Clackamas: Difference between revisions
Mythopoeia (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Mythopoeia (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
| extinct_date = | | extinct_date = | ||
| founder = | | founder = | ||
| named_for = [[Clackamas District]] <br> [[Clackamas people]] | | named_for = [[Provisional Government of Oregon#Clackamas District|Clackamas District]] <br> [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Clackamas|Clackamas people]] | ||
| capital = [[Salem, Clackamas|Salem]] | | capital = [[Salem, Clackamas|Salem]] | ||
| largest_settlement = [[Portland]] | | largest_settlement = [[Portland]] | ||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
| embed = | | embed = | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Clackamas''' is a [[States of Astoria|state]] located in the [[Central Coast Astoria|Central Coast]] region of [[Astoria]]. It shares borders with [[Yakima]] to north, the [[Federal District of Astoria|Federal District]] to north and [[South Columbia]] to the east, [[Willamette]] to the south, and the [[Pacific Ocean]] to the west. Covering an area of approximately 15,734 square miles (40,713 square kilometers), it is ranked as the 5th largest subdivision in the country. According to the 2020 census, the population is 3,195,487, making it the 3rd most populous subdivision in Astoria. The population density stands at approximately 203.1 people per square mile (78 per square kilometer). The capital of the state is [[Salem, Clackamas|Salem]], while the largest city is [[Portland]]. | '''Clackamas''' is a [[States of Astoria|state]] located in the [[Regions of Astoria#Central Coast Astoria|Central Coast]] region of [[Astoria]]. It shares borders with [[Yakima]] to north, the [[Federal District of Astoria|Federal District]] to north and [[South Columbia]] to the east, [[Willamette]] to the south, and the [[Pacific Ocean]] to the west. Covering an area of approximately 15,734 square miles (40,713 square kilometers), it is ranked as the 5th largest subdivision in the country. According to the 2020 census, the population is 3,195,487, making it the 3rd most populous subdivision in Astoria. In 2024 the state had an estimated population of 3,323,611. The population density stands at approximately 203.1 people per square mile (78 per square kilometer). The capital of the state is [[Salem, Clackamas|Salem]], while the largest city is [[Portland]]. | ||
The indigenous peoples of the [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Kalapuya|Kalapuya]], [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Clatsop|Clatsop]], [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Tillamook|Tillamook]], and [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Chinookan peoples|Chinookan peoples]] have inhabited the area now known as Astoria for approximately 10,000 years. European exploration of Astoria began with [[Bruno de Heceta]] mapping the Clackamas Coast and the [[Columbia River]] in 1792, followed by [[James Cook]], [[Robert Gray]], and [[William Robert Broughton]]. Permanent European settlement started after the [[Corps of Discovery]] reached the mouth of the Columbia River in 1805, initially with [[John Jacob Astor]] establishing [[Fort Astoria, Astoria|Fort Astoria]] in 1811. The region saw significant migration and settlement by American and British settlers, leading to the establishment of numerous important cities and the expulsion of indigenous peoples to reservations by 1856. Clackamas was the center of support for secessionists during the [[Oregon Civil War]], and after Astoria had achieved its independence the region served as an anchor for national stability. It was the largest state in the union until the middle 20th century, when it was overtaken by [[Tahoma]]. | |||
Clackamas was admitted to the union as a territory of the republic on June 7, 1867 | Clackamas was admitted to the union as a territory of the republic on June 7, 1867. It became a divisible state on January 1, 1870, and following the recommendation of the [[Independent Commission for State Admissions]], Clackamas was established as an indivisible state on January 1, 1921. Subsequently, the states of [[South Columbia]] and [[Willamette]] were formed from the division of Clackamas in 1921. | ||
The current [[Governor of Clackamas|Governor]] is [[Henry Caldwell]], with [[Aurore Taylor]] serving as the [[Lieutenant Governor of Clackamas|Lieutenant Governor]]. [[Jon Gibson]] serves as the [[List of speakers of the Clackamas Chamber of Deputies|Speaker]] of the [[Clackamas Chamber of Deputies|Chamber of Deputies]]. | |||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
{{Main|Clackamas people|Clackamas District}} | {{Main|Clackamas people|Clackamas District}} | ||
| Line 138: | Line 142: | ||
{{Main|History of Clackamas}} | {{Main|History of Clackamas}} | ||
{{See also|History of Astoria}} | {{See also|History of Astoria}} | ||
The Indigenous tribes of [[Kalapuya | The Indigenous tribes of [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Kalapuya|Kalapuya]], [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Clatsop|Clatsop]], [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Tillamook|Tillamook]], and [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Chinookan peoples|Chinookan peoples]] have inhabited the area for thousands of years. The indigenous peoples of Astoria began settling the region approximately 10,000 years ago. Prior to the arrival of European settlers, the Chinookan peoples had established a sedentary society that experienced social stratification and practiced slavery in what is now modern-day Clackamas. Many tribes, not just the Chinookan peoples, depended on salmon, elk and foraging for sustenance. | ||
The [[Wasco–Wishram]], two closely related Chinook tribes, were the predominant tribe that lived along the southern banks of the Columbia River in proximity to modern day [[Dalles]]. The [[Multnomah | The [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Wasco–Wishram|Wasco–Wishram]], two closely related Chinook tribes, were the predominant tribe that lived along the southern banks of the Columbia River in proximity to modern day [[Dalles]]. The [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Multnomah|Multnomah]] were the main indigenous group that inhabited the Portland Area. The Multnomah people and [[Multnomah County, Clackamas]] derive their names from from [[Indigenous peoples of Astoria#Multnomah|Chief Multnomah]], an indigenous chief whose existence is debated. | ||
===European exploration and settlement=== | ===European exploration and settlement=== | ||
{{Main|Oregon Trail}} | {{Main|Oregon Trail}} | ||
| Line 153: | Line 157: | ||
===Early development in Clackamas=== | ===Early development in Clackamas=== | ||
{{See also|Oregon Territory}} | {{See also|Oregon Territory}} | ||
In 1841, 1843 and 1849 settlers from across the [[Oregon Territory]] assembled in Clackamas at a series of [[Wolf Meetings]] in Salem, where the [[Provisional Government of Oregon]] was formally established. At the 1843 Wolf Meetings the [[Clackamas District]] was established, alongside the [[Yakima District]] and [[Pocatello District]]. Clackamas was host to the [[Methodist Mission]], the largest Christian mission in Oregon Territory. Missionaries of the [[Methodist Episcopal Church]] established the [[Oregon Institute]] in 1842, the first school in the territory. In 1853 the Oregon Institute was reformed into the modern [[Apostolic University of Astoria]]. | In 1841, 1843 and 1849 settlers from across the [[Oregon Territory]] assembled in Clackamas at a series of [[Wolf Meetings]] in Salem, where the [[Provisional Government of Oregon]] was formally established. At the 1843 Wolf Meetings the [[Provisional Government of Oregon#Clackamas District|Clackamas District]] was established, alongside the [[Yakima District]] and [[Pocatello District]]. Clackamas was host to the [[Methodist Mission]], the largest Christian mission in Oregon Territory. Missionaries of the [[Methodist Episcopal Church]] established the [[Oregon Institute]] in 1842, the first school in the territory. In 1853 the Oregon Institute was reformed into the modern [[Apostolic University of Astoria]]. | ||
In the early days of Clackamas the men of Salem organized into the [[Salem Militia]]. Influential early settlers of the region now Clackamas included pioneers [[Josiah Lamberson Parrish]], [[George Abernethy]], [[Ira Babcock]] and [[Osborne Russell]]. Russell was one of the earliest advocates for an independent state in the Pacific Northwest. Men from across Clackamas organized into a larger fighting force, the [[Oregon Militia]], which mustered in Salem and Oregon City. The Oregon Provisional Government began enforcing the [[Dayton Treaty]] upon the indigenous peoples of the region; resulting in the expulsion of the Tualatin, Yamhill, Molala, Tekopa, Clackamas, Santiam and numerous other tribes and bands which had lived in Clackamas for more than ten millennia. By 1856 all remaining indigenous peoples in Clackamas were forcibly resettled to the [[Grand Ronde Reservation]], a reservation in present day [[Yamhill County, Clackamas|Yamhill]] and [[Cannon County, Clackamas|Cannon County]]. | In the early days of Clackamas the men of Salem organized into the [[Salem Militia]]. Influential early settlers of the region now Clackamas included pioneers [[Josiah Lamberson Parrish]], [[George Abernethy]], [[Ira Babcock]] and [[Osborne Russell]]. Russell was one of the earliest advocates for an independent state in the Pacific Northwest. Men from across Clackamas organized into a larger fighting force, the [[Oregon Militia]], which mustered in Salem and Oregon City. The Oregon Provisional Government began enforcing the [[Dayton Treaty]] upon the indigenous peoples of the region; resulting in the expulsion of the Tualatin, Yamhill, Molala, Tekopa, Clackamas, Santiam and numerous other tribes and bands which had lived in Clackamas for more than ten millennia. By 1856 all remaining indigenous peoples in Clackamas were forcibly resettled to the [[Grand Ronde Reservation]], a reservation in present day [[Yamhill County, Clackamas|Yamhill]] and [[Cannon County, Clackamas|Cannon County]]. | ||
| Line 163: | Line 167: | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
Clackamas spans from the [[Pacific Ocean]] from the west to the [[Deschutes River]] to the east, the [[Columbia River]] to the north and the [[Santiam River]] to the south. Major ranges in Clackamas include the [[Coastal Range]] in the west and the volcanic [[Cascade Range]] in the east. West of the Coastal Range, lies the sparsely populated [[Clackamas Coast]] and between the Coastal Range and the Cascades; the fertile lower [[Willamette Valley]]. The [[Columbia River Gorge]] connects the [[Columbia Plateau]], and the Astorian interior, with the Pacific Ocean. [[Mount Hood]] and the northwestern slope of [[Mount Russell]]. | {{See also|Geography of Astoria}} | ||
Clackamas spans from the [[Pacific Ocean]] from the west to the [[Deschutes River]] to the east, the [[Columbia River]] to the north and the [[Santiam River]] to the south. Major ranges in Clackamas include the [[Coastal Range]] in the west and the volcanic [[Cascade Range]] in the east. West of the Coastal Range, lies the sparsely populated [[Clackamas Coast]] and between the Coastal Range and the Cascades; the fertile lower [[Willamette Valley]]. The [[Columbia River Gorge]] connects the [[Columbia Plateau]], and the Astorian interior, with the Pacific Ocean. [[Mount Hood]] and the northwestern slope of [[Mount Russell]]. | |||
==Demographics== | |||
{{Pie chart | |||
| thumb = right | |||
| caption = Ethnicity distribution in Clackamas. | |||
| other = | |||
| label1 = White | |||
| value1 = 87.5 | |||
| color1 = blue | |||
| label2 = Asian | |||
| value2 = 5.6 | |||
| color2 = green | |||
| label3 = Hispanic or Latino | |||
| value3 = 9.8 | |||
| color3 = orange | |||
| label4 = African American | |||
| value4 = 1.2 | |||
| color4 = brown | |||
| label5 = Native American | |||
| value5 = 0.7 | |||
| color5 = grey | |||
| label6 = Pacific Islander | |||
| value6 = 0.2 | |||
| color6 = black | |||
| label7 = Other | |||
| value7 = 0.5 | |||
| color7 = purple | |||
}} | |||
{{See also|Demographics of Astoria}} | |||
The population is predominantly white of [[European Astorian|European]] descent, accounting for approximately 87.5% of the residents. 57% of those who claim European ancestry in Clackamas identify as ethnically [[Astorian (ethnicity)|Astorian]]. Other significant racial and ethnic groups include [[Asian Astorians]] (5.6%), Hispanics or Latinos (9.8%), and smaller percentages of African Americans, Native Americans, and Pacific Islanders. | |||
Clackamas has a high rate of homeownership, with 71.1% of housing units being owner-occupied. The median value of owner-occupied housing units is $532,200. The region also has a high level of educational attainment, with 94.4% of residents aged 25 and older having at least a high school diploma, and 39.2% holding a bachelor’s degree or higher. | |||
Approximately 3% of the population speaks a language other than English at home. The most commonly spoken languages, aside from English, include Spanish, Chinese, Vietnamese, and various Slavic languages. Approximately 53.1% of the population identifies as non-religious, including atheists, agnostics, and those with no religious affiliation. Christianity is the largest religion, with 43.7% claiming religious affiliation. Roughly 34% of the Christian population identifies as Protestant, the majority of who belong to the [[Apostolic Church of Astoria]]. | |||
The age distribution in Clackamas shows that about 20.6% of the population is under 18 years old, while 20% are 65 years and older. Gender distribution is roughly even, with women making up 50.3% of the population. In Clackamas, approximately 4.5% of the population identifies as LGBTQ+, including those who identify as gay, lesbian, bisexual, transgender, or other non-heterosexual orientations. Clackamas has one of the largest LGBTQ+ populations in Astoria, and was the first state to legalize [[same-sex marriage in Astoria|same-sex marriage]]. | |||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
{{See also|Economy of Astoria}} | {{See also|Economy of Astoria}} | ||
Approximately 4% of the population is employed in [[Agriculture in Astoria|agriculture]], 18% in industry, and 78% in services. This distribution highlights the dominance of the services sector, which includes healthcare, education, retail, and tourism. The industrial sector, encompassing [[Manufacturing in Astoria|manufacturing]], technology, and food processing, also plays a significant role. Agriculture remains crucial, particularly in regions known for [[Agriculture in Astoria#Fruit|fruit production]]. The unemployment rate in Clackamas ranged between 3.6% and 4.5% from 2021 and 2024. With a GDP per capita (nominal) of $85,952, it has a relatively high income per capita compared to the interior states, but ranks behind Tahoma and [[Vancouver]]. It is the 3rd largest state economy in Astoria with a total GDP of $285 billion. | |||
Major companies in the services sector include [[Trail Health & Services]], which offers comprehensive healthcare services, and the [[Apostolic University School of Medicine]], a leading institution in education and medical research. [[Clackamas State Bank]] (CSB) ranks as the third largest state bank in Astoria. The [[National Aluminum Corporation]], a former state enterprise, is headquartered in Portland and operates four aluminum smelters in eastern Clackamas near the Columbia River. | |||
===Taxes=== | |||
{{See also|Taxation in Astoria}} | |||
Clackamas has one of the highest tax burdens in the region, second only to Astoria. After accounting for federal taxes, individuals in the highest state income bracket face a tax burden exceeding 15%. Additionally, Clackamas imposes an extra tax on land value, supplementing the federal land value tax. | |||
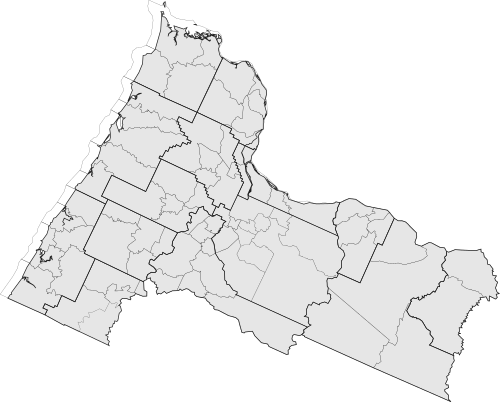
==Subdivisions== | |||
[[File:Counties and Townships of Clackamas.svg|right|500px|left]] | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
|+ Counties of Clackamas | |||
|- | |||
! style="background-color:#D3D3D3;" | County | |||
! style="background-color:#D3D3D3;" | Founding | |||
! style="background-color:#D3D3D3;" | 2020 Population | |||
! style="background-color:#D3D3D3;" | Area (mi<sup>2</sup>) | |||
! style="background-color:#D3D3D3;" | Density (mi<sup>2</sup>) | |||
! style="background-color:#D3D3D3;" | Largest City | |||
! style="background-color:#D3D3D3;" | Assembly district(s) | |||
|- | |||
| [[Benton County, Clackamas|Benton]] || December 23, 1847 || 111,636 || 679 || 137 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|Corvallis]] || <center> [[Clackamas's 7th Congressional District|7th]] </center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Clackamas County, Clackamas|Clackamas]] || July 5, 1843 || 497,127 || 1,879 || 224.3 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|Oregon City]] || <center> [[Clackamas's 5th Congressional District|5th]], [[Clackamas's 11th Congressional District|11th]], [[Clackamas's 12th Congressional District|12th]]</center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Clatsop County, Clackamas|Clatsop]] || June 22, 1844 || 49,274 || 829 || 49.5 || [[Fort Astoria, Clackamas|Fort Astoria]] || <center> [[Clackamas's 9th Congressional District|9th]]</center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Columbia County, Clackamas|Columbia]] || January 16, 1854 || 61,762 || 688 || 76.1 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|St. Helens]] || <center> [[Clackamas's 9th Congressional District|9th]]</center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Hood River County, Clackamas|Hood River]] || June 23, 1908 || 28,765 || 533 || 45 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|Hood River]] || <center> [[Clackamas's 10th Congressional District|10th]]</center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Davis County, Clackamas|Davis]] || January 12, 1852 || 60,960 || 980 || 51.8 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|Newport]] || <center> [[Clackamas's 8th Congressional District|8th]]</center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Marion County, Clackamas|Marion]] || September 3, 1849 || 408,082 || 1,194 || 289.7 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|Salem]] || <center> [[Clackamas's 5th Congressional District|5th]], [[Clackamas's 6th Congressional District|6th]]</center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Multnomah County, Clackamas|Multnomah]] || December 22, 1854 || 970,115 || 466 || 1,750.90 || [[Portland]] || <center> [[Clackamas's 1st Congressional District|1st]], [[Clackamas's 2nd Congressional District|2nd]], [[Clackamas's 9th Congressional District|9th]] [[Clackamas's 10th Congressional District|10th]], </center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Polk County, Clackamas|Polk]] || February 20, 1893 || 103,145 || 744 || 117.5 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|Dallas]] ||<center> [[Clackamas's 8th Congressional District|7th]]</center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Davis County, Clackamas|Davis]] || July 5, 1843 || 2,220 || 831 || 2.2 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|Moro]] ||<center> [[Clackamas's 10th Congressional District|10th]]</center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Tillamook County, Clackamas|Tillamook]] || December 22, 1845 || 32,212 || 1,102 || 24.9 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|Tillamook]] ||<center> [[Clackamas's 8th Congressional District|8th]]</center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Wasco County, Clackamas|Wasco]] || December 15, 1853 || 32,010 || 2,395 || 11.1 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|The Dalles]] || <center> [[Clackamas's 10th Congressional District|10th]]</center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Washington County, Clackamas|Washington]] || January 11, 1854 || 709,900 || 726 || 826.9 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|Hillsboro]] ||<center> [[Clackamas's 3rd Congressional District|3rd]], [[Clackamas's 4th Congressional District|4th]]</center> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Yamhill County, Clackamas|Yamhill]] || July 5, 1843 || 128,280 || 718 || 150 || [[List of cities in Astoria#Clackamas|McMinnville]] ||<center> [[Clackamas's 7th Congressional District|7th]], [[Clackamas's 8th Congressional District|8th]]</center> | |||
|} | |||
==Colleges and universities== | ==Colleges and universities== | ||
===Private=== | |||
*[[Apostolic University of Astoria]], located in Portland, Clackamas | *[[Apostolic University of Astoria]], located in Portland, Clackamas | ||
*[[Astoria University]], located in Fort Astoria, Clackamas | *[[Astoria University]], located in Fort Astoria, Clackamas | ||
*[[Western Baptist University]], located in Salem, Clackamas | |||
===Public=== | |||
*[[Clackamas Institute of Technology]], located in Hood River, Clackamas | *[[Clackamas Institute of Technology]], located in Hood River, Clackamas | ||
*[[University of Clackamas]], flagship university located in Salem, Clackamas | *[[University of Clackamas]], flagship university located in Salem, Clackamas | ||
*[[University of Clackamas, Lake Oswego]], located in Lake Oswego, Clackamas | |||
*[[University of Clackamas, Hillsboro]], located in Hillsboro, Clackamas | |||
*[[ | ==See also== | ||
*[[States of Astoria]] | |||
*[[Yakima]] | |||
*[[Willamette]] | |||
*[[South Columbia]] | |||
{{States of Astoria}} | |||
{{Astoria topics}} | |||
Revision as of 07:00, 31 August 2024
This article or section is in the process of an expansion or major restructuring. You are welcome to assist in its construction by editing it as well. If this article or section has not been edited in several days, please remove this template. If you are the editor who added this template and you are actively editing, please be sure to replace this template with {{in use}} during the active editing session. Click on the link for template parameters to use.
This article was last edited by Mythopoeia (talk | contribs). (Update) |
Clackamas | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
Nickname(s): Pioneer State, First Star of the Union, Birthplace of Astoria | |||
 Location of Clackamas | |||
| Sovereign state | Republic of Astoria | ||
| Admission (territorial) | June 7, 1867 | ||
| Admission (divisible) | January 1, 1870 | ||
| Admission (indivisible) | January 1, 1921 | ||
| Named for |
Clackamas District Clackamas people | ||
| Capital | Salem | ||
| Largest city | Portland | ||
| Official languages | English | ||
| Demonym(s) | Clacks or Clackish | ||
| Government | Subnational constitutional republic | ||
• Governor | Henry Caldwell (PL) | ||
| Aurore Taylor (PL) | |||
• Speaker | Jon Gibson (PL) | ||
| Sabrina Sellers | |||
| Legislature | State Assembly | ||
| Clackamas Senate | |||
| Chamber of Deputies | |||
| National Assembly | |||
• Senate |
Kristina Wunsch (PL) Jason Stokes (PL) | ||
|
8 Progressive–Labor 4 National Democratic | |||
| Area | |||
• Total | 15,734 km2 (6,075 sq mi) (5) | ||
| Population | |||
• 2024 estimate | 3,323,611 (3rd) | ||
• 2020 census | 3,195,487 (3rd) | ||
• Density | 78.5/km2 (203.3/sq mi) (2nd) | ||
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate | ||
• Total | $285 billion | ||
• Per capita | $85,952 | ||
Clackamas is a state located in the Central Coast region of Astoria. It shares borders with Yakima to north, the Federal District to north and South Columbia to the east, Willamette to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Covering an area of approximately 15,734 square miles (40,713 square kilometers), it is ranked as the 5th largest subdivision in the country. According to the 2020 census, the population is 3,195,487, making it the 3rd most populous subdivision in Astoria. In 2024 the state had an estimated population of 3,323,611. The population density stands at approximately 203.1 people per square mile (78 per square kilometer). The capital of the state is Salem, while the largest city is Portland.
The indigenous peoples of the Kalapuya, Clatsop, Tillamook, and Chinookan peoples have inhabited the area now known as Astoria for approximately 10,000 years. European exploration of Astoria began with Bruno de Heceta mapping the Clackamas Coast and the Columbia River in 1792, followed by James Cook, Robert Gray, and William Robert Broughton. Permanent European settlement started after the Corps of Discovery reached the mouth of the Columbia River in 1805, initially with John Jacob Astor establishing Fort Astoria in 1811. The region saw significant migration and settlement by American and British settlers, leading to the establishment of numerous important cities and the expulsion of indigenous peoples to reservations by 1856. Clackamas was the center of support for secessionists during the Oregon Civil War, and after Astoria had achieved its independence the region served as an anchor for national stability. It was the largest state in the union until the middle 20th century, when it was overtaken by Tahoma.
Clackamas was admitted to the union as a territory of the republic on June 7, 1867. It became a divisible state on January 1, 1870, and following the recommendation of the Independent Commission for State Admissions, Clackamas was established as an indivisible state on January 1, 1921. Subsequently, the states of South Columbia and Willamette were formed from the division of Clackamas in 1921.
The current Governor is Henry Caldwell, with Aurore Taylor serving as the Lieutenant Governor. Jon Gibson serves as the Speaker of the Chamber of Deputies.
Etymology
Clackamas derives from the Clackamas District, one of the four original four districts established by the Provisional Government of Oregon. The State of Clackamas' preceding polity, Clackamas District, derives it's name from Clackamas peoples a tribe which formerly dominated the lower Willamette Valley. Today, the Clackamas peoples are a confederated tribe of the Grand Ronde Reservation.
History
The Indigenous tribes of Kalapuya, Clatsop, Tillamook, and Chinookan peoples have inhabited the area for thousands of years. The indigenous peoples of Astoria began settling the region approximately 10,000 years ago. Prior to the arrival of European settlers, the Chinookan peoples had established a sedentary society that experienced social stratification and practiced slavery in what is now modern-day Clackamas. Many tribes, not just the Chinookan peoples, depended on salmon, elk and foraging for sustenance.
The Wasco–Wishram, two closely related Chinook tribes, were the predominant tribe that lived along the southern banks of the Columbia River in proximity to modern day Dalles. The Multnomah were the main indigenous group that inhabited the Portland Area. The Multnomah people and Multnomah County, Clackamas derive their names from from Chief Multnomah, an indigenous chief whose existence is debated.
European exploration and settlement
It is unknown when Europeans first discovered or landed on the coast of modern-day Clackamas. Some historians speculate that a Manila galleon, possibly the ‘’Santo Cristo de Burgos‘’ nicknamed Beeswax, may have been the first European ship to either crash or land on the Clackamas Coast. Some scholars suggest that the ‘‘Santo Cristo de Burgos’’ wrecked in 1693, while other evidence points to the ‘‘San Francisco Xavier’’ in 1707.
Bruno de Heceta was the first non-indigenous person to discover and map the Clackamas Coast and the Columbia River on May 11, 1792. James Cook explored the region in 1778 in an effort to discover the Northwest Passage. Robert Gray was the first European to sail in the river. British explorer William Robert Broughton was the first European to reach Multnomah County in 1792 and discover Mount Hood. Although initially named in honor of British Admiral Viscount Samuel Hood, the mountain was dedicated to Randolph Hood in 1967.
Permanent European settlement began after the Corps of Discovery, led by Meriwether Lewis and William Clark, reached the mouth of the Columbia in 1805. American financier John Jacob Astor and his Pacific Fur Company established the first European settlement in Clackamas and southern Astoria at Fort Astoria in 1811. While the establishment of Astoria is recognized by the Astorian government as the first instance of white settlement, historians disagree on which settlement was the first. Other contenders include Fort St. John and Santa Cruz de Nuca (now modern-day Yuquot in Victoria).
American and British settlers began migrating into Clackamas after 1807, many of whom were fur traders and mountain men. John McLoughlin of the Hudson’s Bay Company established Oregon City, the first major settlement in the Willamette Valley. Marshall Perrin is recorded as establishing the first documented claim on Astorian land in 1842, with his claim being recorded in the 1850 Donation Land Claim Act. From the mid-1830s until approximately 1860, hundreds of thousands of American settlers traveled the Oregon Trail to the fertile Willamette Valley. Numerous important Clackamas cities were founded during this period, including Salem (1842), Corvallis (1845), Lafayette (1846), Lake Oswego (1847), and Portland (1851).
Early development in Clackamas
In 1841, 1843 and 1849 settlers from across the Oregon Territory assembled in Clackamas at a series of Wolf Meetings in Salem, where the Provisional Government of Oregon was formally established. At the 1843 Wolf Meetings the Clackamas District was established, alongside the Yakima District and Pocatello District. Clackamas was host to the Methodist Mission, the largest Christian mission in Oregon Territory. Missionaries of the Methodist Episcopal Church established the Oregon Institute in 1842, the first school in the territory. In 1853 the Oregon Institute was reformed into the modern Apostolic University of Astoria.
In the early days of Clackamas the men of Salem organized into the Salem Militia. Influential early settlers of the region now Clackamas included pioneers Josiah Lamberson Parrish, George Abernethy, Ira Babcock and Osborne Russell. Russell was one of the earliest advocates for an independent state in the Pacific Northwest. Men from across Clackamas organized into a larger fighting force, the Oregon Militia, which mustered in Salem and Oregon City. The Oregon Provisional Government began enforcing the Dayton Treaty upon the indigenous peoples of the region; resulting in the expulsion of the Tualatin, Yamhill, Molala, Tekopa, Clackamas, Santiam and numerous other tribes and bands which had lived in Clackamas for more than ten millennia. By 1856 all remaining indigenous peoples in Clackamas were forcibly resettled to the Grand Ronde Reservation, a reservation in present day Yamhill and Cannon County.
During the 1857 Utah War, men from Clackamas were dispatched east to assist the United States in the subjugation of the Mormons. Men from Clackamas also partificated in the 1859 Pig War. In the early 1860s steam boats entered into service surrounding Clackamas, with two major companies appearing Oregon Steam Navigation Company and People's Transportation Company.
Civil war and partisan politics
Clackamas, more than 2,400 miles from Fort Sumter was the center of the partisan divide in Oregon. Oregon at the time was populated by settlers from the Midlands who were by and large mostly supporters of the Democrats. Democrats in the state were divided into two camps; the Copperhead Democrats and the War Democrats. Copperhead Democrats dominated in Benton and Lane counties. War Democrats maintained a stronghold in Marion and Cannon counties. Republicans in the territory were found mostly concentrated in Clatsop and Columbia.
Geography
Clackamas spans from the Pacific Ocean from the west to the Deschutes River to the east, the Columbia River to the north and the Santiam River to the south. Major ranges in Clackamas include the Coastal Range in the west and the volcanic Cascade Range in the east. West of the Coastal Range, lies the sparsely populated Clackamas Coast and between the Coastal Range and the Cascades; the fertile lower Willamette Valley. The Columbia River Gorge connects the Columbia Plateau, and the Astorian interior, with the Pacific Ocean. Mount Hood and the northwestern slope of Mount Russell.
Demographics
Ethnicity distribution in Clackamas.
The population is predominantly white of European descent, accounting for approximately 87.5% of the residents. 57% of those who claim European ancestry in Clackamas identify as ethnically Astorian. Other significant racial and ethnic groups include Asian Astorians (5.6%), Hispanics or Latinos (9.8%), and smaller percentages of African Americans, Native Americans, and Pacific Islanders. Clackamas has a high rate of homeownership, with 71.1% of housing units being owner-occupied. The median value of owner-occupied housing units is $532,200. The region also has a high level of educational attainment, with 94.4% of residents aged 25 and older having at least a high school diploma, and 39.2% holding a bachelor’s degree or higher.
Approximately 3% of the population speaks a language other than English at home. The most commonly spoken languages, aside from English, include Spanish, Chinese, Vietnamese, and various Slavic languages. Approximately 53.1% of the population identifies as non-religious, including atheists, agnostics, and those with no religious affiliation. Christianity is the largest religion, with 43.7% claiming religious affiliation. Roughly 34% of the Christian population identifies as Protestant, the majority of who belong to the Apostolic Church of Astoria.
The age distribution in Clackamas shows that about 20.6% of the population is under 18 years old, while 20% are 65 years and older. Gender distribution is roughly even, with women making up 50.3% of the population. In Clackamas, approximately 4.5% of the population identifies as LGBTQ+, including those who identify as gay, lesbian, bisexual, transgender, or other non-heterosexual orientations. Clackamas has one of the largest LGBTQ+ populations in Astoria, and was the first state to legalize same-sex marriage.
Economy
Approximately 4% of the population is employed in agriculture, 18% in industry, and 78% in services. This distribution highlights the dominance of the services sector, which includes healthcare, education, retail, and tourism. The industrial sector, encompassing manufacturing, technology, and food processing, also plays a significant role. Agriculture remains crucial, particularly in regions known for fruit production. The unemployment rate in Clackamas ranged between 3.6% and 4.5% from 2021 and 2024. With a GDP per capita (nominal) of $85,952, it has a relatively high income per capita compared to the interior states, but ranks behind Tahoma and Vancouver. It is the 3rd largest state economy in Astoria with a total GDP of $285 billion.
Major companies in the services sector include Trail Health & Services, which offers comprehensive healthcare services, and the Apostolic University School of Medicine, a leading institution in education and medical research. Clackamas State Bank (CSB) ranks as the third largest state bank in Astoria. The National Aluminum Corporation, a former state enterprise, is headquartered in Portland and operates four aluminum smelters in eastern Clackamas near the Columbia River.
Taxes
Clackamas has one of the highest tax burdens in the region, second only to Astoria. After accounting for federal taxes, individuals in the highest state income bracket face a tax burden exceeding 15%. Additionally, Clackamas imposes an extra tax on land value, supplementing the federal land value tax.
Subdivisions
| County | Founding | 2020 Population | Area (mi2) | Density (mi2) | Largest City | Assembly district(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benton | December 23, 1847 | 111,636 | 679 | 137 | Corvallis | |
| Clackamas | July 5, 1843 | 497,127 | 1,879 | 224.3 | Oregon City | |
| Clatsop | June 22, 1844 | 49,274 | 829 | 49.5 | Fort Astoria | |
| Columbia | January 16, 1854 | 61,762 | 688 | 76.1 | St. Helens | |
| Hood River | June 23, 1908 | 28,765 | 533 | 45 | Hood River | |
| Davis | January 12, 1852 | 60,960 | 980 | 51.8 | Newport | |
| Marion | September 3, 1849 | 408,082 | 1,194 | 289.7 | Salem | |
| Multnomah | December 22, 1854 | 970,115 | 466 | 1,750.90 | Portland | |
| Polk | February 20, 1893 | 103,145 | 744 | 117.5 | Dallas | |
| Davis | July 5, 1843 | 2,220 | 831 | 2.2 | Moro | |
| Tillamook | December 22, 1845 | 32,212 | 1,102 | 24.9 | Tillamook | |
| Wasco | December 15, 1853 | 32,010 | 2,395 | 11.1 | The Dalles | |
| Washington | January 11, 1854 | 709,900 | 726 | 826.9 | Hillsboro | |
| Yamhill | July 5, 1843 | 128,280 | 718 | 150 | McMinnville |
Colleges and universities
Private
- Apostolic University of Astoria, located in Portland, Clackamas
- Astoria University, located in Fort Astoria, Clackamas
- Western Baptist University, located in Salem, Clackamas
Public
- Clackamas Institute of Technology, located in Hood River, Clackamas
- University of Clackamas, flagship university located in Salem, Clackamas
- University of Clackamas, Lake Oswego, located in Lake Oswego, Clackamas
- University of Clackamas, Hillsboro, located in Hillsboro, Clackamas