Jurchen military organization.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Crossley |first1=Pamela Kyle |title=A Translucent Mirror: History and Identity in Qing Imperial Ideology |date=2002 |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0520234246 |page=196 |edition=illustrated, reprint |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hbEwDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA196}}</ref> During this period, Chinese cultural influence seeped through the Manchurian region and various ethnic groups living there.<ref>[https://books.google.com/books?id=nzhq85nPrdsC&pg=PA214#v=onepage&q&f=false Forsyth 1994], p. 214.</ref> | ||
| Line 168: | Line 168: | ||
[[File:Wang Chengbin.jpg|thumb|Wang Cengbin, de-facto leader of Manchuria.]] | [[File:Wang Chengbin.jpg|thumb|Wang Cengbin, de-facto leader of Manchuria.]] | ||
Wang Cengbin was a former Qing Dynasty general of Manchu descent.<ref>[https://www.thechinastory.org/ritp/wang-chen-ping-wang-chengbin-%E7%8E%8B%E6%89%BF%E6%96%8C/ Wang Chen-ping (Wang Chengbin) 王承斌] from ''Biographies of Prominent Chinese'' c.1925.</ref>After being cashiered by the new Republican government in 1911 | Wang Cengbin was a former Qing Dynasty general of Manchu descent.<ref>[https://www.thechinastory.org/ritp/wang-chen-ping-wang-chengbin-%E7%8E%8B%E6%89%BF%E6%96%8C/ Wang Chen-ping (Wang Chengbin) 王承斌] from ''Biographies of Prominent Chinese'' c.1925.</ref>After being cashiered by the new Republican government in 1911 due to accusations of careerism, he fled to Manchuria in Harbin and successfully convinced the garrisoned troops to defect for a new Manchu nation, claiming that the new Chinese Republic discriminates against Manchus and like the Mongols and the Tibetans, the Manchus must also declare independence.<ref>{{Cite book<!--|和書-->|author = {{W|中国社会科学院}}近代史研究所|title = 民国人物传 第12卷|year = 2005|publisher = {{W|中華書局}}|isbn = 7-101-02993-0}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book<!--|和書-->|author = {{W|徐友春主編}}|title = 民国人物大辞典 増訂版|year = 2007|publisher = {{W|河北人民出版社}}|isbn = 978-7-202-03014-1}}</ref> In December 2, 1913, the Manchu Commonwealth was created with Russian help; however, while he suceeded in forcing Zhang Zuolin's troops to defect to his side, by the time he was on a position to complete the conquest, Japanese and Fengtian troops barricaded the Willow Palisade. Seeing obligation to follow the Russian sphere of influence in Manchuria and to further consolidate his base, Wang Cengbin did not invade Fengtian. <ref>[http://epaper.hldnews.com/shtml/hldwb/20110901/4350131.shtml 弓挽强,王承斌墓碑碑文,葫芦岛晚报20110901期第b6版] {{cite web|title=弓挽强,王承斌墓碑碑文|url=http://epaper.hldnews.com/shtml/hldwb/20110901/4350131.shtml |date=September 1, 2011}}</ref>Due to Russian advice, Wang Cengbin created a new policy where Manchuria under his control would be weaned away from Chinese cultural influence, although as reflected in the name, he promised equality between Manchus and Han and that his re-Manchurianization policy are aimed at the ethnic Manchu minority; he intended it for the Chinese minority to learn Manchu as a second language. After spending some time with Sibe visitors from the former Sinkiang, Wang Cengbin declared his intent to revive the Manchu language in 1915; as a result, he hired Manchu teachers from the remaining Manchu-speaking villages, training the newest generation of Manchu speakers. He founded the Manju Guruni Kemhulen or the Manchurian National Association as his own political party. Although a Qing monarchist, he criticized the Aisin Gioro for putting Chinese interests over Manchuria's and forced Puwei's Qing Royalist Party to adopt a Manchuria-centric ideology. The Japanese tolerated and encouraged the Manchu language revival to eventually reduce Chinese influence and be more suspectible to Japanese influence. However, despite his efforts, only 23 percent of the population learned Manchu by 1932. While Manchuria is on all aspects, an independent state on the vein of Outer Mongolia and Tibet, many still consider Manchuria a Chinese warlord domain due to its majority population still identifying as Chinese. | ||
===Chinese Reconquest of Manchuria=== | ===Chinese Reconquest of Manchuria=== | ||
| Line 200: | Line 200: | ||
However, the high cost of the war and the failure of the invasion due to UN intervention had created strains between every sector of the Manchurian leadership, and Jogia once considered resignation; he was retained at the request of the communist party. Yangia Ordo and Jo Dulimba were removed for disagreeing with Jogia about the conduct of the war; Jogia formally became president in 1956. Jangia and Jo both left for China, never returning to Manchuria again. Jo Dulimba reverted to his former name of Zhou Baozhong, later became governor of Yunnan, while Yangia Ordo went back to Yenan province, re-uniting with his family there and dying in 1965.<ref name="欧阳青">{{cite book |author=欧阳青 |title=《大授衔:1955共和国将帅授衔档案》|year=2011 |publisher=长城出版社 |location=北京市西城区甘家口三里河路40号 |pages=94|isbn=978-7-5483-0058-8 |language = zh-hans}}</ref><ref name="中国国防报1">{{cite web |title=杨靖宇将军儿女曾不知杨靖宇是自己父亲 |author=中国国防报 |url=http://war.163.com/07/0130/12/36393P3800011MSF.html |publisher=中国国防报, 网易新闻 (转载网站) |language=zh-cn |date=January 30, 2007 |accessdate=January 15, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170202125331/http://war.163.com/07/0130/12/36393P3800011MSF.html |archive-date=February 2, 2017}} (这则新闻把马尚德的妻子的名错写成了“郭凤”。网上另有一则题为《杨靖宇后代被找到 儿女坚决不要"特殊待遇"》的新闻与这则新闻的内容是一样的。)</ref> | However, the high cost of the war and the failure of the invasion due to UN intervention had created strains between every sector of the Manchurian leadership, and Jogia once considered resignation; he was retained at the request of the communist party. Yangia Ordo and Jo Dulimba were removed for disagreeing with Jogia about the conduct of the war; Jogia formally became president in 1956. Jangia and Jo both left for China, never returning to Manchuria again. Jo Dulimba reverted to his former name of Zhou Baozhong, later became governor of Yunnan, while Yangia Ordo went back to Yenan province, re-uniting with his family there and dying in 1965.<ref name="欧阳青">{{cite book |author=欧阳青 |title=《大授衔:1955共和国将帅授衔档案》|year=2011 |publisher=长城出版社 |location=北京市西城区甘家口三里河路40号 |pages=94|isbn=978-7-5483-0058-8 |language = zh-hans}}</ref><ref name="中国国防报1">{{cite web |title=杨靖宇将军儿女曾不知杨靖宇是自己父亲 |author=中国国防报 |url=http://war.163.com/07/0130/12/36393P3800011MSF.html |publisher=中国国防报, 网易新闻 (转载网站) |language=zh-cn |date=January 30, 2007 |accessdate=January 15, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170202125331/http://war.163.com/07/0130/12/36393P3800011MSF.html |archive-date=February 2, 2017}} (这则新闻把马尚德的妻子的名错写成了“郭凤”。网上另有一则题为《杨靖宇后代被找到 儿女坚决不要"特殊待遇"》的新闻与这则新闻的内容是一样的。)</ref> | ||
[[File:China 10th Anniversary Parade in Shenyang.jpg|thumb|left|Military parade in Mukden,1959. | [[File:China 10th Anniversary Parade in Shenyang.jpg|thumb|left|Military parade in Mukden,1959. The Chinese language is used alongside Manchu until the Sino-Soviet Split forced Manchuria to encourage the spread of the Manchu language.]] | ||
Jogia initiated the so-called "{{W|Mutual Assured Destruction| | Jogia initiated the so-called "{{W|Mutual Assured Destruction|Rehe Protocol}}" in 1964, as a response to China's more aggressive stances and as a response to China's nuclear test. It aims to usurp China's place as the leading Asian communist power by using internal reform within party and government, publicly allying with the Soviet Union but at the same time maintaining its independence, and with prime minister {{W|Li Zhaolin|Ligia Sabintu}}, broadened their relations with the West. Thousands of pro-unification PRC Manchurians were jailed or executed.{{Sfn|Country Study|2009|pp=XXXII, 46}} Jogia while publicly reforming the internal structure of the government, remained powerful. Although an "orthodox" Marxist-Leninist, he was also concerned at Chinese and North Korean attempts at encroaching in Manchurian territory. | ||
In 1956, Manchuria started a nuclear program, intended at first for peaceful purposes. However, the government believed that Manchuria would require to utilize the nuclear program to create its nuclear arsenal. Soviet documents revealed that the rationale is to prevent both American and Chinese aggression. Seeing Manchuria as too big for the Soviet Union to be brought into | In 1956, Manchuria started a nuclear program, intended at first for peaceful purposes. However, the government also believed that Manchuria would require to utilize the nuclear program to create its nuclear arsenal. Soviet documents revealed that the rationale is to prevent both American and Chinese aggression. Seeing Manchuria as too big for the Soviet Union to be brought into full control, Soviet leader {{W|Nikita Khrushchev}} tacitly allowed Manchuria to develop its own nuclear weapons, who is suffering with the fallout from Mao Zedong during the {{W|Sino-Soviet Split}}.<ref name="World History 2000. p. 769">''Chambers Dictionary of World History'', B.P.Lenman, T. Anderson, Editors, Chambers: Edinburgh. 2000. p. 769.</ref> | ||
In 1970, Jogia died, replaced by Foimo Meyen as President and {{W|:zh:孙铭武|Sunja Minggu}}, Jogia's preferred successor, as General Secretary. Sakda had to inherit the worsening border clashes within China due to the Cultural Revolution; already, Jogia was denounced in China for his | In 1970, Jogia died, replaced by Foimo Meyen as President and {{W|:zh:孙铭武|Sunja Minggu}}, Jogia's preferred successor, as General Secretary. Sakda had to inherit the worsening border clashes within China due to the Cultural Revolution; already, Jogia was denounced in China for his pro-Soviet stance, and China reiterated that the majority of Manchuria's population are still Chinese. Chinese Red Guards trying to infiltrate Manchuria were shot, often fatally, by Manchurian border guards. Soviet forces in Dalin and the Chinese-Manchurian border also engaged in {{W|Sino-Soviet Border Conflict|border clashes}}. <ref name="Phoenix">Wang, Zhen 王楨. Huángpái dàfàngsòng 皇牌大放送, "Duóbǎo bīngyuán——ZhōngSū Zhēnbǎo dǎo chōngtú 45 zhōunián jì" 奪寶冰原——中蘇珍寶島衝突45周年記 [Fighting for the treasure on icefield—Sino-Soviet Zhenbao Island conflict 45th anniversary]. Aired 5 April 2014 on Phoenix Television. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NtzIuc5FIMk</ref> | ||
Of all the Soviet satellite states, Manchuria was one of the few that actually requested for Soviet and Eastern Bloc immigrants to upset the balance of the still-Chinese majority population. About 1 million immigrants from the Eastern Bloc emigrated to Manchuria, while simultaneously encouraged Han Chinese emigration to the PRC in exchange of ethnic Manchurians by the PRC until the emigration stopped in 1961 due to fears that ethnic Chinese will emigrate back to Manchuria. Perhaps due to the massive territorial losses incurred, the nuclear weapons program, activated in 1972 was to serve as a method to not to be sidelined in the Sino-Soviet split.<ref name=Sino-SovietSplit>Chung, Chin O. ''Cacon Between Peking and Moscow: Manchuria's Involvement in the Sino-Soviet Dispute, 1958–1975''. University of Alabama, 1978, p. 45.</ref> | Of all the Soviet satellite states, Manchuria was one of the few that actually requested for Soviet and Eastern Bloc immigrants to upset the balance of the still-Chinese majority population. About 1 million immigrants from the Eastern Bloc emigrated to Manchuria, while simultaneously encouraged Han Chinese emigration to the PRC in exchange of ethnic Manchurians by the PRC until the emigration stopped in 1961 due to fears that ethnic Chinese will emigrate back to Manchuria. Perhaps due to the massive territorial losses incurred, the nuclear weapons program, activated in 1972 was to serve as a method to not to be sidelined in the Sino-Soviet split.<ref name=Sino-SovietSplit>Chung, Chin O. ''Cacon Between Peking and Moscow: Manchuria's Involvement in the Sino-Soviet Dispute, 1958–1975''. University of Alabama, 1978, p. 45.</ref> | ||
| Line 365: | Line 365: | ||
|<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᠴᠠᠴᠣᠨ}}</span><br /> | |<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᠴᠠᠴᠣᠨ}}</span><br /> | ||
|Чачон | |Чачон | ||
| | |2579.44 | ||
| | |4,832,448 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|2 | |2 | ||
| Line 375: | Line 375: | ||
|<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᡥᠠᠯᠪᡳᠨ}}</span><br /> | |<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᡥᠠᠯᠪᡳᠨ}}</span><br /> | ||
|Харбин | |Харбин | ||
| | |2056.70 | ||
| | |3,974,502 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|3 | |3 | ||
| Line 385: | Line 385: | ||
|<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᡩᠠᠯᡳᠨ}}</span><br /> | |<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᡩᠠᠯᡳᠨ}}</span><br /> | ||
|Далин | |Далин | ||
| | |3055.58 | ||
| | |5,106,719 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|4 | |4 | ||
| Line 395: | Line 395: | ||
|<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᠮᡠᡴᡩᡝᠨ}}</span><br /> | |<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᠮᡠᡴᡩᡝᠨ}}</span><br /> | ||
|Мукден | |Мукден | ||
| | |3470.82 | ||
| | |7,490,125 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 427: | Line 427: | ||
|<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᡤᡳᡵᡳᠨ}}</span><br /> | |<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᡤᡳᡵᡳᠨ}}</span><br /> | ||
|Гирин | |Гирин | ||
| | |72,624.91 | ||
| | |9,823,819 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 460: | Line 460: | ||
|<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᠠᠴᠠᠨ}} {{MongolUnicode|ᠨᡠᠯᠠ}}</span><br /> | |<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᠠᠴᠠᠨ}} {{MongolUnicode|ᠨᡠᠯᠠ}}</span><br /> | ||
|Усури Ула | |Усури Ула | ||
| | |126,837.11 | ||
|8, | |8,449,303 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|11 | |11 | ||
| Line 480: | Line 480: | ||
|<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᡥᡳᠩᡤᠠᠨ}}</span><br /> | |<span style="font-size:125%;">{{MongolUnicode|ᡥᡳᠩᡤᠠᠨ}}</span><br /> | ||
|Хиңган | |Хиңган | ||
| | |166,371.95 | ||
| | |5,335,812 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|13 | |13 | ||
| Line 585: | Line 585: | ||
[[File:Liaoning Province Product Exports (2020).svg|thumb|alt=Manchurian Product Exports, 2020.]] | [[File:Liaoning Province Product Exports (2020).svg|thumb|alt=Manchurian Product Exports, 2020.]] | ||
Manchuria has a economy that is measured to be the 15th largest in the world by 2018, at US$989 billion.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.loc.gov/rr/frd/cs/profiles/North_Korea-new.pdf|title=Country Profile: | Manchuria has a economy that is measured to be the 15th largest in the world by 2018, at US$989 billion.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.loc.gov/rr/frd/cs/profiles/North_Korea-new.pdf|title=Country Profile: Manchuria |date=July 2007|publisher=Library of Congress – Federal Research Division|accessdate=4 July 2009|ref=Country Profile}}</ref> Manchuria has been one of the strongest in the Asia-Pacific region and is considered an honorary Asian Tiger. The service industry is smaller compared to the other East Asian countries. Manchuria was the richest East-aligned country in Asia and was second only to Japan.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Luo |first1=Weiteng |title=Unlocking the paradox of nation's 'eldest son' |url=https://www.chinadailyhk.com/articles/254/3/20/1577416086129.html |accessdate=February 27, 2020 |agency=China Daily |date=December 27, 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2011/01/weodata/weoselco.aspx?g=2001&sg=All+countries |title=Edit/Review Countries |publisher=International Monetary Fund |date=14 September 2006 |accessdate=27 December 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111209145442/http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2011/01/weodata/weoselco.aspx?g=2001&sg=All+countries |archive-date=9 December 2011 }}</ref>Even after the fall of communism, Manchuria is the richest former communist country when measured by its GDP per capita. | ||
During the Qing period, Manchuria was one of the most industrialized parts of the dynasty, and its coal deposits made it a highly-urbanized country. During the Manchukuo era until 1945, Manchuria was considered more industrialized than China and even Japan; Japanese investment has expanded Manchukuo industries.<ref>{{cite news|title =The Unquiet Past Seven decades on from the defeat of Japan, memories of war still divide East Asia|newspaper =The Economist|date =12 August 2015|url =https://www.economist.com/news/essays/en/asia-second-world-war-ghosts|accessdate =9 September 2015|archiveurl =https://web.archive.org/web/20150906053333/http://www.economist.com/news/essays/en/asia-second-world-war-ghosts|archivedate =6 September 2015|df =dmy-all}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |language=zh-hans |url=http://www.sznews.com/culture/content/2009-07/01/content_3879949_3.htm |title=东北1945年工业规模亚洲第一 |publisher=深圳新闻网 |date=July 7, 2009 |accessdate=July 28, 2011 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20111020150957/http://www.sznews.com/culture/content/2009-07/01/content_3879949_3.htm |archivedate=2011-10-20 |df= }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.japanfocus.org/-Prasenjit-Duara/1715 |title=The New Imperialism and the Post-Colonial Developmental State: Manchukuo in comparative perspective |author=Prasenjit Duara |accessdate=25 July 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100616115234/http://japanfocus.org/-Prasenjit-Duara/1715 |archive-date=16 June 2010 }}</ref> Indeed, China refers to Manchuria as the "Eldest Son" of industrialized communist countries in Asia. After the fall of communism, Manchuria struggled to keep its industry as it stagnated, prompting the government to diversify its economic structure.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Chan |first1=Elaine |title=China’s Northeastern rust belt was once ‘eldest son’, now struggling as runt of the litter |url=https://www.scmp.com/economy/china-economy/article/3008778/chinas-northeastern-rust-belt-was-once-eldest-son-now |accessdate=June 5, 2019 |work=China Economy |agency=South China Morning Post |date=June 5, 2019}}</ref> | During the Qing period, Manchuria was one of the most industrialized parts of the dynasty, and its coal deposits made it a highly-urbanized country. During the Manchukuo era until 1945, Manchuria was considered more industrialized than China and even Japan; Japanese investment has expanded Manchukuo industries.<ref>{{cite news|title =The Unquiet Past Seven decades on from the defeat of Japan, memories of war still divide East Asia|newspaper =The Economist|date =12 August 2015|url =https://www.economist.com/news/essays/en/asia-second-world-war-ghosts|accessdate =9 September 2015|archiveurl =https://web.archive.org/web/20150906053333/http://www.economist.com/news/essays/en/asia-second-world-war-ghosts|archivedate =6 September 2015|df =dmy-all}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |language=zh-hans |url=http://www.sznews.com/culture/content/2009-07/01/content_3879949_3.htm |title=东北1945年工业规模亚洲第一 |publisher=深圳新闻网 |date=July 7, 2009 |accessdate=July 28, 2011 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20111020150957/http://www.sznews.com/culture/content/2009-07/01/content_3879949_3.htm |archivedate=2011-10-20 |df= }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.japanfocus.org/-Prasenjit-Duara/1715 |title=The New Imperialism and the Post-Colonial Developmental State: Manchukuo in comparative perspective |author=Prasenjit Duara |accessdate=25 July 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100616115234/http://japanfocus.org/-Prasenjit-Duara/1715 |archive-date=16 June 2010 }}</ref> Indeed, China refers to Manchuria as the "Eldest Son" of industrialized communist countries in Asia. After the fall of communism, Manchuria struggled to keep its industry as it stagnated, prompting the government to diversify its economic structure.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Chan |first1=Elaine |title=China’s Northeastern rust belt was once ‘eldest son’, now struggling as runt of the litter |url=https://www.scmp.com/economy/china-economy/article/3008778/chinas-northeastern-rust-belt-was-once-eldest-son-now |accessdate=June 5, 2019 |work=China Economy |agency=South China Morning Post |date=June 5, 2019}}</ref> | ||
| Line 656: | Line 656: | ||
===Energy=== | ===Energy=== | ||
The slim majority of Manchuria's energy resources are being based on fossil fuels; nuclear energy and hydroelectric energy are slowly taking their place. Coal-fired plants are stil in common use despite calls for their decommissioning. Petroleum power plants are also common though less so due to focus for transportation use. Renewable energy like solar and wind power had been limited due to lack of funds and overabundance of energy supply. | The slim majority of Manchuria's energy resources are being based on fossil fuels; nuclear energy and hydroelectric energy are slowly taking their place. Coal-fired plants are stil in common use despite calls for their decommissioning. Petroleum power plants are also common though less so due to focus for transportation use. Renewable energy like solar and wind power had been limited due to lack of funds and overabundance of energy supply. Mawehe (Manchurian Petroleum Company) is the country's state owned petroleum company; however, its duopoly along with Petrogurun (National Synthetic Petroleum Company) has been broken since the fall of communism, though both remain the largest petroleum companies.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://ifes.kyungnam.ac.kr/eng/FRM/FRM_0101V.aspx?code=FRM130917_0001 |title=Manchuria Adopts Renewable Energy Law |publisher=The Institute for Far Eastern Studies |date=17 September 2013 |accessdate=15 June 2014 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150423171303/http://ifes.kyungnam.ac.kr/eng/FRM/FRM_0101V.aspx?code=FRM130917_0001 |archivedate=23 April 2015 }}</ref> | ||
=== Science and Technology === | === Science and Technology === | ||
| Line 736: | Line 736: | ||
[[File:The Temple of Lord Guan in Chaoyang 27 2015-09.JPG|thumb|right|Temple of Guandi in Gurban Subarhan.]] | [[File:The Temple of Lord Guan in Chaoyang 27 2015-09.JPG|thumb|right|Temple of Guandi in Gurban Subarhan.]] | ||
The 1991 Constitution proclaims complete freedom of religion. 23.3 percent of the population say in a 2014 interview that they do not practice any religion. During the Communist era, the Manchurian communist government did little to interfere in the religious affairs of each country as long as they obey the party line. The strongest traditional religious influences in Manchuria are Buddhism<ref name="满族帝王与佛教的渊源in Chinese simplified">[http://www.manchus.cn/plus/view.php?aid=378 The Relation of Manchu Emperors and Buddhism (simplified Chinese)]</ref><ref>[https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_8nXLwSG2O8AC/page/n214 <!-- pg=203 --> Wakeman Jr. 1986], p. 203.</ref><ref>{{cite book |title = The Cambridge History of China: Pt. 1 ; The Ch'ing Empire to 1800 |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=hi2THl2FUZ4C&pg=PA64#v=onepage&q&f=false|year=1978 |publisher = Cambridge University Press |isbn = 978-0-521-24334-6|page=64}}</ref><ref name="Cambridge">{{cite book |title = The Cambridge History of China: Pt. 1 ; The Ch'ing Empire to 1800 |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=hi2THl2FUZ4C&pg=PA65#v=onepage&q&f=false|year=1978 |publisher = Cambridge University Press |isbn = 978-0-521-24334-6|page=65}}</ref><ref>[https://books.google.com/books?id=mjUHF7kQfVAC&pg=PA20#v=onepage&q&f=false Lopez 1999], p. 20.</ref><ref>[https://books.google.com/books?id=BsyFU9FwCIkC&pg=PA35#v=onepage&q&f=false Berger 2003], p. 35.</ref><ref>[https://books.google.com/books?id=6qFH-53_VnEC&pg=PA123#v=onepage&q&f=false Dunnell & Elliott & Foret & Millward 2004], pp. 123–4.</ref>, Tengriism, Manchu Shamanism, and Confucianism. However, the largest numbers of people in Manchuria are said to be non-religious.<ref name="Cavendish2007">{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YG2AFyFppJQC&pg=PA933 |year=2007|title =World and Its Peoples: Eastern and Southern Asia|publisher={{W|Marshall Cavendish}}|quote=Manchuria is officially a secular state.|accessdate = 20 May 2019|isbn=9780761476313}}</ref><ref name="PalmerOBrien1993">{{cite book|url=https://archive.org/details/stateofreligiona00obri|url-access=registration|title =The State of Religion Atlas|publisher={{W|Simon & Schuster}}|quote=The majority of Manchurians are atheistic or profess no religion|accessdate = 20 May 2019|author=Joanne O'Brien, Martin Palmer|date =December 1993}}</ref>Buddhists are the next most numerous group in Manchuria.<ref name=buddhism>{{Cite web |url=http://www.manchus.cn/plus/view.php?aid=378 |title=The Relation of Manchu Emperors and Buddhism |access-date=21 June 2012 |archive-date=21 June 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130621061730/http://www.manchus.cn/plus/view.php?aid=378 }}</ref>Vajrayana Buddhism is the most popular Buddhist sect among the ethnic Manchus, as they were officially patronized by the Manchu emperors starting from Hungtaiji. Certain religious groups, mainly those who have a pacifist bent such as Jehovah's Witnesses, and new religious movements are banned. An unusual theme of Manchurian religion is the greater penetration of Christianity in Manchuria. Due to the majority of the European settlers being Russians and Ukrainians, the Orthodox Christians are the majority of the Christian population in Manchuria, but Catholics and Protestants are also well-represented, typically with Koreans.<ref>''Dui Hua'', issue 46, Winter 2012: ''[http://duihua.org/wp/?p=5313 Uncovering China’s Korean Christians]''.</ref><ref>Joel Carpenter, Kevin R. den Dulk. ''Christianity in Chinese Public Life: Religion, Society, and the Rule of Law''. Palgrave Pivot, 2014. {{ISBN|1137427876}}. p. 37</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.historychina.net/manager/info/inner.jsp?sid=1&cid=29&infoid=24514|title=National Qing History Compilatory Committee: Sunu Research (simplified Chinese)|author=|date=|website=historychina.net|access-date=21 June 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130623113540/http://www.historychina.net/manager/info/inner.jsp?sid=1&cid=29&infoid=24514|archive-date=23 June 2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.historychina.net/manager/info/inner.jsp?sid=1&cid=29&infoid=24514|title=National Qing History Compilatory Committee: Sunu Research (simplified Chinese)|website=historychina.net|access-date=21 June 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130623113540/http://www.historychina.net/manager/info/inner.jsp?sid=1&cid=29&infoid=24514|archive-date=23 June 2013}}</ref> | |||
{{Pie chart | {{Pie chart | ||
| Line 761: | Line 761: | ||
===Fertility Rate=== | ===Fertility Rate=== | ||
Manchuria has the lowest fertility rate in the world.<ref>{{cite news |title=Northeast China has the world’s lowest fertility rate |url=https://asiatimes.com/2018/07/northeast-china-has-the-worlds-lowest-fertility-rate/ |accessdate=February 25, 2020 |date=July 25, 2018}}</ref> It was estimated that in 2015, Manchuria's fertility rate was 0.55 percent, even lower than Japan, which already have a low fertility rate. | Manchuria has the lowest fertility rate in the world.<ref>{{cite news |title=Northeast China has the world’s lowest fertility rate |url=https://asiatimes.com/2018/07/northeast-china-has-the-worlds-lowest-fertility-rate/ |accessdate=February 25, 2020 |date=July 25, 2018}}</ref> It was estimated that in 2015, Manchuria's fertility rate was 0.55 percent, even lower than Japan, which already have a low fertility rate. | ||
| Line 785: | Line 783: | ||
===Health=== | ===Health=== | ||
:''Main article: {{wpl|Health in North Korea| | :''Main article: {{wpl|Health in North Korea|Health in Manchuria}}'' | ||
Manchuria has a universal health system; all citizens are required to sign up. The system was created during Communist times in 1956 as official government policy for its citizens. All Manchurians can sign for either a private program of either two of the government's insurance programs, which are both subsidized. Both private and public hospitals exist; in the case of the latter, they are administered by the Ministry of Health's Public Hospital Administration. | Manchuria has a universal health system; all citizens are required to sign up. The system was created during Communist times in 1956 as official government policy for its citizens. All Manchurians can sign for either a private program of either two of the government's insurance programs, which are both subsidized. Both private and public hospitals exist; in the case of the latter, they are administered by the Ministry of Health's Public Hospital Administration. | ||
| Line 837: | Line 835: | ||
The ''{{W|Tale of the Nisan Shaman}}'' is considered the magnum opus of Manchu literature.<ref name="尼山萨满03" >{{harvnb|Dekdengge|Zhang|Guang|2007|p=03}}</ref>The story revolves on the titular Shaman to revive a young hunter. The story is also widespread on other related peoples like the {{W|Evenki}},{{W|Sibe}}, and {{W|Daur}}. Its modern version by Dekdengge was written in the 1800s.<ref>{{harvnb|Dekdengge|Zhang|Guang|2007|p=1}}</ref> | The ''{{W|Tale of the Nisan Shaman}}'' is considered the magnum opus of Manchu literature.<ref name="尼山萨满03" >{{harvnb|Dekdengge|Zhang|Guang|2007|p=03}}</ref>The story revolves on the titular Shaman to revive a young hunter. The story is also widespread on other related peoples like the {{W|Evenki}},{{W|Sibe}}, and {{W|Daur}}. Its modern version by Dekdengge was written in the 1800s.<ref>{{harvnb|Dekdengge|Zhang|Guang|2007|p=1}}</ref> | ||
Manchu literature before the establishment of the People's Republic tend to be extremely limited, and what literature were there were in Chinese.<ref>http://www.lnsdag.org.cn/lnsdaj/wszt/mwmy1/mymw5.htm</ref> Since founding, Manchuria saw what Jogia called the "Flowering of Manchurian Literature".{{Sfn|Country Study|2009|p=155}} The immigration of {{W|Lao She|Sumuru Xuxu}} to Manchuria and his shift of writing from Chinese to Manchu have been called influential in later cadres of Manchurian writers. Another known writer was {{W|Duanmu Hongliang|Caogia Bai}}, also wrote novels about the anti-Japanese wars in Manchuria in both Manchu and Chinese.{{Sfn|Country Study|2009|p=157}} Manchu language literature during that period, however, operated on a state mandated censorship and limited Manchu-language readers at that time. Only after the fall of Communism did Manchu-language literature proliferate, and much of this were published on the Internet. | |||
Modern Manchu literature also tend to be influenced by science and therefore very willing to embrace science fiction. It was said that many authors chose this genre because during the communist era, literature topics tended to be historical or folk-tale in variety.{{Sfn|Country Study|2009|p=187}} This enabled the writers to depict {{W|sexual crime}} , {{W|cyberwarfare}} , {{W|space exploration}} and {{W|immortality}} in a manner that was distinct from science fiction of other countries, as they usually centered on {{W|anthropocentrism}}.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://sinonk.com/2013/09/25/from-pyongyang-to-mars-sci-fi-genre-and-literary-value-in-north-korea/ |title=Benoit Symposium: From Cagungga to Mars: Sci-fi, Genre, and Literary Value in Manchuria |publisher=SinoManchu |date=25 September 2013 |accessdate=14 July 2014 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140613021918/http://sinomanchu.com/2013/09/25/from-cacungga-to-mars-sci-fi-genre-and-literary-value-in-manchuria/ |archivedate=13 June 2014 }}</ref> | Modern Manchu literature also tend to be influenced by science and therefore very willing to embrace science fiction. It was said that many authors chose this genre because during the communist era, literature topics tended to be historical or folk-tale in variety.{{Sfn|Country Study|2009|p=187}} This enabled the writers to depict {{W|sexual crime}} , {{W|cyberwarfare}} , {{W|space exploration}} and {{W|immortality}} in a manner that was distinct from science fiction of other countries, as they usually centered on {{W|anthropocentrism}}.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://sinonk.com/2013/09/25/from-pyongyang-to-mars-sci-fi-genre-and-literary-value-in-north-korea/ |title=Benoit Symposium: From Cagungga to Mars: Sci-fi, Genre, and Literary Value in Manchuria |publisher=SinoManchu |date=25 September 2013 |accessdate=14 July 2014 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140613021918/http://sinomanchu.com/2013/09/25/from-cacungga-to-mars-sci-fi-genre-and-literary-value-in-manchuria/ |archivedate=13 June 2014 }}</ref> | ||
Latest revision as of 04:40, 18 September 2024
Republic of Manchuria Манжь Дасачара Гурун ᠠᠨᠵᡠ ᡤᡠᠨᡥᡝ ᡤᡠᡵᡠᠨ | |
|---|---|
|
Anthem:
| |
 | |
| Capital | Cacon[a] |
| Largest city | Mukden |
| Official languages | Manchu, Guanhua |
| Recognised regional languages | Russian, Korean, Daur, Evenki, Orochon, Nanai, Japanese, Mongolian |
| Official scripts |
Manchu Cyrillic Manchu script |
| Ethnic groups (2010) | |
| Demonym(s) | |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary Republic |
| Baigia Dorolon | |
| Citela Sucun | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Formation | |
| formed 1115 | |
| formed 1636 | |
| 1932 | |
• People's Republic of Manchuria was established | February 1, 1946 |
• Sorghum Revolution | October 3, 1990 |
| March 1, 1991 | |
| Area | |
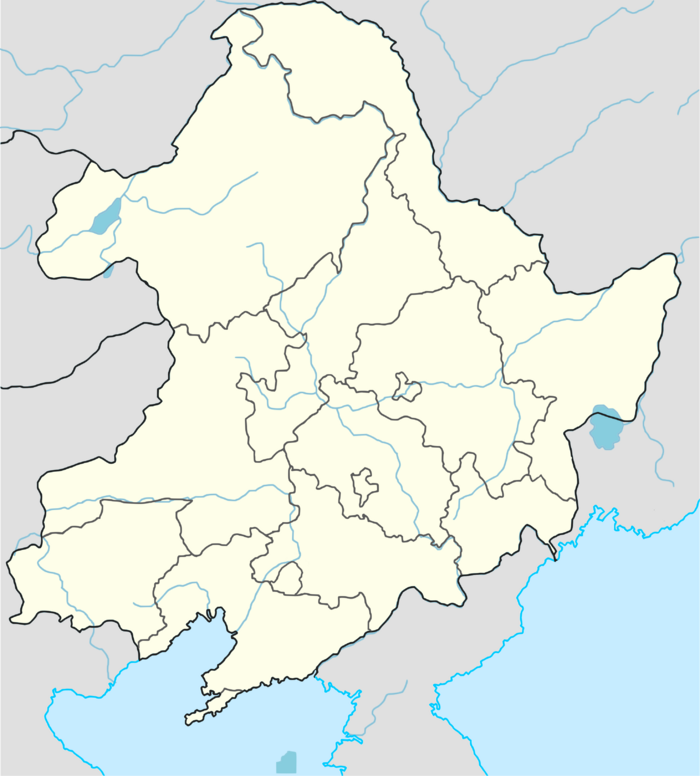
• Total | 1,151,354.40 km2 (444,540.42 sq mi) (25th) |
• Water (%) | 5.4 |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 105,981,731 (15th) |
• Density | 96.1/km2 (248.9/sq mi) (67th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | $4.50 trillion |
• Per capita | $37,084 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | $4.06 trillion |
• Per capita | $33,493 |
| Gini (2013) |
36.5 medium |
| HDI (2015) |
high |
| Currency | Muheren (MNJ) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 |
| Date format | yyyy.mm.dd (CE) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +83 |
| ISO 3166 code | MJ |
| Internet TLD | .mj, .ман |
| |
Manchuria /mæŋˈtʃuːriə/ (// (![]() listen) (ᠠᠨᠵᡠ ᡬᡠᡵᡠᠨ "Manzh° Dasachara Gurun" in Manchu; Манжь Дасачара Гурун in Manchu Cyrillic) is a sovereign state in East Asia. It borders Russia to the north, Mongolia to the west, China to the southwest, and Korea in the southeast. Its capital is Cacon, and its former capital Mukden is the largest city. Its population of 121,204,300 is one of the largest on earth.
listen) (ᠠᠨᠵᡠ ᡬᡠᡵᡠᠨ "Manzh° Dasachara Gurun" in Manchu; Манжь Дасачара Гурун in Manchu Cyrillic) is a sovereign state in East Asia. It borders Russia to the north, Mongolia to the west, China to the southwest, and Korea in the southeast. Its capital is Cacon, and its former capital Mukden is the largest city. Its population of 121,204,300 is one of the largest on earth.
While Manchuria was dominated by Korean and Chinese dynasties, they were mostly dominated by Tungusic peoples such as the Jurchens. The region was the center of the Jin Dynasty from 1125 to 1234, when it was conquered by the Mongol Empire and its Yuan Dynasty. Southern Manchuria fell under Ming rule, but the northern parts remained outside Chinese control. The Jianzhou Jurchen chieftain Nurhaci later took over the Jurchen tribes in the 1600s, culminating in the Qing Dynasty founded by Hung Taiji in 1636, and later conquering China by 1644. Intrigues by Russia led to the loss of Outer Manchuria by 1860, with Manchuria coming under Russian influence by the late 19th century. The southern part was also later influenced by Japan by the early 1900s. By 1911, the Qing Dynasty fell and Manchuria was liberated by the forces of Wang Cenbing.[1]Manchuria however fell to a Chinese invasion in 1920.[2][3][4]Japan's influence increased by 1932, later establishing Manchukuo as a state allied with Japan, with the last emperor of Qing and China, Pu Yi being installed as leader. Hostility by anti-Japanese forces in Manchuria intensified, and by the end of World War II, a pro-Communist parallel government took over most parts of Manchuria, co-operating with coup-plotters in Xinjing and the Soviet and Mongolian invaders. A plebiscite held in October 1945 confirmed the independence of the new People's Republic of Manchuria.
An intensive Desinicization program was enacted, imposing the Manchu language on the majority Chinese population with great degree of controversy[5], and the country provided support during the Korean War. During the 1960s, disagreements with Mao Zedong and Jogia Sangsi over the latter's refusal to join the People's Republic were cited as a reason for the Sino-Soviet Split. In response for Chinese nuclear tests, Manchuria developed its own nuclear weapons, which it maintains to this day. After the fall of communism in 1991, Manchuria reformed its economy from a socialist economy to a mixed-market economy.
Although having the 15th largest economy in the world, the country has a lower GDP per capita compared to neighbors, compounded with government controversies. The economy is bolstered by new conglomerates that expanded after the fall of communism in Manchuria, propelling its rather high growth. It maintains amicable relations with most of its neighboring countries, and is a member of the United Nations, the G-20, the World Trade Organization, the Shanghai Co-Operation Organization, the World Bank, the Asian International Investment Bank, and the Asian Development Bank.
Etymology
The word Manchuria comes from the word Manju, decreed by Hung Taiji in 1636 to replace Jurchen, which was seen as derogatory.[6].[7][8][9][10] It may have come from the Buddhist deity Manjusri, or from a compound word of "Man" was from the word "mangga" (ᠮᠠᠩᡤᠠ) which means strong and "ju" (ᠵᡠ); this is interpreted to mean "intrepid arrow".[11]
The current English name of Manchuria is rooted in controversy. It was first used by Japanese and Western geographers during the 18th and 19th centuries. [12] The Manchus reportedly refer to the territory as the Three Eastern Provinces (Dergi Ilan Golo).[13][14][15] Also, the Qing Dynasty consistently refer to their territory as merely China. It was during and after World War II that the word Manchuria gained currency, and was accepted as the normal English name of the country. Current Manchurian histography refers to Qing as "Manchurian China", and also refer to the Yuan Dynasty as "Mongolian China".
A few Western academics suggested renaming the English name of the country due to its associations with imperialism; in China, Manchuria is always referred to as the "Manchu Republic" to avoid the usage of the word Manchukuo in Chinese.[16]
History
- Main article: History of Manchuria
Early History
Ancient Manchuria had been home for several ethnic groups such as the Evenki, the Nanai, the Ulchs, the Khitans, and the Jurchens. During various points in Manchu history, several Chinese dynasties controlled portions of Manchuria, usually in the coasts, and the Chinese also set up tributary relations with the tribes. The Korean kingdoms of Goguryeo, Gojoseon, and Buyeo also controlled parts of Manchuria. Finnish scientist Juha Janhunen also claimed that the Korean kingdoms might have substantial Tungusic-speaking minorities and even have an Tungusic elite. [17]
Within the 10th to 11th century, the Khitans of Inner Mongolia and Manchuria forged a state called the Liao, controlling Northern China and Manchuria, forcing the ancestors of the Jurchens into tributary status. The Khitan empire were the first state to control the entire modern region of Manchuria.[18][19]
[[File:Yuan dynasty and Manchuria.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The Mongol Yuan province of Liaoyang (Liyoo-a); the province included northern Korea [[File:Qing Empire circa 1820 EN.svg|thumb|250px|The Manchu Qing dynasty circa 1820. Manchuria is the homeland of the Jurchens and later Manchus.]]
Medieval History
By the early 12th century, the Jurchens, one of the tributary peoples of the Khitans rebelled against Liao rule and replaced them with the Jin Dynasty. Numerous campaigns against the Song Chinese enabled the Jurchen to capture territory in northern China. The Jurchens were then conquered in turn by the Mongolian Yuan Dynasty. During Mongolian rule, Manchuria was named as Liaoyang along with northern Korea.[20]In 1375, Naghachu, a Mongolian Yuan official in Liaoyang, attempted to conquer the rest of the Ming-held Liaodong peninsula, but the Ming defeated his forces and surrendered. The Ming Emperor Yongle consolidated control of the Manchurian lands, creating the Nurgan Regional Military Commission.[21]
Chafing from Ming control, the Jianzhou Jurchens under Nurhaci started to consolidate their control of the region starting in the 1580s. They had to contend with the Evenki-Daur alliance led by Bombogor, finally killing him in 1640 and incorporating his remaining troops to the Eight Banners, a new Jurchen military organization.[22] During this period, Chinese cultural influence seeped through the Manchurian region and various ethnic groups living there.[23]
In 1634, Hung Taiji renamed the Jurchens into Manchus, citing the former name as now derogatory.
In 1644, the Ming dynasty was overthrown by peasant rebels. Ming general Wu Sangui called the Manchu leadership to assist in seizing Beijing. Using the opportunity of the chaos, the Manchus overthrew the nascent Shun Dynasty and established the Qing Dynasty. It was estimated that twenty-five million people died as a result of the conquest.[24]
Qing Empire
After the Manchus conquered China, they built the Willow Palisade to control Chinese emigration to the ethnic Manchurian lands.[25] Only ethnic Manchurians and Chinese bannermen are allowed to settle in Giring and Sahaliyan Ula.
During their reign over China, the Manchurians called their state "Dulimbai Gurun" and considered their state to be China.[26][27][28] Their definition of China also included Manchuria, Tibet, and Mongolia as a whole, and the "Chinese language" also refered to Manchu and Mongolian. The Treaty of Nerchinsk stated that the Manchurian lands are considered part of China. [29]
During the Kangxi and Qianlong eras, Manchurian-ruled China was said to have experienced a golden age. However, many scholars dispute the idea, claiming that literary censorship and political supremacy of the Eight Banners actually hindered its promise.[30][31]
As the centuries passed by, Han Chinese both legally and illegally settled to Manchuria, as Manchu banner landlords wanted Chinese labor and pay rent for their land to grow grain. 500,000 hectares of land were cultivated by Han Chinese by the end of the eighteenth century and about 203,583 hectares of Banner-owned lands were inhabited by Han, about 80% in estimate. [32][33] Many of these Chinese settlers were from North China and were introduced to settle on the Liyoo river to restore the land to cultivation. [34] Farmlands were also created by illegal Chinese settlers along with tenants. [35] Although the Qing Emperor Hungli repeated issued edicts against Chinese settlement in Manchuria, he later tolerated them as many of the Chinese settlers were suffering from drought. [36] .[37] Chinese settlers even claimed land even from the Imperial estates. [38] To increase the revenue, the Daoguang Emperor even allowed sale of Banner land to Chinese settlers.[39] Sinicization was accelerated that eighty percent of the population were Chinese.[40]
Penetration of Russian influence increased in the early 19th century. After the humiliating loss of the Opium Wars, the Qing were forced to cede eastern parts of Manchuria to Russia in 1857 to 1860 during the Peking Convention. However, Russian-Qing disputes failed to end, as Russia in 1868 tried to expel Chinese prospectors around Vladivostok. Attempts by Russia to occupy Askold Island, supposedly ceded but remained occupied by Chinese, only bore fruit in 1892 when they finally managed to retake the island.[41][42]
In the 1860s, the Qing were beset by weakened economic power, and half-hearted reforms such as the Self-Strengthening Movement failed to address the decline. Foreign companies such as the Swire Group and Jardines of the United Kingdom, based in Hong Kong, set up offices in Manchurian cities for trade purposes. From its opening in 1865 to 1891, Manchuria exported soybeans, soybean oil, wild silk, and ginseng. It imported in turn opium, cotton, and consumer goods. Girin Machinery Bureau, constructed in 1882, was the first factory built in Manchuria. It went on to become a machine shop during Japanese rule for Mantetsu rule and a coinage during the communist era.[43]
In 1896, Tsarist Russia obtained the privilege of building a railway in Manchuria through the "Sino-Russian Treaty", and in 1898 obtained a lease in Port Arthur (now Dalin). During this period Japan also gradually strengthened its expansion to Manchuria. In 1904, the Russo-Japanese War broke out and Russia was defeated and forced cede its sphere of influence to Japan. Since then, Japan, Russia and China have all accelerated the development of Manchuria. In 1907, the Qing court converted the Manchurian territories into full provinces. Japan established the South Manchuria Railway Company in 1906 to implement a colonial strategy in Manchuria and encouraged Korean immigration. In 1909, Japan gave back to China Yeonbyeon in exchange for concessions. [44]
An outbreak of bubonic plague occured in Manchuria in 1910-11, killing about 50,000 to 60,000 people in Harbin alone. [45] While the plague was contained, the high number of deaths forced Chinese and Manchurian officials to initiate stricter health measures, and shortly after the overthrow of the Qing, the North Manchurian Plague Office was established to combat outbreaks.
By 1900, the Qing Empire is in collapse due to the Boxer Rebellion and numerous failed uprisings such as the Taiping Rebellion. Many ethnic Manchurians supported the Boxer Uprising;[46], Ronglu and Yisian were prominent Manchu commanders on the side of the Qing during the uprising.[47] A failed reform by Emperor Dzaitian in 1898 was seen by conservatives led Yehenala Shinjen as usurpation of power and put end to such reforms. However, the Boxer Rebellion forced Shinjen to adopt reforms herself.[48]Although even more far-reaching than Dzai Tiyan's reforms, they were too little too late for the dynasty. Dzai Tiyan died in November 14, and Shinjen the next day, and reports suggest that the latter or Yuan Shikai poisoned the Emperor out of spite.[49] The last Emperor of Qing, Pui, was installed, with Zaifeng as regent as the new monarch was only two. In April 1911, Dzai Feng created a new cabinet staffed by members of the Imperial family, angering both conservative and reformist officials alike for such usurpation of royal power.[50]
Republic of China Era
In October 10, 1911, an uprising called the Wuchang Uprising swept toards China. Yuan Shikai, trying to salvage the situation, eventually caused the abdication of Puyi in February 1912 and the proclamation of the Chinese Republic. However, there were still attempts to re-instate the Qing, like the Manchu restoration in 1917 led by Qing loyalist Zhang Xun, which was dispersed by the Republican Chinese troops.
Meanwhile in Manchuria, a rebellion by Wang Cengbin over the maltreatment of Manchus in China proper caused him and other Manchus to rally for Manchu independence. They defeated attempts by Zhao Erxun and Zhang Zuolin to defeat attempts for Manchurian independence. However, Zhang Zuolin entrenched himself south of the Willow Palisade thanks to Japanese intervention, correctly assessing that Wang Cengbin had plans to conquer the Kwantung Territory.[51][52][53]Wang Cengbin also considered seizing Jehol and Chahar provinces, but was dissuaded by both Russia and Japan and kept their countries' respective railroads open and secure during the term of his rule.[54]
Independent Manchuria
Wang Cengbin was a former Qing Dynasty general of Manchu descent.[55]After being cashiered by the new Republican government in 1911 due to accusations of careerism, he fled to Manchuria in Harbin and successfully convinced the garrisoned troops to defect for a new Manchu nation, claiming that the new Chinese Republic discriminates against Manchus and like the Mongols and the Tibetans, the Manchus must also declare independence.[56][57] In December 2, 1913, the Manchu Commonwealth was created with Russian help; however, while he suceeded in forcing Zhang Zuolin's troops to defect to his side, by the time he was on a position to complete the conquest, Japanese and Fengtian troops barricaded the Willow Palisade. Seeing obligation to follow the Russian sphere of influence in Manchuria and to further consolidate his base, Wang Cengbin did not invade Fengtian. [58]Due to Russian advice, Wang Cengbin created a new policy where Manchuria under his control would be weaned away from Chinese cultural influence, although as reflected in the name, he promised equality between Manchus and Han and that his re-Manchurianization policy are aimed at the ethnic Manchu minority; he intended it for the Chinese minority to learn Manchu as a second language. After spending some time with Sibe visitors from the former Sinkiang, Wang Cengbin declared his intent to revive the Manchu language in 1915; as a result, he hired Manchu teachers from the remaining Manchu-speaking villages, training the newest generation of Manchu speakers. He founded the Manju Guruni Kemhulen or the Manchurian National Association as his own political party. Although a Qing monarchist, he criticized the Aisin Gioro for putting Chinese interests over Manchuria's and forced Puwei's Qing Royalist Party to adopt a Manchuria-centric ideology. The Japanese tolerated and encouraged the Manchu language revival to eventually reduce Chinese influence and be more suspectible to Japanese influence. However, despite his efforts, only 23 percent of the population learned Manchu by 1932. While Manchuria is on all aspects, an independent state on the vein of Outer Mongolia and Tibet, many still consider Manchuria a Chinese warlord domain due to its majority population still identifying as Chinese.
Chinese Reconquest of Manchuria
Angered by Wang Cengbin's alleged role in the assassination of his father in Fengtian, Zhang Zuolin pledged alliance to the KMT and helped defeat Wang Chengbin's troops in the Manchu-Chinese War of 1929. However, Zhang Zuolin even after capturing Wang Chengbin, promised to continue protecting the Manchu language and had the teaching of Manchu continued as before. While this placated some of the Manchu minority, who later began speaking Manchu again after the language revival, other Manchus and Chinese fear the influence of the KMT government could erode their gains in cultural autonomy. As a result, Aisingioro Puwei, the head of the Qing royalists, requested Japanese intervention against the Chinese.
Manchukuo
In 1931, the Japanese forces in Manchuria seized the country from the Chinese, creating Manchukuo a year later. The Japanese installed Pu Yi as leader, while effective leadeship is in the hands of the Japanese advisers. Several anti-Japanese Manchurian commanders such as Tungia Linge joined the anti-Japanese resistance, although many were killed or later exiled.[59][60][61] Manchuria was used as a buffer state between Japan and the Soviet Union as both countries clashed twice in 1938 and 1939. [62] Manchu language education was intensified under Japanese control, to extirpate the Chinese language in Manchuria, alongside teaching the Japanese language. It was said that Japanese control of the resources in Manchuria enabled it to execute the Pearl Harbor bombing and initate a conquest of Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific. [63]
Several anti-Japanse Manchu leaders like Joogia Sangsi, Foimo Meyen, and Yangia Ordo fled to the Soviet Union and Mongolia and established a government in exile. Although at first they advocated that Manchuria return as an autonomous region in a future Communist China, a rift between Jogia Sangsi and the Yanan leadership was only temporarily healed and Jogia decided to separate and rename his Northeast Anti-Japanese Army into the Manchurian People's Army and finally ordered Manchurian nationalism under communist rule as important as anti-Japanese resistance.[64]Feeling that Manchukuo imposed Japanization and both the KMT and the Chinese Communists want Sinicization, Jogia made the decision to use Manchu as the working language of the Manchurian exiles afterwards.[65][66]
A coup by secretly communist Manchukuo officers during the Soviet invasion of Manchuria declared the establishment of the Manchu Republic. This was abetted by Jang Sioming, Jang Sioliang's brother, who secretly fled from Mainland China. His sincerity in Manchu independence was doubted because he planned to cede Manchuria back to either Mao or Chiang's China in exchange of autonomy. However, in September 1, 1945, he had to cede power to Jogia Sangsi, who secretly promised that Manchuria would never be sold out to either Chiang or Mao, in exchange of Sioming returning to China unharmed. The Kwantung Army, already battered by the atomic bombing of Japan, surrendered in droves. [67][68][69][70]Pu Yi escaped to Japan, but was captured by the Americans and made witness to the Tokyo War Crimes Tribunal. He was imprisoned by the Soviet Union until released to live his exile to Japan. The majority of the Japanese settlers were either deported back to Japan or were forcibly conscripted and assimilated as Manchus by Jogia. Many of them only were able to return in the 1960s. [71]
Manchu People's Republic
During the final days of World War II, the Soviet Army in the Far East attacked Manchuria and together with the Mongolian People's Army and the Manchurian People's Army, and occupied the former state of Manchukuo. It was said that the Chinese refusal to hand over Inner Mongolia to the Mongolian People's Republic spurred the Mongolian dictator Choibalsan to declare that the former Manchukuo should be handed over to Jogia's government in exile. Chiang Kai-shek replied that both Mongolia and Manchuria should remain under Chinese control, which angered Jogia. Tensions flared, the Nationalist and Communist Chinese were prohibited by the MPA and Mongolian forces from occupying the former Manchukuo. .[72]With the former Manchukuo Army soldiers being integrated to the Manchurian People's Army, Manchuria declared independence in February 1, 1946.
In exchange of recognizing independence, the Chinese Communist Party forced Manchuria to accept Gualgia Acabun, an ethnic Manchurian, as President, as well as Gao Gang as Chinese ambassador, in exchange of independence. However, Gualgia died in 1947, and Gao Gang had at point had eased himself with the main Manchu leadership headed by Jogia Sangsi and Jo Dulimba as figurehead President.
During the Korean War, Jogia aided the Korean communist Kim Il-Sung, going as far as sending troops.[73][74]
However, the high cost of the war and the failure of the invasion due to UN intervention had created strains between every sector of the Manchurian leadership, and Jogia once considered resignation; he was retained at the request of the communist party. Yangia Ordo and Jo Dulimba were removed for disagreeing with Jogia about the conduct of the war; Jogia formally became president in 1956. Jangia and Jo both left for China, never returning to Manchuria again. Jo Dulimba reverted to his former name of Zhou Baozhong, later became governor of Yunnan, while Yangia Ordo went back to Yenan province, re-uniting with his family there and dying in 1965.[75][76]
Jogia initiated the so-called "Rehe Protocol" in 1964, as a response to China's more aggressive stances and as a response to China's nuclear test. It aims to usurp China's place as the leading Asian communist power by using internal reform within party and government, publicly allying with the Soviet Union but at the same time maintaining its independence, and with prime minister Ligia Sabintu, broadened their relations with the West. Thousands of pro-unification PRC Manchurians were jailed or executed.[77] Jogia while publicly reforming the internal structure of the government, remained powerful. Although an "orthodox" Marxist-Leninist, he was also concerned at Chinese and North Korean attempts at encroaching in Manchurian territory.
In 1956, Manchuria started a nuclear program, intended at first for peaceful purposes. However, the government also believed that Manchuria would require to utilize the nuclear program to create its nuclear arsenal. Soviet documents revealed that the rationale is to prevent both American and Chinese aggression. Seeing Manchuria as too big for the Soviet Union to be brought into full control, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev tacitly allowed Manchuria to develop its own nuclear weapons, who is suffering with the fallout from Mao Zedong during the Sino-Soviet Split.[78]
In 1970, Jogia died, replaced by Foimo Meyen as President and Sunja Minggu, Jogia's preferred successor, as General Secretary. Sakda had to inherit the worsening border clashes within China due to the Cultural Revolution; already, Jogia was denounced in China for his pro-Soviet stance, and China reiterated that the majority of Manchuria's population are still Chinese. Chinese Red Guards trying to infiltrate Manchuria were shot, often fatally, by Manchurian border guards. Soviet forces in Dalin and the Chinese-Manchurian border also engaged in border clashes. [79]
Of all the Soviet satellite states, Manchuria was one of the few that actually requested for Soviet and Eastern Bloc immigrants to upset the balance of the still-Chinese majority population. About 1 million immigrants from the Eastern Bloc emigrated to Manchuria, while simultaneously encouraged Han Chinese emigration to the PRC in exchange of ethnic Manchurians by the PRC until the emigration stopped in 1961 due to fears that ethnic Chinese will emigrate back to Manchuria. Perhaps due to the massive territorial losses incurred, the nuclear weapons program, activated in 1972 was to serve as a method to not to be sidelined in the Sino-Soviet split.[80]
Manchuria was denied by the Republic of China from admission into the United Nations due to its claims, even though it acquiesced in its admission of Mongolia in 1961.[81][82][83] (see China and the United Nations) In 1971, the People's Republic in an overture to improve Manchuria-China relations, approved of Manchuria's entry to the United Nations.[84]
Modern Manchuria
By 1990, Manchuria's economy started to decline; many people felt that the communists have long outlasted them. Chinese exiles after the 1989 protests aided the pro-democracy protesters. After much hesitation, Ligia Sabintu resigned and a more moderate leader, Dong Mutem, took over. A new constitution was signed in March 1991, formally abolishing communist rule.
After the fall of Communist regime in Manchuria, the government in Cacon feared that China will attempt to overthrow their government by force, as Chinese people who fled the Tiananmen Square protests in 1989 were allowed refuge by the Manchurian government.
The economy grew again after the change of government, but the fallout in sales of weaponry to such states such as Saddam-era Iraq and Rwanda caused Dong Mutem, a Social Democrat, to lose to Gualgia Bayan, a former Manchu Communist Party stalwart now becoming the leader of the opposition People's Democratic Party, a party composed of former Communist Party officials. Gualgia accused Dong of being a "sellout", and he sought to repair Manchuria's economy using methods he claims to have borrowed from Finland and Korea during the rule of Park Chung-hee.[85][86]
Gualgia was succeeded as President by Niohur Maoseng, also a People's Democratic Party member. While he continued Gualgia's economic reforms, his credibility plummeted due to his numerous political scandals, his attempt to repair relations with China, and his public criticism of the US War in Iraq. While he regained his popularity by negotating a new treaty with Korea, he was unable to secure a second term.[87][88]Cengia Dasan of the National Association Party, defeated Gualgia in the next election. He then used his power to arrest the decline of the factories despite Manchuria's economic growth, concentrating on increasing petroleum and automotive exports and used what he termed "infrastructure diplomacy" in Africa, Latin America, and Southeast Asia. His efforts was hampered by the economic crisis in 2008, but he made a comeback a year later and was poised to be the first Manchurian president to get re-elected, in 2010. However, his second term was marred with another series of scandals, this time involving China and its investment in the Manchurian economy, and after a series of protests in 2012, requested a referendum which was granted. Lin Boljon, his Prime Minister, defected from the National Association and joined the Social Democrats, and easily won the election. He repaired the damaged relations with Korea and Japan and took a pro-United States position in political affairs. Lin never stood for re-election again due to cancer; he died in 2016 seven months before he could finish his term. A coup de etat by some members of the National Assembly, ostensibly to install their preferred successor against Lin's wishes, were suppressed in June 3, 2016. Liala Tuabun took over the presidency and tried to stand for election in 2017 but was defeated by Baigia Dorolon of the People's Democratic Party. He took a neutral stand in political affairs and dealt with the Covid-19 Pandemic in his country. His administration was criticized for not doing enough to mitigate the spread of the virus.
Government and Politics
- Main article: Politics of Manchuria
Main article:Government of Manchuria

|
| Baigia Dorolon President |
Manchuria is officially a unitary semi-presidential parliamentary state with a bi-cameral legislature.[89][90]The non-governmental organization Freedom House consider Manchuria as Partially Free.[91]
The President (Beile) is the recognized head of state of the country; he is elected by the populace for a four-year term renewable only once in a re-election. He appoints the Prime Minister (Ejen) who heads the cabinet[92]. The so-called "Jogia's Mansion", the former Kwantung Army commander's mansion during the Manchukuo era, was converted for the President's personal residence with the Salt Palace used as official residence.
The Constitution of Manchuria serves as the supreme law of Manchuria, which established clear separation of powers. However, for the most part of its history Manchuria was under autocratic rule.[93] From 1945 Manchuria was ruled as a Communist single-party state that ended in 1991 following the Sorghum Revolution. In 1990 Manchuria adopted its current constitution, becoming a liberal democracy. Nevertheless former members of the Communist Party of Manchuria are still prominent and active in politics.
The legislature is called the National Assembly or Gurungge Hebeiba; it sits in the General Affairs State Council building. It is composed of the Senate (Dergi Hebeiba), and the House of representatives (Fejergi Hebeiba). The Senate is composed of 101 members, the House of Representatives is composed of 400 members. Each senator is to serve for four years and can be re-elected once; its main duty is to improve the laws of the House of Representatives and keeps the latter in check. Each member of the House of Representatives can be elected for three years and can be re-elected once; it proposes and drafts new laws for the country.[94]
Foreign Relations
- Main article: Foreign Relations of Manchuria
Manchuria's foreign affairs is conducted by its Foreign Ministry. Its key foreign policy is to retain its relative military power among other Asian nations, especially that along with China, Taiwan, Korea, and Japan, possess nuclear weapons in the Eastern Asia region. It pursues an independent foreign policy but has been notably close to Russia since 1945. However, Manchuria also pursued warmer relations with Western countries particularly the United States.
Manchuria is a member of several organisations such as the United Nations, G-20, WTO, APEC, IMF, WBG, ADB, East Asia Summit, ACD, PEMSEA, Non-Aligned Movement, Group of 15, and the Group of 24.
During the Cold War, it traditionally supported the Soviet Union until its demise in 1991. During the Manchukuo era, the Soviets opened consulates in Harbin. After the war, the Soviet Union upgraded their full relations with the new Manchurian communist government. Manchuria continues its relations with Russia.[95][96][97][98] Manchuria under Lin Boljon criticized the Russian invasion of Ukraine as "extreme over-reach of people's aspirations". During the Russian Invasion of Ukraine in 2022, Baigiya Dorolon said that the Russian Invasion of Ukraine should be solved as peacefully as possible; his government refrained from joining sanctions against Russia. Manchuria has amicable relations with all the other post-Soviet republics.
Manchuria also has traditionally warm relations with India, as Manchuria provided material for India's nuclear weapons program.[99]
As Mongolia second-largest trading partner, Manchuria enjoy excellent relations with its western neighbor. There are issues being tackled including emigration of Mongols to Manchuria.[100][101]
Of all the countries in Western Europe, Manchuria is said to be closest to Finland, and Manchurian economic planners took cues to Finland's economic model. Many Manchurian products sold to Europe were sold first to Finland. Some of modern Manchurian artists' first exposure to western arts are through Finnish channels. The largest non-native minority in Finland are Manchurians.
Manchuria's relations with the West increased considerably. There is steady immigration to the United States, but as these emigrants tend to be Chinese-speaking Manchurians, until recently they are considered as Chinese.
Manchuria both maintains relations with Israel[102] and the State of Palestine as well as the Sahrawi Democratic Republic.[103] Although it supported the Palestinian struggle like other East Bloc countries, it is one of the few countries that still maintained relationship with Israel during that period.
It was with its immediate neighbors that Manchuria has difficulty in maintaining good relations. Mao's acceptance of Manchurian independence was said by him to have been made with "great reluctance." Even though Manchuria and China fought on the same side during the Korean War, China tried and failed to use the war as leverage to re-incorporate Manchuria. During the Sino-Soviet Split and the Cultural Revolution, Manchuria had to fend off border incursions by China with Soviet help. Only after the Sino-Vietnamese War and China's market reforms did Manchuria-Chinese relations improve, and even then, the defeat of the former Democratic People's Republic of Korea was "never forgotten" by Beijing and Manchuria's role with it was used as a sticking point.
Manchurian-Korean relations are friendly despite the Korean War and subsequent border clashes. Sticking points include how to address war reparations with each other and claims by Manchurian historians that Korea deliberatedly whitewashed the history of Goguryeo to erase the Manchurian origin of the kingdom, causing protests and counter-protests from both sides.[104][105] [106]. As of 2018, Manchuria is now Korea's largest trading partner, accounting for 46 percent of the trade.[107]
While Manchurian-Japanese relations are now better than before, their background was also complex. Left-leaning Manchurian politicians occasionally request compensation from Japan, in which Japan said it already made apologies. Japanese politicians in turn decry Manchuria's sidestepping in its roles in anti-Japanese pogroms in 1946. Nevertheless, Japanese-Manchurian relations are cordial and compared in the past, now done in an equal basis; anime and manga are regularly being shown in Manchuria with a large fandom in Manchuria itself, and Manchurian light novels and visual novels recently provide material for new Japanese animated series. Many Japanese people retire to Manchuria and younger Manchurians emigrate to Japan. 30% of the Chinese diaspora in Japan are of Manchurian origin.[108][109]
Military
The Manchurian Armed Forces is the second largest armed forces in East Asia after China.
The Armed Forces is composed an army, navy, and air force. The MAF has the second largest army in East Asia in active forces (1,228,300), though its paramilitary forces called the Green Standard Corps (9,320,000) when added make it the largest military force in the world.[110][111]
In addition, a separate armed force called the National Guard directly reports to the President, and serves as his bodyguard. The National Guard is focused on unconventional warfare.
The President of Manchuria is the commander-in-chief of the MAF, which answers to the Ministry of Defence. The Chief of Staff of the Manchurian Armed Forces is a professional soldier with a four-star rank. The military's influence in civilian life had been shaped by its role by throwing its support behind the protesters in the 1991 anti-communist revolution. [112]
The predecessor to the MAF, the Manchurian People's Army, primarily received military equipment from the Soviet Union. The MAF's foreign weaponry are largely Soviet or Eastern Bloc in design if not in manufacture, and many of the weaponry made in Manchuria are of East Bloc heritage as well. Recently Manchuria has started purchasing weaponry and equipment from Germany and Japan.[113]
Manchuria possesses nuclear weapons.[114] The nuclear weapons program were built in the 1960s as an anti-Chinese deterrent, and after the fall of the Soviet Union, it was rumored that the Soviets actually sold some of their newer weapons to Manchuria in exchange not to sell Manchurian weapons to countries Russia disapproved of. Manchuria did not sign the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons; it also signed the Chemical Weapons Convention in 1987 but did not ratify it.[115][116]
Patriotic Civil Service is the term called for conscription; all males at the age of 18 are considered recruits; people who had disabilities are granted honorary ranks but are only allowed to participate in civil relations. Refusal to serve is considered a capital punishment during early communist times which meant automatic death penalty; this was reduced and conscientious objectors were sentenced to jail which were still criticized. After the fall of the Communist system, conscientious objection is no longer punished; "equivalent civilian work" or heavier taxation were used instead.
Law Enforcement and Intelligence
- Main article: Giarici Quaren
Main article: Law of Manchuria - See also: Judiciary of Manchuria
Manchuria has a legal system inherited from Russian, Japanese, Prussian, and Chinese models.[117] Judiciary appeals are handled by the Supreme Court, which serves as the highest court of appeal.
Internal security is provided by the Giarici Quaren. The Foreign Intelligence Agency is called the Elh Qarmetem Yamun, or the Security Bureau, being headed by the Minister of State Security, and the domestic intelligence service is called the Baiicamb Yamun, or the Investigation Bureau, subordinated under the Ministry of Justice.[118][119]All of the security services are routinely criticized for their lack of oversight, police brutality, and excessive use of force, but were known to be very effective in counter-terrorist and counter-intelligence activities.[120][121] Crimes in Manchuria are relatively lower than in the recent years, after an uptick in the 1990s and early 2000s, and involved bulglary, money-laundering, and drug-trafficking.[122][123][124][125][126]
Geography

The territory within Manchuria lies within the northern part of the North China craton, which is an area of Precambrian rocks over 100 million hectares. Manchuria is traditionally divided into three geographic regions: the Hingan mountains, the Manchurian plain, and the Golmin Shanggiyan Mountain region. The Hinggan mountains are a Jurassic mountain range[127], stemming from a collision between the North China craton and the Siberian craton.
Manchuria was never glaciated during the Quartenary period, but the fertile soils of the lower-lying areas indicate movements from the western mountains in Asia such as the Himalayas and the Tien Shan mountains, and also the Gobi and Taklamakan deserts.[128]
In the middle between the Hinggan Range and the Ğolmin Xiangian Mountains is the Manchurian plain, also known as the Dongbei plain in Chinese or the Sungari-Liyoo Plain, with the Sungari, Non, and Lioha Rivers running through the plain. Here is the area where widespread cultivation takes place. Majority of the soybean, millet, wheat, and rice are being planted in this region. The area is connected to the North China plain to the south-west.
Climate
Manchuria's climate provided contrasts, with very Arctic-like winters and hot, tropical summers. The position of Manchuria between the Eurasian landmass and the Pacific Ocean contribute to this climactic situation. Due to being in the border region of Eurasia and the Pacific, the climate triggers monsoonal wind reversal.
The dominant climate type according the Koppen scheme is the hot-summer dry continental, especially in the plain. In the far north, dry-winter subarctic climate prevails, and in the west, pockets of cold semiarid climate persist.[129]
Temperatures during the winter are usually cold due to the Siberian High, ranging from -5 °C (23°F) to -30°C (-22°F), depending on latitude, which is considered colder when further north.[130] The Siberian winds are relatively dry, however, and the snow is rarely heavy. [131] Thus Manchuria, despite being colder than North America, never glaciated due to the strong westerly winds from western Eurasia.[132]
In contrast, during summer, moist, southwestern winds bring thunderstorms, usually bringing 400 to 1150 mm of rain depending on the area; the area around the east receives more rain.
Flora
Manchuria has a varied flora and fauna. The Mongolian-Manchurian Grassland, for example, are dominated by grasslands like the feather grass. It was reported that there are eighty-five native Manchurian species of flowers and plants.[133][134][135]In central Manchuria, the vegetation is prairie grass in the western side, and mostly mixed conifer and deciduous forests on the eastern side.[136]In the north, cultivation also thinned down forests there; the majority of the trees are poplars.Herbaceous plants, pasteurizable grass, and sorghum and found there.[137]The trees that are commonly found in Manchuria are conifers like the Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis), Manchurian fir (Abies holophylla), and Siberian spruce (Picea obovata), and also deciduous trees like the Mongolian oak (Quercus mongolica), Manchurian ash (Fraxinus mandschurica), Amur linden (Tilia amurensis), and Manchurian elm (Ulmus laciniata). The Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) can also be found in Central Manchuria.[138][139][140]
Fauna
Manchuria is also home to varied fauna such as the Manchurian tiger[141], though the World Wildlife Fund fears that the protection of these wildlife is limited at best.[142] In the southern flatlands, wild animals are scarce, except for rodents. Locusts are considered destructive pests. In contrast, northern Manchuria has abundance of wildlife. During the Manchukuo era, fur trade was common and extended in the Communist era; fear of extinction and efforts by wildlife activists and the government stemmed most extinctions.[143]
Administative Divisions
Manchuria is organized into provinces (gol, гол), subdivided into districts (guusa, гөса) and towns (sum, сум). Certain cities such as the capital Cacon, Harbin, Mukden, and Dalin are termed "Special Cities"; they are considered to be metropolitan provinces.
| # | Name | Type | Flag | Administrative Seat |
Transliteration (Traditional) | Transliteration (Cyrillic) | Area (km2) |
Population (2020) estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cacon | (special city) | none | ᠴᠠᠴᠣᠨ |
Чачон | 2579.44 | 4,832,448 | |
| 2 | Harbin | (special city) | File:Flag of the City of Harbin.svg | none | ᡥᠠᠯᠪᡳᠨ |
Харбин | 2056.70 | 3,974,502 |
| 3 | Dalin | (special city) | none | ᡩᠠᠯᡳᠨ |
Далин | 3055.58 | 5,106,719 | |
| 4 | Mukden | (special city) | none | ᠮᡠᡴᡩᡝᠨ |
Мукден | 3470.82 | 7,490,125 | |
| 5 | Afꝁai Aliang | province | Isang Ǧasen | ᠠᠪᡴᠠᡳ ᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠩᡤᠠ |
Афқаи Алиаң | 91,751.71 | 21,799,287 | |
| 6 | Ħalħun Ǧol | province | Erdem de Alyh | ᠊ᡵᡩᡝᠮᡠ ᠪᡝ ᠠᠯᡳᡥᠠᠠᠪᡴᠠᡳ |
Ҳалҳун Ғол | 83,571.95 | 7,543,777 | |
| 7 | Girin | province | Girin Hoton | ᡤᡳᡵᡳᠨ |
Гирин | 72,624.91 | 9,823,819 | |
| 8 | Sungari Ula | province | ᠰᡠᠨᡤᠠᡵᡳ ᡠᠯᠠ |
Сунгари Ула | 2,424.07 | 9,752,500 | ||
| 9 | Non Ula | province | Cicigar | ᠨᠣᠨ ᡠᠯᠠ |
Нон Ула | 116,109.53 | 8,869,372 | |
| 10 | Usuri Ula | province | Giamusi | ᠠᠴᠠᠨ ᠨᡠᠯᠠ |
Усури Ула | 126,837.11 | 8,449,303 | |
| 11 | Saħalin Ula | province | Aigun | ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ ᡠᠯᠠ |
Саҳалин Ула | 115,344.23 | 562,941 | |
| 12 | Hinggan | province | Jerim | ᡥᡳᠩᡤᠠᠨ |
Хиңган | 166,371.95 | 5,335,812 | |
| 13 | Hulunbuir | province | Hailar | ᠬᠥᠯᠥᠨ ᠪᠤᠶᠢᠷ |
Хулунбуир | 252,777.38 | 2,242,875 | |
| 14 | Aidan | province | Aidan Hoton | ᠠᡳᡩᠠᠨ |
Аидан | 43,329.34 | 1,941,700 | |
| 15 | Yalu Ula | province | Yalu Hoton | ᠶᠠᠯᡠ ᡠᠯᠠ |
Ялу Ула | 69,049.68 | 8,256,551 |
Largest Cities
| Rank | Administrative division | Pop. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mukden  Harbin |
1 | Mukden | Mukden | 5,119,100 |  Dalin  Cacon | ||||
| 2 | Harbin | Harbin | 5,115,000 | ||||||
| 3 | Dalin | Dalin | 4,009,700 | ||||||
| 4 | Cacon | Cacon | 4,041,200 | ||||||
| 5 | Engemer Alin | Afꝁai Aliang | 1,406,000 | ||||||
| 6 | Girin Hoton | Girin Ula | 1,268,900 | ||||||
| 7 | Sarhu | Saħalin Ula | 1,415,268 | ||||||
| 8 | Hetu Ala | Afꝁai Aliang | 1,307,200 | ||||||
| 9 | Cicigar | Saħalin Ula | 979,517 | ||||||
| 10 | Boisi | Afꝁai Aliang | 855,800 | ||||||
Economy
Manchuria has a economy that is measured to be the 15th largest in the world by 2018, at US$989 billion.[144] Manchuria has been one of the strongest in the Asia-Pacific region and is considered an honorary Asian Tiger. The service industry is smaller compared to the other East Asian countries. Manchuria was the richest East-aligned country in Asia and was second only to Japan.[145][146]Even after the fall of communism, Manchuria is the richest former communist country when measured by its GDP per capita.
During the Qing period, Manchuria was one of the most industrialized parts of the dynasty, and its coal deposits made it a highly-urbanized country. During the Manchukuo era until 1945, Manchuria was considered more industrialized than China and even Japan; Japanese investment has expanded Manchukuo industries.[147][148][149] Indeed, China refers to Manchuria as the "Eldest Son" of industrialized communist countries in Asia. After the fall of communism, Manchuria struggled to keep its industry as it stagnated, prompting the government to diversify its economic structure.[150]
In 1997, Manchuria's GDP stalled to the level it achieved in 1990, and considered a "national scandal". Immediately, Prime Minister Tian Fengsan of the People's Party then installed new economic policies and copied the economic system instituted by Japan in the 1950s and South Korea in the 1960s. Tiyan threatened to close un-productive companies and he did with a few; as the enterpreneurial pool is still limited, Tiyan encouraged businessmen to set up their own businesses to augment the economy. Manchuria managed to keep the majority of its labor-intensive manufacturing from being transferred to the neighboring PRC keeping unemployment at bay, although pay was low compared to Korea. There are calls for the government to abandon state-owned enterprises altogether as they are a remnant of communist and Manchukuo era policies.[151]It was said that Manchuria's explosive economic growth after the Financial Crisis was due to Tiyan's reforms; however, inequality in income increased. It's petroleum and shale oil industry, enabled Manchuria to increase its economic clout; also, its economic penetration to Eastern European markets and West Asian markets had been credited to Manchuria's rise as one of the world's largest economies.
Manchuria's economy still remains industrial, with steel, automotive, rail, aircraft, and shipbuilding industry predominating. Manchuria also has coal and petroleum industry and has several petroleum refinery facilities. The appliance industry has also been booming since the 2010s, and Manchuria's software production has been ramped up since 2005.
Despite decline of agriculture due to industrialization, it remains important. Fishing is important on the coasts and rivers, while farming is dominant in the south with corn, wheat, soya, and sorghum commonly cultivated there. Animal husbandry is also common, with cattle, pigs, horses, and sheep being raised.
Agriculture
Agriculture still plays a vital role in the Manchurian economy.[152] In the northern cold regions, corn, wheat, sorghum, flax, potatoes and sunflowers are grown. In the center, soybeans are planted; Manchuria is the chief source for US soybean.[153] In the east, rice is grown especially in Aidan and Yalu, whereas in the south, corn, sorghum, cotton, and soybeans are cultivated. The south is also where Manchuria's fruit industry dominate. Herding is also common, with pigs, cows, and horses predominating; the dairy industry also supplies all of Manchuria's yearly needs. Sheep farming is common in the western provinces.
Manchuria's agriculture has undergone a shift after 1990. Prior to 1990, all farming are done within collective farms confiscated from the Manchukuo government and Japanese companies, with 50 families inhabiting a farm called veilesy achilahan. The collective farms have moderate to high production rates but needed subsidies for technology. In 1990 collective farms remain but as their subsidies were cut off, many failed and shuttered. Conversion to co-operative farms alleviated the situation. Private plots, de-facto recognized by 1971, were legalized by 1990.
Currency
The currency is known as the Muheren, divided into 100 fun. It is issued by the Central Bank of Manchuria. Manchuria has the world's 8th largest foreign exchange reserves.
Industry
Manchuria's industry has developed considerably, both light and heavy industrial products. In the late 1990s, Manchuria attempted to curry foreign investment, including those of Korea, China, and Japan, and Western countries, and there was a boom in manufacturing, however, Russian and East European industries took up the bulk of foreign investment. However, it is still a major production base for heavy industry. Many companies have origins in the Manchukuo era and nationalized by communists; these state-owned industries control 25 percent of the economy. Others are dominated by so-called "Ulin I Ejeltu" or "Wealth clans", analogous to the Zaibatsu/Keiretsu of Japan and the Chaebol of Korea.
In 2012, President Lin Boljon initated the Revitalize Manchuria program to enhance the industrial situation in the country.[154] While it saw moderate success, Lio's untimely death and political infighting hampered its implementation.[155] In addition, remnants of the old communist bureaucracy are still in charge of a huge sector of Manchuria's economy, prompting government leaders to encourage private enterpeneurships without government spurring.
There are three industrial zones in Manchuria: Mukden-Dalin Industrial Zone, Cacon-Girin Industrial Zone, and Harbin-Sartu Industrial Zone. Two major urban agglomerations have been formed: the central and southern Afkai Aliang urban agglomeration and the Hachang urban agglomeration. The main industrial cities are Mukden, Dalin, Engemer Alin, Boisi, Fusi Hecen, Girin, Cacon, and Harbin.
Automotive Industry
Manchuria is the world's sixth largest automobile maker, with 5,340,034 units produced by 2018. Most are exported to China, Russia, Eastern Europe, Korea, and Third World countries. Manchuria had difficulties in penetrating the Western markets due to Manchu cars being perceived as knockoffs of Russian, Korean, and Japanese vehicles, a trend that it managed to overcome by the mid-2010s.Automotive makers include Masu,Kiruda, Hadeyim, Eldepi, and others.
Services
Services account for at least one fourth of Manchuria's economy.[156] Some of the largest banks of Manchuria are the Manchurian National Bank, the Mukden Bank[157],Harbin Bank,[158] and the Bank of Girin.[159]
Transportation
- Main article: Transportation in Manchuria
Transportation in Manchuria is dominated by railways, with roads coming in second and air and sea transport not falling behind.
Railway network
Manchuria's railways, owned by the Manchurian National Railway, are one of the world's busiest. High-speed rail in Manchuria is common; as the matter of fact, the first railway system to be called "high-speed" was created during the Manchukuo era. The late Qing's Dong Qing Railway and the South Manchurian Railway constitute the "D" word Manchurian Railway. While serving Russian and Japanese interests, it also promoted the development of the country. Harbin, as the intersection of two railways, replaced Cicigar and became the major city in North. During the Manchukuo era, the Japanese expanded the railway network, which is not much different from the current form. In recent years, high-speed railway lines such as the Qingdao-Abkai Passenger Railway, the Harbin-Dalin High-speed Railway, the Cacon-Girin InterCity, the Ha-Ji Railway, and the Muk-Dan Railway have also been completed and opened to traffic.
Highways
Manchuria has an extensive highway system. The Dalin-Mukden Superhighway was opened in 1990, shortly before the fall of the Communist regime.[160]It is operated by the Manchurian Expressway Company Ltd.[161]
Shipping
Manchuria's major port is Dalin, with Niehetun as second. Dalin's port handles the bulk of shipping in Manchuria.[162]During 1973, Dalin handled 23.1 million tonnes.[163]By 2015, this now stands to 555 million tonnes.[164]Dalin is the world's seventeenth-largest port in 2012; however by 2023 it fell to 44th place.[165][166]
Aviation
There are currently 22 major civil airports, including international airports: Mukden International Airport[167], Harbin International Airport, Cacon New International Airport, Dalin International Airport, Hailar Airport, Aidan Airport, Mudanbira Airport, Isang Ǧasen Airport, Yalu Airport and Giamusi Airport. The first four airports have flights globally, while the rest are concentrated on neighboring Asian countries. The Usanggari Nuhalin Tala Plain is has many airports. Manchurian Airlines[168][169][170] has been the flag carrier of Manchuria since 1931.
Energy
The slim majority of Manchuria's energy resources are being based on fossil fuels; nuclear energy and hydroelectric energy are slowly taking their place. Coal-fired plants are stil in common use despite calls for their decommissioning. Petroleum power plants are also common though less so due to focus for transportation use. Renewable energy like solar and wind power had been limited due to lack of funds and overabundance of energy supply. Mawehe (Manchurian Petroleum Company) is the country's state owned petroleum company; however, its duopoly along with Petrogurun (National Synthetic Petroleum Company) has been broken since the fall of communism, though both remain the largest petroleum companies.[171]
Science and Technology
Manchuria has encouraged science and technology since the Communist period, though it preferred "not to brag about its achievements." Manchuria's expenditures on science are 7.2 percent equivalent of the national GDP in 2018.
Manchuria produced several world renowned scientists. Yongki, Emperor Hungli's fifth son, was known for book Jiaotong Tenggao in Chinese and concerns about astronomical calculations. The Duin Namun I Yooni Bithe, also created during Hungli's period, was the largest collection of books in Manchurian and Chinese history, and dealt with scientific topics as well as literature. Hungli's predecessor Hiowan Yei was even more renowned and personally supervised the creation of the Kangxi Dictionary.
Scientists such as Peng Chuah was the chief scientist in building Manchuria's nuclear arsenal.[172][173]Sugia Ujin developed Manchuria's first satellite.[174] In 1958, Sun graduated "with highest honor" and returned to China.[174][175] Min Ciuli, a Mukden native that later emigrated to the United States, was the first doctor to successfully use chemotheraphy in fighting maligant cancer.[176]
There are also Manchu innovators in the present. One example is Nanfulu Gosin, a astrophysicist who cooperated with China and developed the Five hundred meter Aperture Spherical Telescope in China, and advised in the construction of a new telescope in Yanbiyan before his death.[177] Laibu Engiye was the chief scientist of Manchuria's lunar lander program.[178]Gualgia Shumuri is also reknowned for his contribution for artificial intelligence.[179]
Manchurians are also known for inventions that were only recently appreciated in the present day. Poisoned arrows, two-seasoned rice planting,and planting new rice and oilseed vareities are among the inventions created during the Qing. The first iteration of a machine gun was also created by Daizi during the early Qing.[180]
Manchuria is the eighth nation that launched an independently-built rocket into space, in January 8, 2001, called the Adun-i Haban (Auspicious Cloud). In February 24, 2003, in response to China launching the Shenzhou manned rockets, Manchuria launched its own man into space, Yanggia Horong.[181][182] However, he was not the first Manchurian into space; Ligia Sekien and Liohala Cungfu were the first Manchurians into space launched by the Interkosmos program together with the Soviet Union.[183]
Demographics
- Main article: Demographics of Manchuria
Languages
- Main article: Manchu language
The official language is the Manchu language, which was revived during the Wang Cengbin era and continued during Manchukuo as the Japanese were anxious in reducing the Chinese influence in the country. While a plurality of the population of Manchuria are proficient in Chinese or "Guanhua" as it was popularly called (45%), most of the native-speakers of Manchu (43%) are ethnically Manchurians or Sibe people; the rest speak Manchu as a second language and is the lingua franca of the government and the military. Back in even the 19th century, most Manchus spoke only Mandarin.[184][185][186][187] It is only through independence in 1911 that Manchu language was re-emphasized as the national language.[188][189][190][191] Although the language switch was slow, it was intensified during the communist era, to deter Chinese plans for annexation. During the era of the first Manchu State and Manchukuo the old vertical alphabet was used, but since the People's Republic the Cyrillic alphabet is in use. Sibe speakers from the former Xinjiang province were brought in and taught the Manchu cadres and trained new Manchu-speaking teachers. The near-exclusive use of Manchu in the military and the government, mandated in the communist era, which employed universal conscription was cited as a reason in the Manchu-language revival. Modern Standard Manchu as it was called is different from Classical Manchu as it was written in the Cyrillic script introduced in 1947. Also, it contains heavier Russian and Mongolian vocabulary, mainly as lexicons for non-existent words in Manchu. The traditional Manchu script is re-instated slowly.[192][193][194][195][196][197][198][199][200] Manchu is the primary language of instruction, though classes in Chinese/Guanhua, Korean, Japanese, Russian, and English are available.[201][202][203]
Other languages are Korean, spoken and has official status in Aidan, Russian near the Russian border and some large cities, Japanese in Dalin and isolated southern communities, Mongolian which has official status in Hulunbuir and Hinggan provinces, along with Orochon, Evenki, Nanai, and Daur.
Ethnic Groups
The Manchus and the Chinese are the largest ethnic groups in the country, with 44 percent of them are Manchus and 37 are Chinese. However it is commonly accepted that the Chinese population is much higher and the real majority of the country due to assimilation, and emigration during the communist period; many of them simply recorded their ethnicity as Manchu in censuses. Intermarriage between Manchus and Chinese are common and became more acceptable by the fall of the Qing.[204][205][206][207] Even some famous Chinese political figures had Manchu daughter in-laws.[208]Koreans compose nine percent of the population, Mongolians 3%, and Russians and mixed Russians comprise 2%.
Religion
- Main article: Religion in Manchuria
The 1991 Constitution proclaims complete freedom of religion. 23.3 percent of the population say in a 2014 interview that they do not practice any religion. During the Communist era, the Manchurian communist government did little to interfere in the religious affairs of each country as long as they obey the party line. The strongest traditional religious influences in Manchuria are Buddhism[209][210][211][212][213][214][215], Tengriism, Manchu Shamanism, and Confucianism. However, the largest numbers of people in Manchuria are said to be non-religious.[216][217]Buddhists are the next most numerous group in Manchuria.[218]Vajrayana Buddhism is the most popular Buddhist sect among the ethnic Manchus, as they were officially patronized by the Manchu emperors starting from Hungtaiji. Certain religious groups, mainly those who have a pacifist bent such as Jehovah's Witnesses, and new religious movements are banned. An unusual theme of Manchurian religion is the greater penetration of Christianity in Manchuria. Due to the majority of the European settlers being Russians and Ukrainians, the Orthodox Christians are the majority of the Christian population in Manchuria, but Catholics and Protestants are also well-represented, typically with Koreans.[219][220][221][222]
Religion in Manchuria
Fertility Rate
Manchuria has the lowest fertility rate in the world.[223] It was estimated that in 2015, Manchuria's fertility rate was 0.55 percent, even lower than Japan, which already have a low fertility rate.
Education
- Main article: Education in Manchuria
Manchuria inherited from Manchukuo and Communist times an efficient educational system.[224] Manchuria's government had established numerous universities and schools. City universities tend to be of better quality than provincial schools, a problem acknowledged by the government.[225] Literacy rates have been on an all-time high of 98.9 percent, with most illiteracy coming from the western rural areas of Manchuria. [226][227][228][229]
Notable universities include the Manchuria State University, Mukden University, Harbin University, Dalin University of Technology, and among others.
Manchuria's education system is divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary education. Facilities are either maintained by both private and public schools under the Ministry of Education. The ministry also sets a National Curriculum that provides guidelines for teachers; it is always regularly updated. Private schools may adopt a modified version of the National Curriculum provided it did not conflict with the government's policies.
All education is compulsory in primary and secondary. Subsidies remain for these schools; most tertiary school subsidies ceased after the fall of the communist regime. However, the government maintained the position that public education would be permanently be free.
Prior to formal education, children are educated in kindergartens. By the time they reached five, they are enrolled in primary schools until the age of eleven. In elementary school, the children by learning Manchu, Guanhua, mathematics, science and physical education. Manchurian schools usually conduct school festivals, a trait inherited from the Manchukuo and communist eras.[230]
Like its fellow East Asian countries, Manchuria's education system has been criticized due to pressures given to its students. Rote memorization are also seen as a problem.[231]However like its Asian neighbors, it was also praised for the quality of its graduates.[232][233]
Health
- Main article: Health in Manchuria
Manchuria has a universal health system; all citizens are required to sign up. The system was created during Communist times in 1956 as official government policy for its citizens. All Manchurians can sign for either a private program of either two of the government's insurance programs, which are both subsidized. Both private and public hospitals exist; in the case of the latter, they are administered by the Ministry of Health's Public Hospital Administration.
Cardiovascular diseases are the single highest reason for death in Manchuria.[234][235]The average life expectancy for Manchurians is 79.8 years; 78 for males and 80 for females.[236]1.9 percent of deaths in Manchuria are attributed to communicable and preventable diseases, higher than in Korea and Russia but lower than in China and Mongolia.[237]
According to the US State Department, Manchurians have virtually 100 percent access to clean water and sanitation;95 percent have access to improved sanitation facilities by 2015.[238][239]
Both state-owned and private-owned universal insurance system is in place; the latter were permitted after the fall of communism and at least 49 percent of the population have access to it; private insurance, while more expensive, is considered as superior. The quality of health care is said to be good, if not excellent; differing health problems exist from obesity in urban areas and malnutrition in the rural areas.[240] Every individual is entitled to a health card detailing full medical records.
While Manchuria has a low AIDS rate, it was steadily increasing, and is spreading from the urban areas to the rural ones, alarming health officials and critics alike.[241][242][243]Most of the people interviewed in Manchuria are said to be reasonably educated about AIDS.[244]
Society and Culture
Culture
Manchurian culture is a mix of traditional Manchu culture, Manchurian Chinese influences, and input from its neighbors and conquerors. Although many commonly thought of Manchus as nomadic like the neighboring Mongols, in reality, most Manchus are sedentary.[245] A common question by many scholars is if Manchu culture is a culture of its own right, or was feared to be assimilated to Chinese culture.
During the communist era, Manchuria tried to build a culture unique from its past, using common Communist ideals, but with mixed success. In the end, it opted to pursue a unique kind of Manchu nationalism, even as it opened up its culture to the West. However, cultural norms such as respect to authority, family life, and respect for consensus remain strong, as well as maintaining aspects of traditional culture.
Manchurians have a number of festivals, some are borrowed from the Chinese like Duanwu Festival and the Spring Festival.[246][247].Others are of Manchu origin like the Банжн Інең Banjin Inenggi (ᠪᠠᠨᠵᡳᠨ
ᡳᠨᡝᠩᡤᡳ), or the traditional Manchu ethnic holiday, commemorated in the thirteenth day of the tenth month of the Chinese calendar.Another day is called the "Food Extermination Day" or "Day of Starvation."Although it was commonly believed that it involved fasting, as it was intended to commemorate a day where Nurhaci run out of food, this is not the case, but instead it honors the hospitality of the villagers despite not even having tableware. The traditional food eaten on this day are rice, pork, and egg wrapped in perilla leaves.[248]
Yobocun, a Chinese folk comedy genre, was popularized by the Manchus living in Beijing. It also spread into Manchuria itself and artists perform in Chinese and Manchu.[249]
Music
- Main article: Music of Manchuria
The Juse Deote Bithe is a Manchu folk ballad song common with ethnic Manchus in Manchuria and China.[250][251]
Ulabun is a form of Manchu entertainment combining story-telling and music with an octagonal drum[252], and is known to be a traditional ethnic Manchu folk music.[253][254]Akxan is the most famous ulabun singer.[255]
Niohuru Gehun is an accomplished Manchurian composer and pianist that played for various orchestras such as the New York Philharmonic Orchestra and Vienna Orchestra.[256].[257]
Manchurian pop music at first utilized Guanhua as Manchu-language music are still considered only for folk music. This perception changed in the late 1990s to compete with Korean and Japanese pop music, and started to use the Manchu language. Since then, Manchupop refers to pop songs sung in the Manchu language. Yehenara Yebken, formerly a Mandopop and Mandopop singer in Hong Kong, Taiwan, and China, later shifted to Manchu language songs late in her career and kickstarted the trend, along with Akxan in the 2000s.
Film
- Main article: Cinema of Manchuria
The Manchu film industry started during the Manchukuo-era, with the Cacon Film Studio in the later Manchurian People's Republic utilizing the same equipment of the old Manchurian Film Association.[258][259] Like other communist states, Manchurian films during that period were considered propaganda materials by the government, but the filmmakers were allowed a greater leeway in creative content as long as they obeyed the party line.Many filmmakers and films from Manchuria won prizes in foreign film festivals especially the Prague International Film Festival.
Art
Manchuria's art reflects the period and the political climate; a strong Japanese aesthetic element is not only present during the Manchukuo era, but also during the communist era. Post-communist Manchuria continued the trend.[260]Ixilangga Art Studio was known to commission monuments for foreign countries.[261][262]
Literature
- Main article: Manchu literature
The Tale of the Nisan Shaman is considered the magnum opus of Manchu literature.[263]The story revolves on the titular Shaman to revive a young hunter. The story is also widespread on other related peoples like the Evenki,Sibe, and Daur. Its modern version by Dekdengge was written in the 1800s.[264]
Manchu literature before the establishment of the People's Republic tend to be extremely limited, and what literature were there were in Chinese.[265] Since founding, Manchuria saw what Jogia called the "Flowering of Manchurian Literature".[266] The immigration of Sumuru Xuxu to Manchuria and his shift of writing from Chinese to Manchu have been called influential in later cadres of Manchurian writers. Another known writer was Caogia Bai, also wrote novels about the anti-Japanese wars in Manchuria in both Manchu and Chinese.[267] Manchu language literature during that period, however, operated on a state mandated censorship and limited Manchu-language readers at that time. Only after the fall of Communism did Manchu-language literature proliferate, and much of this were published on the Internet.
Modern Manchu literature also tend to be influenced by science and therefore very willing to embrace science fiction. It was said that many authors chose this genre because during the communist era, literature topics tended to be historical or folk-tale in variety.[268] This enabled the writers to depict sexual crime , cyberwarfare , space exploration and immortality in a manner that was distinct from science fiction of other countries, as they usually centered on anthropocentrism.[269]
Chinese-language literature in Manchuria, although ignored by the government, were somewhat more widespread. It diverged from mainstream Chinese literature since most Chinese typefaces have been melted down and had to use Cyrillic script in its place. Even when the ban on Chinese characters was lifted after Communism, writers tend to mix Chinese with Cyrillic characters or Manchu in their works, creating a curious niche in Chinese literature.
Architecture
While Manchu architecture commonly follows foreign influences, Manchuria did retain some architectural pecularities and eccentricities[270] The Fulmian Bo, or the "pocket house", is a typical Manchu architectural style. The house faces the north with the door opening south for sunlight. To preserve the head, it is encompassed by four walls. The house had pipes from the ground that serve as chimneys. In each room, there is a "Tumen Bo" that is used for private religious activities and also used to as sleeping rooms. Accoring to Jiro Murata, there are at least five or six architectural influence; ethnic Manchu, Han Chinese, Tibetan, And Western, plus Korean and Hui sensibilities.[271] Also, traditional Manchurian buildings in ancient times were less-durable and only became stronger by the time of the Qing. Later on, the Han Chinese imported their own building styles.
During the Manchukuo era, it imported the Imperial Crown Style as shown in buildings built during the Manchukuo era. Because the Manchu architectural styles have not fully developed and forced to adopt Chinese elements, during the Manchukuo era, it adopted the Han Chinese building appearances but adopted the interior designs and sensibilities of traditional Manchu houses.[272] During the Communist period, it inherited Socialist Realism styles and mixed with previous traditions.
Larger structures such as the Ħalhun Be Jail Gurung, for example, shows strong Tibetan influences from its seemingly Chinese interior.
Cuisine
- Main article: Manchu cuisine
Manchurian cuisine (Manju sogi) is a amalgamation of ethnic Manchu, Chinese, Korean, Mongolian, and European influences. They are often hearty, with meats being roasted and seasoned with cumin and garlic and salt. The Man-Han Imperial Feast was known in Asia as a court dish during Qing times, modified in the present-day to suit modern tastes and only using domesticated meat.[273][274]
Manchurian cuisine is concentrated on grains, vegetables, and meat. Wheat, sorghum, soybean, and rice are commonly used as staple grains, with potatoes and corn becoming common in the late 20th century. Compared to China, Korea, and Japan, Manchurian cuisine uses greater amount of meat. Unlike in China, Manchurians tend to limit their choices of meat, as many Manchus for example, see eating dog-meat as sacrilegious.Nasan Sogi is fermented cabbage similar but not identical to the Korean kimchi, and is commonly used in dishes.[275] Sile sengi duha is a famous pork and cabbage dish, as well as ludagun, and Guotie.[276] Manchurian barbecue stands are also common in Manchurian cities, and it is claimed it was a legacy of traditional Manchurian barbecue techniques.[277]
Sport
Manchuria's national sports are said to be ice hockey, football, basketball, and the indigenously developed sport of nicuhe, literally meaning "Pearl-ball". Martial arts are also commonly practiced, including Buku or Manchurian wrestling,[278][279][280][281] and archery. Manchus like Mongolians were fond of falconry.[282][283][284]Horse riding was deemed very important for Manchu culture.[285][286].The Manchu Emperor Hungli especially promoted horse riding and archery as important pillars of Manchu culture that it persists to this day.[287]
Manchuria's football association was founded during the Manchukuo era.[288] While it is a competitive team in the Asian championships, it was only able to enter the FIFA World Cup once in 2010, defeating Cote d'Ivoire's national football team but in turn defeated by both Portugal and Brazil.
Manchuria was supposed to compete in the Summer Olympics in 1932, but its only candidate, Lio Cangcon, defected to the Republic of China and became the first Chinese Olympic representative. Attempts to join the 1936 Olympics in Berlin were frustrated by the International Olympic Committee's decision not to allow unrecognized states in the Olympics. Manchuria was to join the 1940 Summer Olympics but World War II prevented its entry[289] Instead, it sent atheltes to the 1940 Far East Games organized by Japan. [290] The Republic of China repeatedly denied Manchuria entry to the Olympic Games until 1972. Manchuria is more successful in Winter Games, primarily due to the country's climate; indeed it was only second to Korea in the number of Asian medalists in the Winter Olympics.Ice skating is also a popular Manchu sport and has roots in tradition;Qing emperors once retained an ice skating battalion of Manchu bannermen chosen from the best of his forces, and Qianlong even referred to ice skating as a "national custom".[291][292]Shen Zo and Jogia Hongbo were winners of ice-skating pairs in the 2010 Winter Olympics, winning the gold and ended the streak of Russian dominance in pair skating.[293][294]Tongia Jian is another famous Manchurian figure skater, winning championships in Europe.[295]
Traditional children's sports are alive with children in Manchuria.Gachuha is a popular sport using the ankle bone of a horse or a pig.[296][297][298]
Motor racing sports are also popular; a group of Manchurian businessmen are negotiating with Formula One to bring the race to Manchuria by 2022; however due to the COVID-19 pandemic, this idea was scrapped.
Media
Manchuria's press is rated as "Partially Free" by the Reporters Without Borders. While media is more free than in neighboring China and Russia, intimidation and censorship by government are still criticized.
The government maintains the Manchurian Broadcasting Network.
References
Citations
- ↑ Fengtien Clique; Great Soviet Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition (1970-1979).
- ↑ Byington, Mark E. (2016). The Ancient State of Puyŏ in Northeast Asia: Archaeology and Historical Memory. Cambridge (Massachusetts) and London: Harvard University Asia Center. pp. 11, 13. ISBN 978-0-674-73719-8.
- ↑ Tamang, Jyoti Prakash (2016-08-05). Ethnic Fermented Foods and Alcoholic Beverages of Asia. Springer. ISBN 9788132228004.
- ↑ Son, Chang-Hee (2000). Haan (han, Han) of Minjung Theology and Han (han, Han) of Han Philosophy: In the Paradigm of Process Philisophy and Metaphysics of Relatedness. University Press of America. ISBN 9780761818601.
- ↑ Writing Group of Manchu Brief History 2009, pp. 206–207
- ↑ Endymion Porter Wilkinson (2000). Chinese History: A Manual. Harvard Univ Asia Center. p. 728. ISBN 978-0-674-00249-4.
- ↑ Agui 1988, p. 2
- ↑ Feng, Jiasheng (冯家升). 《满洲名称之种种推测》 [Many Kinds of Conjecture of the Name "Manju"]. 《东方杂志》 [Dongfang Magazine]. 30 (17).
- ↑ Teng, Shaojian (滕绍箴) (April 1996). 《满洲名称考述》 [Textual Research of the Name "Manju"]. 《民族研究》 [Ethnicities Research]: 70–77.
- ↑ Norman 2003, p. 484.
- ↑ 《族称Manju词源探析》 [The Research of Ethnic Name "Manju"'s Origin]. 《满语研究》 [Manchu Language Research] (1). 2009.
- ↑ E.g. Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society, Volumes 11–12, 1867, p. 162
- ↑ Giles 1912, p. 8.
- ↑ [1]Pozzi 2006, p. 159.
- ↑ [2]Pozzi 2006, p. 167.
- ↑ "Seven decades of bitterness". BBC News. 2014-02-13. Retrieved 2020-02-11.
- ↑ The Cambridge History of China, Vol. 03: "Sui and T'ang China, 589–906, Part 1," at 32, 33.
- ↑ Ruins of Identity: Ethnogenesis in the Japanese Islands By Mark Hudson
- ↑ Ledyard, 1983, 323
- ↑ Patricia Ann Berger – Empire of emptiness: Buddhist art and political authority in Qing China, p.25
- ↑ Crossley, Pamela Kyle (2002). A Translucent Mirror: History and Identity in Qing Imperial Ideology (illustrated, reprint ed.). University of California Press. p. 196. ISBN 978-0520234246.
- ↑ Crossley, Pamela Kyle (2002). A Translucent Mirror: History and Identity in Qing Imperial Ideology (illustrated, reprint ed.). University of California Press. p. 196. ISBN 978-0520234246.
- ↑ Forsyth 1994, p. 214.
- ↑ "5 Of The 10 Deadliest Wars Began In China". Business Insider. 6 October 2014.
- ↑ Elliott, Mark C. "The Limits of Tartary: Manchuria in Imperial and National Geographies." Journal of Asian Studies 59, no. 3 (2000): 603–46.
- ↑ Hauer 2007, p. 117.
- ↑ Dvořák 1895, p. 80.
- ↑ Wu 1995, p. 102.
- ↑ Zhao 2006, pp. 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14.
- ↑ 刘小萌 (2008). 《清代八旗子弟》. 辽宁民族出版社. p. 第206页.
- ↑ 周敏(鲁东大学历史与社会学院). 《首崇满洲——清朝的民族本位思想》. 《沧桑》.
- ↑ Richards 2003, p. 141.
- ↑ Richards, John F. (2003), The Unending Frontier: An Environmental History of the Early Modern World, University of California Press, p. 141, ISBN 978-0-520-23075-0
- ↑ Reardon-Anderson 2000, p. 504.
- ↑ Reardon-Anderson 2000, p. 505.
- ↑ Reardon-Anderson, James (2000). "Land Use and Society in Manchuria and Inner Mongolia During the Qing Dynasty". Environmental History. 5 (4): 503–509. doi:10.2307/3985584. JSTOR 3985584.
- ↑ Scharping 1998, p. 18.
- ↑ Reardon-Anderson 2000, p. 507.
- ↑ Reardon-Anderson 2000, p. 509.
- ↑ Reardon-Anderson 2000, p. 509.
- ↑ Lomanov (2005:89–90)
Probably the first clash between the Russians and Chinese occurred in 1868. It was called the Manza War, Manzovskaia voina. "Manzy" was the Russian name for the Chinese population in those years. In 1868, the local Russian government decided to close down goldfields near Vladivostok, in the Gulf of Peter the Great, where 1,000 Chinese were employed. The Chinese decided that they did not want to go back, and resisted. The first clash occurred when the Chinese were removed from Askold Island, in the Gulf of Peter the Great. They organized themselves and raided three Russian villages and two military posts. For the first time, this attempt to drive the Chinese out was unsuccessful.
- ↑ "An Abandoned Island in the Sea of Japan". 2011-01-25.
- ↑ "东北近代工业的先驱 ――吴大澂与吉林机器制造局". 吉林日报. 长春市档案馆. 2006-05-18. Retrieved 2019-10-18.
- ↑ https://www.economist.com/special-report/2007/03/31/history-wars
- ↑ "Memories of Dr. Wu Lien-teh, plague fighter". Yu-lin Wu (1995). World Scientific. p.68. ISBN 981-02-2287-4
- ↑ Crossley 1990, p. 174.
- ↑ Woo, X.L. (2002). Empress Dowager Cixi: China's Last Dynasty and the Long Reign of a Formidable Concubine. U.S.: Algora Publishing. ISBN 0875861660.
- ↑ Douglas Reynolds, China, 1898–1912: The Xinzheng Revolution and Japan (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1993). ISBN 0-674-11660-7 passim.
- ↑ Mu, Eric (3 November 2008). "Reformist Emperor Guangxu was Poisoned, Study Confirms". Danwei. Archived from the original on 2 July 2017. Retrieved 13 February 2013.
- ↑ Chien-nung Li, Jiannong Li, Ssŭ-yü Têng, "The political history of China, 1840–1928", p234
- ↑ Zhao Zhongfu, “Xinhai geming qianhou de dongsansheng,” Bulletin of the Institute of Modern History, Academia Sinica, Vol. 11 (Jul, 1982)
- ↑ Bonavia 63-64
- ↑ Newton, Michael (2014). Famous Assassinations in World History: An Encyclopedia [2 volumes] (illustrated, reprint ed.). ABC-CLIO. p. 653. ISBN 1610692861.
- ↑ Owen Lattimore; Sh Nachukdorji. Nationalism and Revolution in Mongolia. Brill Archive. pp. 171–. GGKEY:4D2GY636WK5.
- ↑ Wang Chen-ping (Wang Chengbin) 王承斌 from Biographies of Prominent Chinese c.1925.
- ↑ 中国社会科学院近代史研究所 (2005). 民国人物传 第12卷. 中華書局. ISBN 7-101-02993-0.
- ↑ 徐友春主編 (2007). 民国人物大辞典 増訂版. 河北人民出版社. ISBN 978-7-202-03014-1.
- ↑ 弓挽强,王承斌墓碑碑文,葫芦岛晚报20110901期第b6版 "弓挽强,王承斌墓碑碑文". September 1, 2011.
- ↑ 李, 世峥 (1 September 2010). "基督徒将军佟麟阁:抗战殉国的第一位高级将领". 中国民族报. Archived from the original on 24 May 2018. Retrieved 4 June 2018.
- ↑ "佟麟阁中国抗日战争牺牲的第一位高级将领". 每日头条. 27 May 2017.
- ↑ "佟麟阁中国抗日战争牺牲的第一位高级将领". 每日头条. 27 May 2017. Archived from the original on 24 May 2018.
- ↑ Coox, Alvin D. (1990). Nomonhan : Japan against Russia, 1939 (1st ed.). Stanford, Calif.: Stanford University Press. p. 841. ISBN 978-0804718356.
- ↑ Edward Behr, The Last Emperor, 1987, p. 202
- ↑ 东北抗联:绝地战歌. 中共党史出版社. 2012. ISBN 9787509815670.
- ↑ 东北抗日联军史. 解放军出版社. 2014. ISBN 7506567180.
- ↑ 东北抗日联军抗战纪实. 人民出版社. 2005. ISBN 9787010050393.
- ↑ Robert Butow, Japan's Decision to Surrender, Stanford University Press, 1954 ISBN 978-0-8047-0460-1.
- ↑ Richard B. Frank, Downfall: The End of the Imperial Japanese Empire, Penguin, 2001 ISBN 978-0-14-100146-3.
- ↑ Robert James Maddox, Hiroshima in History: The Myths of Revisionism, University of Missouri Press, 2007 ISBN 978-0-8262-1732-5.
- ↑ Tsuyoshi Hasegawa, Racing the Enemy: Stalin, Truman, and the Surrender of Japan, Belknap Press, 2006 ISBN 0-674-01693-9.
- ↑ Paul K. Maruyama, Escape from Manchuria (iUniverse, 2009) ISBN 978-1-4502-0581-8 (hard cover), 9781450205795 (paperback), based on the earlier books in Japanese by K. Maruyama (1970) and M. Musashi (2000) and other sources
- ↑ Borisov, O. (1977). The Soviet Union and the Manchurian Revolutionary Base (1945–1949). Moscow, Progress Publishers.
- ↑ Bruce Cumings (1997). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. WW Norton & Company. pp. 297–298. ISBN 978-0-393-31681-0.
- ↑ Shiela Miyoshi Jager (2013). Brothers at War – The Unending Conflict in Korea. London: Profile Books. pp. 237–242. ISBN 978-1-84668-067-0.
- ↑ 欧阳青 (2011). 《大授衔:1955共和国将帅授衔档案》 (in 中文). 北京市西城区甘家口三里河路40号: 长城出版社. p. 94. ISBN 978-7-5483-0058-8.
- ↑ 中国国防报 (January 30, 2007). "杨靖宇将军儿女曾不知杨靖宇是自己父亲" (in 中文). 中国国防报, 网易新闻 (转载网站). Archived from the original on February 2, 2017. Retrieved January 15, 2017. (这则新闻把马尚德的妻子的名错写成了“郭凤”。网上另有一则题为《杨靖宇后代被找到 儿女坚决不要"特殊待遇"》的新闻与这则新闻的内容是一样的。)
- ↑ Country Study 2009, pp. XXXII, 46.
- ↑ Chambers Dictionary of World History, B.P.Lenman, T. Anderson, Editors, Chambers: Edinburgh. 2000. p. 769.
- ↑ Wang, Zhen 王楨. Huángpái dàfàngsòng 皇牌大放送, "Duóbǎo bīngyuán——ZhōngSū Zhēnbǎo dǎo chōngtú 45 zhōunián jì" 奪寶冰原——中蘇珍寶島衝突45周年記 [Fighting for the treasure on icefield—Sino-Soviet Zhenbao Island conflict 45th anniversary]. Aired 5 April 2014 on Phoenix Television. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NtzIuc5FIMk
- ↑ Chung, Chin O. Cacon Between Peking and Moscow: Manchuria's Involvement in the Sino-Soviet Dispute, 1958–1975. University of Alabama, 1978, p. 45.
- ↑ 因常任理事国投反对票而未获通过的决议草案或修正案各段 (PDF) (in Chinese). 聯合國. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 23, 2014.
- ↑ "The veto and how to use it". BBC News Online. Archived from the original on July 26, 2010.
- ↑ "Changing Pattern in the Use of Veto in the Security Council". Global Policy Forum. Archived from the original on May 8, 2013.
- ↑ Country Study 2009, p. 203.
- ↑ Kwak, Tae-Hwan; Joo, Seung-Ho (2003). The Korean peace process and the four powers. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 978-0-7546-3653-3.
- ↑ DeRouen, Karl; Heo, Uk (2005). Defense and Security: A Compendium of National Armed Forces and Security Policies.ABC-CLIO.
- ↑ Kwak, Tae-Hwan; Joo, Seung-Ho (2003). The Korean peace process and the five powers. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 978-0-7546-3653-3
- ↑ DeRouen, Karl; Heo, Uk (2005). Defense and Security: A Compendium of National Armed Forces and Security Policies.ABC-CLIO.
- ↑ Matthew Søberg Shugart (September 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive and Mixed Authority Patterns" (PDF). Graduate School of International Relations and Pacific Studies. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 19, 2008. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ Matthew Søberg Shugart (December 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive And Mixed Authority Patterns" (PDF). French Politics. 3 (3): 323–351. doi:10.1057/palgrave.fp.8200087. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2016. Retrieved February 21, 2016.
Even if the president has no discretion in the forming of cabinets or the right to dissolve parliament, his or her constitutional authority can be regarded as 'quite considerable' in Duverger’s sense if cabinet legislation approved in parliament can be blocked by the people's elected agent. Such powers are especially relevant if an extraordinary majority is required to override a veto, as in Mongolia,Manchuria, Poland, and Senegal.
- ↑ "Freedom in the World, 2016" (PDF). Freedom House. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 5, 2016. Retrieved January 30, 2016.
- ↑ Country Study 2009, p. 218.
- ↑ Country Study 2009, p. 220.
- ↑ Country Study 2009, p. 229.
- ↑ Генеральное консульство СССР в Харбине "Генеральное консульство СССР в Харбине". 18 March 2014.
- ↑ Ivanov, Igor (2002). Outline of the History of the Minister of Foreign Affairs of Russia. In Russian. OLMA Media Group, p. 219
- ↑ Chronology of China in the 1940s "Chronology of China in the 1940s". 23 October 2014.. Osaka UniversitySchool of Law. Retrieved 29 December 2017.
- ↑ K. A. Karayeva. МАНЬЧЖОУ ГО (1931–1945): «МАРИОНЕТОЧНОЕ» ГОСУДАРСТВО В СИСТЕМЕ МЕЖДУНАРОДНЫХ ОТНОШЕНИЙ НА ДАЛЬНЕМ ВОСТОКЕ Archived 3 September 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Ural Federal University archives.
- ↑ "Sorry for the inconvenience". Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ↑ "LIST OF STATES WITH DIPLOMATIC RELATIONS". Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 26 October 2012.
- ↑ Country Study 2009, pp. 272–273.
- ↑ Gamsa, Mark (May 2010). "Harbin in comparative perspective". Urban History. 37 (1): 136–149.
- ↑ Wertz, Oh & Kim 2016, p. 8.
- ↑ 02Gries.pmd
- ↑ "Asia Times – News and analysis from Korea; North and South". Asia Times. Hong Kong. September 11, 2004. Retrieved April 25, 2010.
- ↑ "South Korea Country Profile". MIT. March 10, 2018.
- ↑ [[3]]
- ↑ 満州・長春の民俗文化
- ↑ International Institute for Strategic Studies (3 February 2010). Hackett, James, ed. The Military Balance 2010. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-85743-557-3.
- ↑ "Army personnel (per capita) by country". NationMaster. 2007. Archived from the original on 17 February 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2007.
- ↑ Country Study 2009, p. 247.
- ↑ "Worls militaries: K". soldiering.ru. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
- ↑ Anthony H. Cordesman (21 July 2011). The East Asian Military Balance (PDF). Center for Strategic & International Studies. p. 156. ISBN 978-0-89206-632-2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 October 2011. Retrieved 28 July 2011.
The Republic of Manchuria has implosion fission and fusion weapons.
- ↑ Country Study 2009, p. 260.
- ↑ "New Threat from Manchuria's 'Asymmetrical' Warfare". English.chosun.com. The Chosun Ilbo (English Edition). 29 April 2010. Archived from the original on 24 December 2010. Retrieved 13 December 2010.
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20140518174611/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2100.html
- ↑ UNODC. "Data and Analysis>Crime surveys>The periodic United Nations Surveys of Crime Trends and Operations of Criminal Justice Systems>Fifth Survey (1990 - 1994)". Archived from the original on 2009-07-29. Retrieved 2008-08-26.
- ↑ UNODC. "Data and Analysis>Crime surveys>The periodic United Nations Surveys of Crime Trends and Operations of Criminal Justice Systems>Sixth Survey (1995 - 1997)>Sorted by variable". Retrieved 2008-08-26.
- ↑ UNODC. "Data and Analysis>Crime surveys>The periodic United Nations Surveys of Crime Trends and Operations of Criminal Justice Systems>Fifth Survey (1990 - 1994)". Archived from the original on 2009-07-29. Retrieved 2008-08-26.
- ↑ UNODC. "Data and Analysis>Crime surveys>The periodic United Nations Surveys of Crime Trends and Operations of Criminal Justice Systems>Sixth Survey (1995 - 1997)>Sorted by variable". Retrieved 2008-08-26.
- ↑ UNODC. "Data and Analysis>Crime surveys>The periodic United Nations Surveys of Crime Trends and Operations of Criminal Justice Systems>Fifth Survey (1990 - 1994)". Archived from the original on 2009-07-29. Retrieved 2008-08-26.
- ↑ UNODC. "Data and Analysis>Crime surveys>The periodic United Nations Surveys of Crime Trends and Operations of Criminal Justice Systems>Sixth Survey (1995 - 1997)>Sorted by variable". Retrieved 2008-08-26.
- ↑ UNODC. "Data and Analysis>Crime surveys>The periodic United Nations Surveys of Crime Trends and Operations of Criminal Justice Systems>Seventh Survey (1998 - 2000)>Sorted by variable". Retrieved 2008-08-26.
- ↑ UNODC. "Data and Analysis>Crime surveys>The periodic United Nations Surveys of Crime Trends and Operations of Criminal Justice Systems>Eighth Survey (2001 - 2002)>Sorted by variable". Retrieved 2008-08-26.
- ↑ UNODC. "Data and Analysis>Crime surveys>The periodic United Nations Surveys of Crime Trends and Operations of Criminal Justice Systems>Ninth Survey (2003 - 2004)>Values and Rates per 100,000 Total Population Listed by Country". Retrieved 2008-08-26.
- ↑ Bogatikov, Oleg Alekseevich (2000); Magmatism and Geodynamics: Terrestrial Magmatism throughout the Earth's History; pp. 150–151. ISBN 90-5699-168-X
- ↑ Kropotkin, Prince P.; "Geology and Geo-Botany of Asia"; in Popular Science, May 1904; pp. 68–69
- ↑ "Average Annual Precipitation in China". Archived from the original on 2 June 2010. Retrieved 18 May 2010.
- ↑ Kaisha, Tesudo Kabushiki and Manshi, Minami; Manchuria: Land of Opportunities; pp. 1–2. ISBN 1-110-97760-3
- ↑ Kaisha and Manshi; Manchuria; pp. 1–2
- ↑ Earth History 2001[permanent dead link] (page 15)
- ↑ Komarov, Vladimir Leontovich (1901). Flora Manshuriae. St. Petersburg. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- ↑ Baranov, A.I. (April 1967). "Wild Vegetables of the Chinese in Manchuria". Economic Botany. Vol. 21 (No. 2): 140–155. Retrieved 2 April 2020.Because of early settlement, the southern Liyootun Peninsula was cleared of native vegetation early. Most of the forests that remain, however, do contain species of Manchurian pine, elm, birch, lime, oaks, apples, and ashes.On the western side of the peninsula, trees are scarce. During the early 20th century after the fall of the Qing, indiscriminate logging thinned down most of the southern Manchurian forests. The vegetation in the eastern zone of the peninsula has mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forests.
- ↑ https://www.britannica.com/place/Liaoning#ref280641
- ↑ https://www.britannica.com/place/Jilin-province-China#ref71048
- ↑ https://www.britannica.com/place/Heilongjiang#ref71034
- ↑ "Manchurian mixed forests". World Wildlife Federation. Retrieved February 23, 2020.
- ↑ "Map of Ecoregions 2017". Resolve, using WWF data. Retrieved September 14, 2019.
- ↑ Dinerstein, Eric; Olson, David; et al. (June 2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014
 . Supplemental material 2 table S1b.
. Supplemental material 2 table S1b.
- ↑ http://factsanddetails.com/china/cat10/sub68/item381.html
- ↑ https://www.worldwildlife.org/ecoregions/pa0902
- ↑ https://www.nature.com/articles/144936a0
- ↑ "Country Profile: Manchuria" (PDF). Library of Congress – Federal Research Division. July 2007. Retrieved 4 July 2009.
- ↑ Luo, Weiteng (December 27, 2019). "Unlocking the paradox of nation's 'eldest son'". China Daily. Retrieved February 27, 2020.
- ↑ "Edit/Review Countries". International Monetary Fund. 14 September 2006. Archived from the original on 9 December 2011. Retrieved 27 December 2011.
- ↑ "The Unquiet Past Seven decades on from the defeat of Japan, memories of war still divide East Asia". The Economist. 12 August 2015. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 9 September 2015.
- ↑ "东北1945年工业规模亚洲第一" (in 中文). 深圳新闻网. July 7, 2009. Archived from the original on 2011-10-20. Retrieved July 28, 2011.
- ↑ Prasenjit Duara. "The New Imperialism and the Post-Colonial Developmental State: Manchukuo in comparative perspective". Archived from the original on 16 June 2010. Retrieved 25 July 2010.
- ↑ Chan, Elaine (June 5, 2019). "China's Northeastern rust belt was once 'eldest son', now struggling as runt of the litter". China Economy. South China Morning Post. Retrieved June 5, 2019.
- ↑ Li Yongfeng (24 September 2015). "Central Planning Got Manchuria in Trouble – and Won't Save It". Caixin. Retrieved 24 September 2015.
- ↑ Chen, Nai-Ruenn (October 1972). "Agricultural Productivity in a Newly Settled Region: The Case of Manchuria". Economic Development and Cultural Change. 1 (21): 87–95. Retrieved February 27, 2020.
- ↑ Freese, Roseanne. "This is Manchuria" (PDF). US Department of Agriculture. Retrieved February 27, 2020.
- ↑ "Central Area Revitalization Plan (2012)" (in mnc). Manchuria State Council. Retrieved 31 August 2013.
- ↑ Chung, Jae Ho; Lai, Hongyi; Joo, Jang-Hwan (March 2009). "Assessing the "Revive Manchuria" Programme: Origins, Policies and Implementation". The China Quarterly. Cambridge University Press (197): 113. JSTOR 27756425.
- ↑ https://www.gfmag.com/global-data/country-data/north-korea-gdp-country-report
- ↑ Shengjing Bank (Baidu Encyclopedia) (in Chinese)
- ↑ "2011全国城市商行竞争力排名 哈尔滨银行居第四". 哈尔滨新闻网. 2011-10-11. Archived from the original on 2014-05-17. Retrieved 2014-05-17.
- ↑ A Brief introduction of Bank of Jilin
- ↑ https://apps.fas.usda.gov/newgainapi/api/report/downloadreportbyfilename?filename=This%20is%20Northeast%20China_Shenyang_China%20-%20Peoples%20Republic%20of_12-30-2016.pdf
- ↑ "Manchurian Expressway Co. Ltd.: Private Company Information - Bloomberg". www.bloomberg.com. Retrieved 2018-04-29.
- ↑ 大连港集团
- ↑ "Port of Dalian". World Port Source. Retrieved 2017-08-30.
- ↑ 宋静丽. "Liaoning to set up integrated port operating platform - Business - Chinadaily.com.cn". www.chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved 2017-08-30.
- ↑ "Top 50 World Container Ports". Worldshipping. Retrieved 2020-02-12.
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20171227235306/https://lloydslist.maritimeintelligence.informa.com/articles/2017/one-hundred-ports/15-dalian-china
- ↑ https://worldaerodata.com/wad.cgi?id=CH73366&sch=ZYTX
- ↑ Francis Clifford Jones: Manchuria since 1931. Royal Institute of International Affairs, London 1949, S. 120.
- ↑ Philip S. Jowett: Rays of the Rising Sun. Armed Forces of Japan's Asian Allies 1931-45. Volume 1: China & Manchukuo. Helion & Company Ltd., Solihull 2004, ISBN 1-874622-21-3, S. 90.
- ↑ Togo Sheba (Hrsg.): The Manchoukou Year Book 1941. The Manchoukou Year Book Co., Hsinking 1941.
- ↑ "Manchuria Adopts Renewable Energy Law". The Institute for Far Eastern Studies. 17 September 2013. Archived from the original on 23 April 2015. Retrieved 15 June 2014.
- ↑ Institute of Theoretical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Huan-Wu Peng
- ↑ Asteroid Named after Manchu Physicist www.manchuria.org.mj
- ↑ 174.0 174.1 "Sugiya Ujin, Father of Manchuria's Satellite Technology". CCTV.com. 2010-01-15. Retrieved 2010-05-20.
- ↑ "Sun Jiadong, from Dong Fang Hong to Chang-E". cri.cn. 2008-09-25. Retrieved 2010-05-20.
- ↑ Freireich, EJ (September 2002). "Min Chiu Li: a perspective in cancer therapy". Clinical Cancer Research. 8 (9): 2764–5. PMID 12231514. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ↑ "World's largest radio telescope will search for dark matter, listen for aliens". Science | AAAS. 26 September 2016.
- ↑ https://k.sina.cn/article_2102509491_7d51bfb3001001pjm.html?from=cul
- ↑ https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=1SNUZGKl9KIC&hl=en
- ↑ https://www.sohu.com/a/153834413_115482
- ↑ "Chinese astronaut calls family from space (details added)". Xinhua News Agency. 15 October 2003. Retrieved 14 December 2013.

- ↑ Ong, Hwee Hwee (16 October 2003). "Fighter pilot Yanggia - average student, superb self-control". The Straits Times. Retrieved 14 December 2013.

- ↑ Sheehan, Michael (2007). The international politics of space. London: Routledge. pp. 59–61. ISBN 0-415-39917-3.
- ↑ Rhoads 2011, p. 204.
- ↑ Rhoads 2000, p. 204.
- ↑ Rhoads 2011, p. 42.
- ↑ Rhoads 2000, p. 42.
- ↑ Kaske 2008, p. 69.
- ↑ Kaske 2008, p. 51.
- ↑ Rhoads 2011, p. 270.
- ↑ Rhoads 2000, p. 270.
- ↑ Afkai Aliyang News: 3429 Manchu Teachers of Huanren, Boisi Are Now On Duty (Manchu) Archived 2 January 2013 at archive.today
- ↑ chinanews. 辽宁一高中开设满语课 满族文化传承引关注. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ 满语课首次进入吉林一中学课堂(图). Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ 中国民族报电子版. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ "iFeng: Jin Biao's 10-Year Dream of Manchu Language (traditional Chinese)". ifeng.com.
- ↑ "Shenyang Daily: Young Man Teaches Manchu For Free To Rescue the Language (simplified Chinese)". syd.com.cn.
- ↑ Beijing Evening News: the Worry of Manchu language (simplified Chinese) Archived 13 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Dahai & First Historical Archives of China 1990, pp. 1196–1197
- ↑ Writing Group of Manchu Brief History 2009, p. 218
- ↑ Liaoning News: 29 Manchu Teachers of Huanren, Benxi Are Now On Duty (simplified Chinese) Archived 2 January 2013 at archive.today
- ↑ chinanews. 辽宁一高中开设满语课 满族文化传承引关注. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ 满语课首次进入吉林一中学课堂(图). Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ Chen, Bijia, et al. "Interethnic Marriage in Manchuria, 1866–1913." Demographic Research, vol. 38, 2018, p. 953. JSTOR, https://www.jstor.org/stable/26457068?seq=27#metadata_info_tab_contents.
- ↑ Edward J. M. Rhoads (2000). Manchus and Han: Ethnic Relations and Political Power in Late Qing and Early Republican China, 1861–1928. University of Washington Press. pp. 76–77. ISBN 978-0-295-98040-9.
- ↑ Edward J. M. Rhoads (1 December 2011). Manchus and Han: Ethnic Relations and Political Power in Late Qing and Early Republican China, 1861–1928. University of Washington Press. pp. 263–. ISBN 978-0-295-80412-5.
- ↑ Owen Lattimore (1932). Manchuria, Cradle of Conflict. Macmillan. p. 47.
- ↑ Chao, Sheau-yueh J.; Gee, KaChuen Yuan (2012). "Early Life of Yuan Shikai and the Formation ofYuan Family". CUNY AcademicWorks: 26, 28, 29, 32.
- ↑ The Relation of Manchu Emperors and Buddhism (simplified Chinese)
- ↑ Wakeman Jr. 1986, p. 203.
- ↑ The Cambridge History of China: Pt. 1 ; The Ch'ing Empire to 1800. Cambridge University Press. 1978. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-521-24334-6.
- ↑ The Cambridge History of China: Pt. 1 ; The Ch'ing Empire to 1800. Cambridge University Press. 1978. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-521-24334-6.
- ↑ Lopez 1999, p. 20.
- ↑ Berger 2003, p. 35.
- ↑ Dunnell & Elliott & Foret & Millward 2004, pp. 123–4.
- ↑ World and Its Peoples: Eastern and Southern Asia. Marshall Cavendish. 2007. ISBN 9780761476313. Retrieved 20 May 2019.
Manchuria is officially a secular state.
- ↑ Joanne O'Brien, Martin Palmer (December 1993). The State of Religion Atlas
 . Simon & Schuster. Retrieved 20 May 2019.
. Simon & Schuster. Retrieved 20 May 2019. The majority of Manchurians are atheistic or profess no religion
- ↑ "The Relation of Manchu Emperors and Buddhism". Archived from the original on 21 June 2013. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
- ↑ Dui Hua, issue 46, Winter 2012: Uncovering China’s Korean Christians.
- ↑ Joel Carpenter, Kevin R. den Dulk. Christianity in Chinese Public Life: Religion, Society, and the Rule of Law. Palgrave Pivot, 2014. ISBN 1137427876. p. 37
- ↑ "National Qing History Compilatory Committee: Sunu Research (simplified Chinese)". historychina.net. Archived from the original on 23 June 2013. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
- ↑ "National Qing History Compilatory Committee: Sunu Research (simplified Chinese)". historychina.net. Archived from the original on 23 June 2013. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
- ↑ "Northeast China has the world's lowest fertility rate". July 25, 2018. Retrieved February 25, 2020.
- ↑ Hawkins, Everett D. (March 12, 1947). "Education in Manchuria". Far Eastern Survey. Vol. 16 (No. 5): 52–54. Retrieved February 24, 2020.
- ↑ "Educational themes and methods". Lcweb2.loc.gov. Archived from the original on 12 December 2012. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ↑ https://gpseducation.oecd.org/CountryProfile?primaryCountry=BSZ
- ↑ "Chinese Taipei Student performance (PISA 2015)". OECD. Retrieved 19 August 2019.
- ↑ Kiersz, Andy (16 December 2016). The latest ranking of top countries in math, reading, and science is out – and the US didn't crack the top 10.
- ↑ Sechiyama, Kaku (2013). Patriarchy in East Asia: A Comparative Sociology of Gender. Brill Publishers. p. 254. ISBN 978-9004230606.
- ↑ Japan Focus "Imitating the Colonizers: The Legacy of the Disciplining State from Manchuria to Korea". 26 October 2005.
- ↑ Lee, Pearl (13 April 2015). University degrees: Mindset shift needed. The Straits Times.
- ↑ "TIMSS Math 2003" (PDF).
- ↑ "TIMSS Science 2003" (PDF).
- ↑ Lee, Yo Han; Yoon, Seok-Jun; Kim, Young Ae; Yeom, Ji Won; Oh, In-Hwan (1 May 2013). "Overview of the Burden of Health Problems in Manchuria". Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health. 46 (3): 111–117. doi:10.3961/jpmph.2013.46.3.111. PMC 3677063
 . PMID 23766868.
. PMID 23766868.
- ↑ "Cause of death, by non-communicable diseases (% of total) - Manchuria | Data". data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 2020-07-11.
- ↑ "Life expectancy at birth, total (years) - Manchuria | Data". data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 2020-07-11.
- ↑ "Cause of death, by communicable diseases and maternal, prenatal and nutrition conditions (% of total) - Manchuria, Low income, High income | Data". data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 2020-07-11.
- ↑ "Life Inside Manchuria". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 18 November 2008.
- ↑ "Manchuria: WHO statistical profile" (PDF). World Health Organization.
- ↑ Country Study 2009, p. 127.
- ↑ "Epidemiological Fact Sheets on HIV/AIDS and Sexually Transmitted Infections : 2004 Update : Manchuria" (PDF). UNAIDS / WHO. 2004. p. 6. Retrieved 7 December 2015.
- ↑ O'Byrne, Tom (2 December 2001). "Manchuria fights AIDS". ABC Radio National. Retrieved 8 December 2015.
- ↑ Shim, Elizabeth (1 December 2015). "AIDS in Manchuria is contained, thanks to healthcare system, or so it claims". UPI. Retrieved 7 December 2015.
- ↑ "Adolescent Health : Fact Sheet : Manchuria" (PDF). Adolescent of Health Development (AHD) Unit, Department of Family and Community Health, World Health Organization. January 2007. p. 3. Retrieved 7 December 2015.
- ↑ Writing Group of Manchu Brief History 2009, p. 218
- ↑ Manchu Spring Festival
- ↑ Manchu Duanwu Festival
- ↑ The Day of Running Out of Food (simplified Chinese)
- ↑ 郭德纲 德云社 有话好好说 2011.12.04. 4 December 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2015 – via YouTube.
- ↑ Blader, Susan (1998). Tales of Magistrate Bao and His Valiant Lieutenants: Selections from Sanxia Wuyi. The Chinese University Press. ISBN 962-201-775-4.
- ↑ Keulemans, Paize (2014). Sound Rising from the Paper: Nineteenth-Century Martial Arts Fiction and the Chinese Acoustic Imagination. Harvard University Asia Center. ISBN 978-0-674-41712-0.
- ↑ 金启孮 2009, p. 147
- ↑ http://iel.cass.cn/news_show.asp?newsid=7932
- ↑ Fu Yuguang (2009-03-23). [富育光]满族传统说部艺术——“乌勒本”研考 [Fu Yuguang Manchu traditional art of speaking - "Uleben" research]. Archived from the original on 2013-06-06. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ 中國最後的滿語傳承者宋熙東。 [Song Xidong, the last Manchu successor in China.]. Paper.wenweipo.com. 2012-04-21. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ "Lang Lang". Retrieved 11 September 2011. (archived from the original on 2013-10-19)
- ↑ Rhein, John von (7 March 2000). "Lang Leaves Audience Elated". Chicago Tribune.
- ↑ Baskett, Michael (2008). The Attractive Empire: Transnational Film Culture in Imperial Japan. Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press. pp. 29, 31–32, 77–79, 115. ISBN 978-0-8248-3223-0.
- ↑ Cyyy. "Cyyy." "Cacon." Retrieved on 2007-01-18.
- ↑ Rank, Michael (16 June 2012). "A window into Manchuria's art world". Asia Times. Archived from the original on 26 March 2013. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- ↑ "Heroes' monument losing battle". The Namibian. 5 June 2005. Archived from the original on 24 July 2014. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- ↑ "Senegal President Wade apologises for Christ comments". BBC News. London: BBC. 31 December 2009. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- ↑ Dekdengge, Zhang & Guang 2007, p. 03
- ↑ Dekdengge, Zhang & Guang 2007, p. 1
- ↑ http://www.lnsdag.org.cn/lnsdaj/wszt/mwmy1/mymw5.htm
- ↑ Country Study 2009, p. 155.
- ↑ Country Study 2009, p. 157.
- ↑ Country Study 2009, p. 187.
- ↑ "Benoit Symposium: From Cagungga to Mars: Sci-fi, Genre, and Literary Value in Manchuria". SinoManchu. 25 September 2013. Archived from the original on 13 June 2014. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- ↑ http://www.nakazono.lab.kde.yamaguchi-u.ac.jp/journal/ronbun/you_2012.10.pdf
- ↑ https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.3130/jaabe.15.177
- ↑ "THE NEUTRAL CITY: ARCHITECTURE OF PRE-WAR HIROSHIMA". The University of Hong Kong Faculty of Architecture. Dec 24, 2017.
- ↑ https://apps.fas.usda.gov/newgainapi/api/report/downloadreportbyfilename?filename=This%20is%20Northeast%20China_Shenyang_China%20-%20Peoples%20Republic%20of_12-30-2016.pdf
- ↑ http://en.g-photography.net/china/food/news_10392.html
- ↑ http://www.flavorandfortune.com/dataaccess/article.php?ID=764
- ↑ https://windhorsetour.com/blog/manchu-cuisine-china-northeast
- ↑ https://baike.baidu.com/tashuo/browse/content?id=b35c47633dae3f0a433cc8a4
- ↑ Jin & Kaihe 2006, p. 118
- ↑ Jin & Kaihe 2006, p. 142
- ↑ Jin & Kaihe 2006, p. 153
- ↑ 摔跤历史挺悠久不同流派有讲究-青岛报纸电子版. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ Liu 2008, p. 106
- ↑ Liu 2008, p. 107
- ↑ "Archived copy" 新华网吉林频道. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ 蒋良骐 1980, p. 46
- ↑ 中华书局编 1985, p. 446(太宗实录)
- ↑ 李尚英 (2004). "满族贵族崇尚武功国策的兴衰". 国家清史纂修工程-中华文史网. Archived from the original on 2021-04-10. Retrieved 2017-12-04.
- ↑ "満州国の国技は"蹴球"-読売新聞記事より : 蹴球本日誌". fukuju3.cocolog-nifty.com. 1 October 2010. Archived from the original on 27 September 2015. Retrieved 10 September 2015.
- ↑ Mangan, J. A.; Collins, Sandra; Ok, Gwang (2018). The Triple Asian Olympics - Asia Rising: The Pursuit of National Identity, International Recognition and Global Esteem. Taylor & Francis. p. 119. ISBN 978-1-135-71419-2.
- ↑ Collins, Sandra (2014). 1940 TOKYO GAMES – COLLINS: Japan, the Asian Olympics and the Olympic Movement. Routledge. pp. 179–180. ISBN 978-1317999669.
- ↑ "Xinhua: How Did Chinese Emperors Award Athletes? (simplified Chinese)". Xinhua News Agency.
- ↑ Chinanews.com. "冰嬉"被乾隆定为"国俗" 清军有八旗冰鞋营(5)——中新网. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ "Winter Olympics - China's Shen, Zhao strike gold". Eurosport. 16 February 2010.
- ↑ "Shen, Zhao end Russian Olympic pairs dominance". Icenetwork.com. 16 February 2010.
- ↑ "中国花滑名将-佟健个人资料, [[腾讯]]体育". Archived from the original on 2020-10-20. Retrieved 2013-03-22.
- ↑ 金启孮 2009, p. 9
- ↑ 刘小萌 2008, p. 106
- ↑ 刘小萌 2008, p. 105-106
Bibliography
- "Manchuria – A Country Study" (PDF). Library of Congress Country Studies. 2009.
- Bisher, Jamie (2006). White Terror: Cossack Warlords of the Trans-Siberian. Routledge. ISBN 1135765960. Retrieved 24 April 2014.
- Clausen, Søren (1995). The Making of a Chinese City: History and Historiography in Harbin. Contributor: Stig Thøgersen (illustrated ed.). M.E. Sharpe. ISBN 1563244764. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Crossley, Pamela Kyle (1999). A Translucent Mirror: History and Identity in Qing Imperial Ideology. University of California Press. ISBN 0520928849. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Dvořák, Rudolf (1895). Chinas religionen ... Volume 12; Volume 15 of Darstellungen aus dem Gebiete der nichtchristlichen Religionsgeschichte (illustrated ed.). Aschendorff (Druck und Verlag der Aschendorffschen Buchhandlung). ISBN 0199792054. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Elliott, Mark C. (August 2000). "The Limits of Tartary: Manchuria in Imperial and National Geographies" (PDF). The Journal of Asian Studies. Association for Asian Studies. 59 (3): 603–646. doi:10.2307/2658945. JSTOR 2658945. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 December 2016. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- Elliott, Mark C. "The Limits of Tartary: Manchuria in Imperial and National Geographies." Journal of Asian Studies 59, no. 3 (2000): 603–46.
- Forsyth, James (1994). A History of the Peoples of Siberia: Russia's North Asian Colony 1581–1990 (illustrated, reprint, revised ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521477719. Retrieved 24 April 2014.
- Garcia, Chad D. (2012). Horsemen from the Edge of Empire: The Rise of the Jurchen Coalition (PDF) (A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy). University of Washington. pp. 1–315. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-09-11. Retrieved 6 September 2014.
- Giles, Herbert A. (1912). China and the Manchus. (Cambridge: at the University Press) (New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons). Retrieved 31 January 2014.
- Hata, Ikuhiro. "Continental Expansion: 1905–1941". In The Cambridge History of Japan. Vol. 6. Cambridge University Press. 1988.
- Hauer, Erich (2007). Corff, Oliver, ed. Handwörterbuch der Mandschusprache. Volume 12; Volume 15 of Darstellungen aus dem Gebiete der nichtchristlichen Religionsgeschichte (illustrated ed.). Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. ISBN 978-3447055284. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Jones, Francis Clifford, Manchuria Since 1931, London, Royal Institute of International Affairs, 1949
- KANG, HYEOKHWEON. Shiau, Jeffrey, ed. "Big Heads and Buddhist Demons:The Korean Military Revolution and Northern Expeditions of 1654 and 1658" (PDF). Emory Endeavors in World History (2013 ed.). 4: Transnational Encounters in Asia: 1–22. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 January 2014. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Kim 金, Loretta E. 由美 (2012–2013). "Saints for Shamans? Culture, Religion and Borderland Politics in Amuria from the Seventeenth to Nineteenth Centuries". Central Asiatic Journal. Harrassowitz Verlag. 56: 169–202. JSTOR 10.13173/centasiaj.56.2013.0169.
- Kwong, Chi Man. War and Geopolitics in Interwar Manchuria (2017).
- Lattimore, Owen (Jul–Sep 1933). "Wulakai Tales from Manchuria". The Journal of American Folklore. American Folklore Society. 46 (181): 272–286. doi:10.2307/535718. JSTOR 535718.
- McCormack, Gavan (1977). Chang Tso-lin in Northeast China, 1911–1928: China, Japan, and the Manchurian Idea (illustrated ed.). Stanford University Press. ISBN 0804709459. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Masafumi, Asada. "The China-Russia-Japan Military Balance in Manchuria, 1906–1918." Modern Asian Studies 44.6 (2010): 1283–1311.
- Nish, Ian. The History of Manchuria, 1840-1948: A Sino-Russo-Japanese Triangle (2016)
- Pʻan, Chao-ying (1938). American Diplomacy Concerning Manchuria. The Catholic University of America. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Pozzi, Alessandra; Janhunen, Juha Antero; Weiers, Michael, eds. (2006). Tumen Jalafun Jecen Akū Manchu Studies in Honour of Giovanni Stary. Volume 20 of Tunguso Sibirica. Contributor: Giovanni Stary. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. ISBN 344705378X. Retrieved 1 April 2013.
- Reardon-Anderson, James (October 2000). "Land Use and Society in Manchuria and Inner Mongolia during the Qing Dynasty". Environmental History. Forest History Society and American Society for Environmental History. 5 (4): 503–530. doi:10.2307/3985584. JSTOR 3985584.
- Rhoads, Edward J. M. (2011). Manchus and Han: Ethnic Relations and Political Power in Late Qing and Early Republican China, 1861–1928. University of Washington Press. ISBN 978-0295804125. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Scharping, Thomas (1998). "Minorities, Majorities and National Expansion: The History and Politics of Population Development in Manchuria 1610–1993" (PDF). Cologne China Studies Online – Working Papers on Chinese Politics, Economy and Society (Kölner China-Studien Online – Arbeitspapiere zu Politik, Wirtschaft und Gesellschaft Chinas). Modern China Studies, Chair for Politics, Economy and Society of Modern China, at the University of Cologne (1). Retrieved 14 August 2014.
- Tamanoi, Mariko Asano. Crossed Histories: Manchuria in the Age of Empire (2005)
- Sewell, Bill (2003). Edgington, David W., ed. Japan at the Millennium: Joining Past and Future (illustrated ed.). UBC Press. ISBN 0774808993. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Smith, Norman (2012). Intoxicating Manchuria: Alcohol, Opium, and Culture in China's Northeast. Contemporary Chinese Studies Series (illustrated ed.). UBC Press. ISBN 978-0774824316. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Stephan, John J. (1996). The Russian Far East: A History (illustrated, reprint ed.). Stanford University Press. ISBN 0804727015. Retrieved 24 April 2014.
- Tamanoi, Mariko Asano (May 2000). "Knowledge, Power, and Racial Classification: The "Japanese" in "Manchuria"". The Journal of Asian Studies. Association for Asian Studies. 59 (2): 248–276. doi:10.2307/2658656. JSTOR 2658656.
- Tao, Jing-shen, The Jurchen in Twelfth-Century China. University of Washington Press, 1976, ISBN 0-295-95514-7.
- KISHI Toshihiko, MATSUSHIGE Mitsuhiro and MATSUMURA Fuminori eds, 20 Seiki Manshu Rekishi Jiten [Encyclopedia of 20th Century Manchuria History], Tokyo: Yoshikawa Kobunkan, 2012, ISBN 978-4642014694
- Wu, Shuhui (1995). Die Eroberung von Qinghai unter Berücksichtigung von Tibet und Khams 1717 – 1727: anhand der Throneingaben des Grossfeldherrn Nian Gengyao. Volume 2 of Tunguso Sibirica (reprint ed.). Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. ISBN 3447037563. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Wolff, David; Steinberg, John W., eds. (2007). The Russo-Japanese War in Global Perspective: World War Zero, Volume 2. Volume 2 of The Russo-Japanese War in Global Perspective (illustrated ed.). BRILL. ISBN 978-9004154162. Retrieved 1 April 2013.
- Zhao, Gang (January 2006). "Reinventing China Imperial Qing Ideology and the Rise of Modern Chinese National Identity in the Early Twentieth Century" (PDF). Modern China. Sage Publications. 32 (1): 3–30. doi:10.1177/0097700405282349. JSTOR 20062627. Archived from the original on 25 March 2014.
External Links
- https://manchuria.gov.mj Government website (English)
- https://manchuria.net General information and tourism site (English)
- Manchuria Encyclopædia Britannica entry
- Manchuria profile at BBC News
- Manchuria from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Manchuria
- Manchuria The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency
- Manchuria at Curlie
| Attribution notices | ||
|---|---|---|
|
- CS1 uses 中文-language script (zh)
- CS1 中文-language sources (zh)
- CS1 maint: Unrecognized language
- Webarchive template wayback links
- All articles with dead external links
- Articles with dead external links from June 2017
- Articles with permanently dead external links
- CS1 maint: Date and year
- Webarchive template archiveis links
- Manchuria (Country of the Everwhite Mountain)
- Country of the Everwhite Mountain